The Four Humors
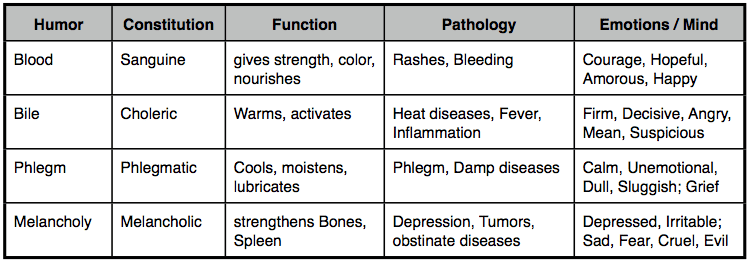
As with the Elements, the terms ‘Blood’, ‘Bile’, ‘Phlegm’, and ‘Melancholy’ are not taken in their normal or literal sense. Rather they refer to the basic building blocks of the body, both physical and energetic. They have commonly been translated in these names because they do refer to the physical Blood, Bile and Phlegm of the body, but are much broader and philosophical in their meaning. Thus, the Phlegm Humor does relate to both Mucous Membranes and the Mucous Secreted, but also, for example, relates the the Cerebrospinal fluid of the Brain and Spinal Column, and the lubricating fluid of the joints. Energetically, Phlegm is also related to the lethargy and mental dullness experienced by the Phlegm-type, and spiritually, Phlegm also is associated with Ignorance. As Salmon said the Humors are digested and ‘changed into the substance of the parts’.The 3 Humors of the Tibetan and Ayurvedic systems are:
1. Bile (Pitta)
2. Phlegm (Kapha)
3. Air (Vata)
The 4 Humors of Galenic Medicine are:
1. Blood (Sanguineous Humor)
2. Bile (Choler, Bilious Humor)
3. Melancholy (Black Bile, Artra-bilious Humor)
4. Phlegm. (Serous Humor)
Traditionally, 3 main Humors have been recognised in Galenic Medicine, Ayurveda, and Tibetan Medicine. Galen listed Blood as the Fourth but said that the other 3 Humors composed Blood in its entirety. Blood can also be found when the body is cut, whereas the other Humors (in the broadest sense) cannot. Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine also recognised Blood, and also said that it was composed of an equal balance of the 3 Humors.
The Humors are the substances which nourish the 7 Constituents of the body. They cannot be found in the body, but are essential for the nourishment of all parts of the body. Each constituent and Every Organ has a desire for a certain compound of the Humors; the Heart is Hot and Dry, and attracts those Humors to itself, while the Kidneys draw Watery Humors to itself.
Finally, Humoral differentiation may be of 2 main types: Physiological and Pathological. Physiological refers to the constitution-type, for example a Sanguine Temperament is a person whose nature is dominated by Blood.
Pathologically, Humor refers to an excess of one of the Humors responsible for disease or imbalance within the body. So it is potential for a person to have a Choleric or Bilious Nature (Hot and Dry), but a disease caused by Phlegm (Cool and Moist). Further, someone may have different Humors affecting different regions of the body, for example Hot and Dry (Bile) affecting the Heart and Cold and Moisture (Phlegm) affecting the Kidneys, for example.
