Zanthoxylum, Sichuan Pepper, Hua Jiao 花椒Chinese: Hua Jiao (TCM)Tumburu, Tejabala (Ayurveda) Faghir, Kabab-Khanda (Unani) Gyer ma གཡེར་མ (Tibet) |

|
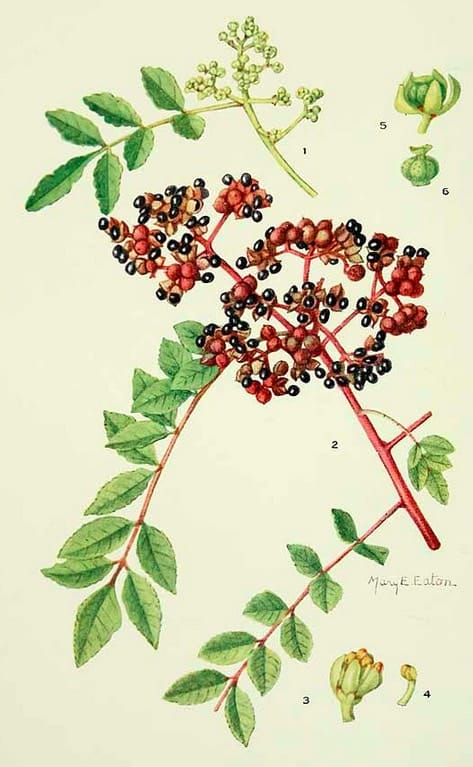 Zanthoxylum schinifolium (Sichuan, China)
Zanthoxylum schinifolium (Sichuan, China)Addisonia, vol. 10 (1925)
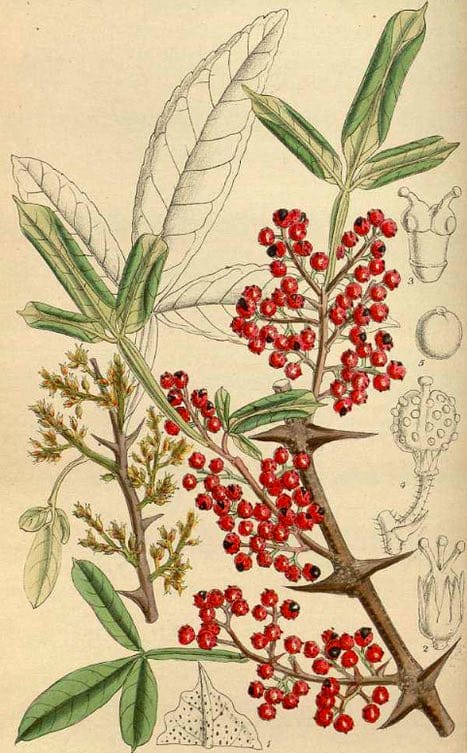 Zanthoxylum armatum (India)
Zanthoxylum armatum (India)Curtis’s Botanical Magazine (1918)
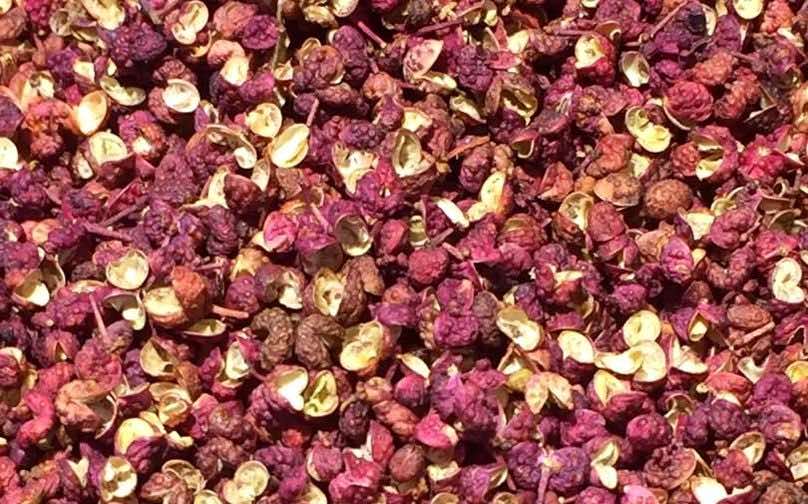 Red Sichuan Pepper
Red Sichuan Pepper |
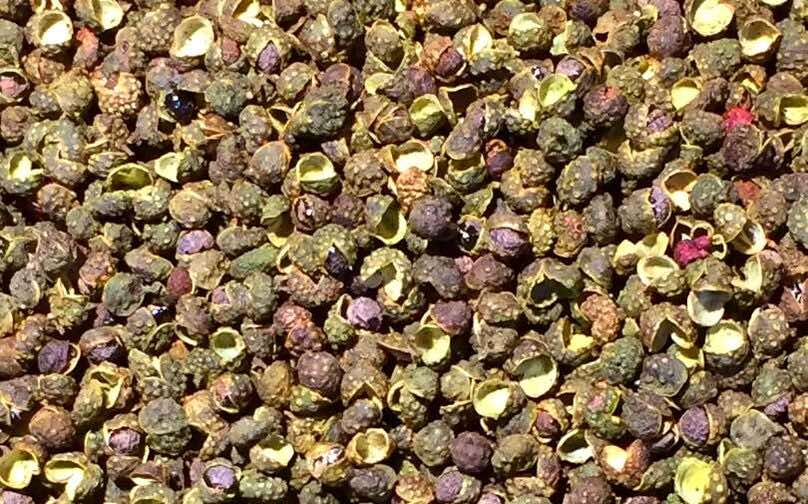 Green Sichuan Pepper
Green Sichuan Pepper |
Botanical name:
Zanthoxylum spp.