Blood
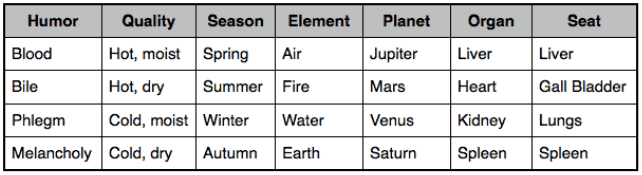
Qualities: Hot and moist
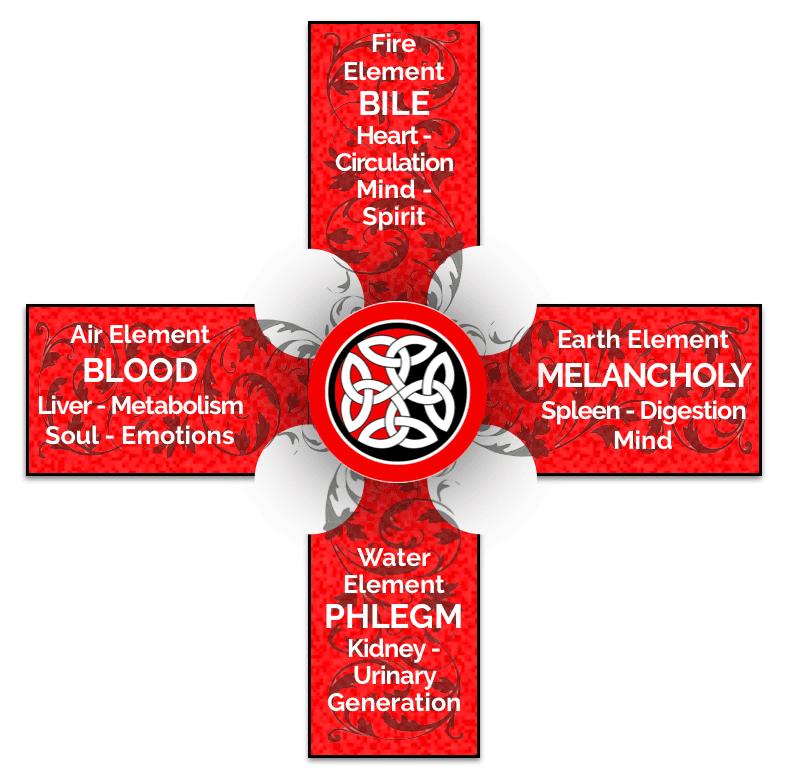
Element: Air
Organ: Liver organ
Receptacle: was said to be the Veins.
Planet: Jupiter
Blood is said to be made of food perfectly concocted.
Functions of Blood
1. Nourishes the Organs, Tissues, and Judgement.
2. Fortifies the digestive faculty.
Blood is, of course, recognised in all traditional medical systems. In Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine, there is emphasis on the 3 Humors, Wind, Bile and Phlegm, as Blood is the foundation, and all of these Humors rely on the Blood for their basis and movement to a greater or lesser extent, while Blood is inactive or ‘Dead’ without the 3 Humors.
Traditional Western Medicine recognised Blood as one of the 4 Humors. Blood Humor was said to be the most important, and to form the basis of what we call blood, yet it was also said that the body and the blood needed the other 3 Humors in correct proportion to live in health: too much or too little would cause disease.
Therefore it can be seen that all 3 systems fairly equally equate Blood as being the foundation substance, and the more variable aspects to be the remaining 3 Humors. So the balance of the other Humors largely govern the quality of the blood;
Phlegm: cools, moistens and moderates the heat of Bile
Air: promotes movement, activates the dense Humors
Bile: warms, quickens, and strengthens
Melancholy: quietens, calms, stabilises
The Blood Humor is either normal or abnormal. Normal Blood is Red, sweet tasting with no unpleasant odor. Often old physicians would talk of needing to sweeten the blood, and in this case they referred to the removing of the unhealthy or acid portions which tainted the Blood, making it sharp.
Sanguine (Blood) Temperament
Well-formed, prominent Joints, Muscular, round or oval Face, thick, strong hair, skin is warm to touch, veins prominent, pulse is full and strong. They have strong appetite and digestion, sleep well, and tend to have a good Faculty of Judgement. Generally positive, extrovert, confident, enthusiastic with good social skills, and are romatic and passionate. They tend to be adversely affected by excess Heat and prefer Cold and dry foods and cool weather.
Signs of an excess of Blood
Signs of excess Blood manifests as Plethora, that is, excess.
-sense of heaviness, especially the eyes, and head
-drowsiness or mental dullness
-a sweet taste,
-Tongue is red
-Boils, Ulcers or the Tongue
-Bleeding from the Gums, Nose or Bowels, and excess Menstruation
-Dreams of Red things, Blood
Typical Blood Diseases
-Inflammations, Headache, Tonsillitis, Epilepsy, Gout, Blood nose, Bleeding and Blood disorders
Bile (Choler)
‘That part of the Nutriment which is roasted, so to speak, or burnt (this will be the warmest
and Sweetest part of it, like Honey and Fat), becomes Yellow Bile, and is cleared away through
the so-called Biliary vessels’. (Galen, ‘On the Natural Faculties’, 170AD)
Also called Yellow Bile and Choler (Galen), Pitta (Ayurveda), mKhris-pa (Tibetan)
Quality: Hot and Dry; Hot and Moist in Tibetan Medicine; Galen said the ‘Yellow Bile is Warm and Dry, even though for the most part it appears Moist’; he concluded Bile was ‘Virtually Dry’, but ‘Apparently Moist’.