- Z. schinifolium, Z. bungeanum (syn. Z. simulans) (TCM)
- Z. peperitum Qin Jiao is related with bigger fruit. It has the same functions (TCM)
- Z. armatum (syn. Z. planispinum), and Z. alatum (Ayurveda)
- Z. nepalense (Tibet)
Parts used:
Pericarp of ripe fruit
Temperature & Taste:
Hot, dry. Pungent, Spicy
Classification:
M. Warm to Clear Cold
Uses:
1. Warms the Stomach, Eases Pan: (TCM, Ayurveda, Unani, Tibet)
-Indigestion, Bloating, poor appetite
-cold abdominal pain, Colic
-Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea from Cold
-dries Dampness from the Spleen
2. Clears Wind-Cold, Opens the Channels: (TCM, Ayurveda, Unani, Tibet)
-used at the beginning of Wind-Cold attack to promote sweat
-Cough, Catarrh, Sore Throat
-Vocal obstructions (Tibet)
-clears Wind-Cold-Damp from the channels
-pain, discomfort and congestion in the chest (Ayurveda)
-Wind disorders of the Heart (Tibet)
3. Warms the Kidneys, Supports Yang:
-frequent Urination and Night urination from Kidney deficiency
-Spermatorrhea
4. Kills Worms: (TCM, Ayurveda, Unani, Tibet)
-Roundworms and abdominal pain associated with Worms
-extract is used for Roundworms in India
-abdominal pain due to Worms (Tibet)
-Fungal Infections, Trichomonas (Tibet)
5. Externally:
-Toothache, place a Sichuan Pepper at the base of the tooth against the gum (Sichuan Folk remedy and in India with local variety)
-can be used in tooth powders for diseases of the mouth and gums (Ayurveda)
-fruits are chewed as a mouth freshener; twigs are used as a toothbrush in India
-Stomatitis, decoction is used as a gargle
-to Warm the Stomach, wrap in gauze and apply to the Navel
-Eczema, Dermatosis and other Itchy skin diseases (TCM, Ayurveda, Tibet)
-in errhine for heaviness of the Head, Migraine, Coryza, loss of smell (Ayurveda)
-topically for pain, numbness or atrophy of the limbs (as a paste)
-traditionally to stimulate hair growth

Dose:
Decoction: 3–6 grams;
Powder: 500mg–2 grams
Comment:
1. This is the main unique ingredient of Sichuan cooking, responsible for the numbing, tingly spicy sensation found throughout Sichuan cuisine.
2. The Indian and Chinese fruit of the respective local varieties seem similar in function and use.
Preparation:
1. They are often Stir-Fried to yellowish. This lessens their Heat and mild toxicity while helping the effect of warming the Stomach.
Main Combinations:
1. Stomach-Abdomen Coldness:
i. regularly combined with Chilli, fresh Ginger and Garlic in Sichuan Cooking to warm the Stomach and relieve the Dampness that affects much of Sichuan province.
ii. with Atractylodes Cang Zu (as in Jiao Zhu Wan from Pu Ji Fang [Prescriptions of Universal Relief]).
iii. with Vomiting, Diarrhea, Abdomional pain, with Galangal (Gao Liang Jiang) (TCM)
iv. Abdominal pain from Stomach Cold with deficiency, with Ginger (Gan Jiang) and Ginseng (Ren Shen)
v. abdominal pain and diarrhea from Damp-Heat clumping, with Coptis Huang Lian.
vi. Cold-type Diarrhea:
vii. with Nutmeg (Rou Dou Kou) (as in Chuan Jiao Wan from Xiao Er Wei Sheng Zhong Wei Fang Lun [Treatise on Formulas for Infantile Health Care]).
viii. with Citrus Chen Pi, Costus (Mu Xiang)
2. Eczema, Itching, externally as a wash with Sophora Ku Shen, Kochia Di Fu Zi
3. Pruritis Vulva, with Evodia Wu Zhu Yu, Cnidium She Chuang Zi
Major Formulas:
Da Jian Zhong Tang
Li Zhong An Hui Tang
Lian Mei An Hui Tang
Wu Mei Tang
Cautions:
1. Not used in excess Heat conditions, Yin deficiency, or Deficient Heat (Heat from Yin deficiency).
2. Not used in Pregnancy