Elements: Fire and Water
Tastes which Increases: Pungent
Tastes which Reduces: Sweet, Bitter, Astringent tastes clear Bile.
Nature: Hot, oily, light, pungent, sharp, sour, acid, violent, slightly unctuous, mobile, penetrating, liquid and flowing. Under Mars, and Yang in nature.
Receptacle is the Gall Bladder, which is nourished by it. Its Region, according to Ayurveda, is the Small Intestines, Sweat, the Watery discharges from the surface of soft tissues, the Blood, Chyle, the Eyes and the Skin, the area of the Small Intestine being its seat.
Natural Bilious Humor is the ‘Froth’ of the Blood. It is bright red in color, light and pungent. The more Red it is, the Hotter it is. It is formed in the Liver, and may either travel with the Blood, or is passed to the Gall Bladder.
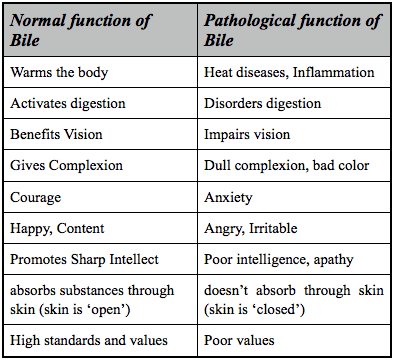
The functions of Bile:
That which travels in the Blood:
1. Nourishes tissues which require Bile Humor (Skin, Eyes etc.)
2. Keeps the blood thin and piercing
3. Warms the Body
4. Clarifies other Humors and Water with its Heat
5. Strengthens the Attractive Virtue
6. Promotes softness and luster of the Body
That which travels to the Gall Bladder:
1. Promotes Appetite and Digestion
2. Helps removal of waste and stimulates the Bowels
3. Cleanses residue of undigested food and phlegm from the Bowels
Bile diseases accumulate during the Summer, break out during the Autumn, and subside during the Winter.
Choleric (Bile) Temperament
Medium stature, strong build, sharp or strong features, yellowish complexion, penetrating eyes, prominent veins, hairy body with hair that is thick, Pulse is rapid and strong. They don’t feel the Cold but don’t like the Heat. They have good appetite and digestion, but tend to sleep light and short. They are energetic, bold, courageous, with good intellect, but prone to be irritable, short-tempered and impatient, and anger easily. They are persistent, with strong drive, and a strong libido, but can be revengeful.
Signs of an excess of Bile
Yellow complexion and eyes, bitter taste in the mouth, rough and dry tongue, rapid pulse, excess thirst, lack of eppetite, nausea, vomiting of bile, red or burning sensation of the skin after hot water or sun exposure. Dreams tend to be of Fire, Heat, Anger, Fighting or yellow things,
Typical Bile Diseases
Urticaria, Hyperacidity, Erysipelas, Hypertension, Headache, Stress, Cardiovascular diseases.
Phlegm
‘Nature has made no organ for clearing away Phlegm, this being Cold and Moist, and, as it were,
half-digested nutriment; such a substance, therefore, does not need to be evacuated, but remains
in the body and undergoes alteration there’. (Galen, On the Natural Faculties, 170AD)
Also called Serous Humor, Kapha (Ayurveda), Bad-kan (Tibetan Medicine)
Quality: Cold, Moist.
Elements: Earth and Water.
Taste which Increases: Sweet
Tastes which Reduce: Sour, Salty, Pungent tastes clear Phlegm.
Nature: cool, moist, oily, sticky, slimy, heavy, slow, sluggish, static, soft, solid, dense, sweet, steady. Related to the Moon and Venus; Yin in nature.
Region: the Receptacle organ for Phlegm was said by Galen to be the Lungs; TCM also says the Lungs collect Phlegm waiting for the Spleen to transform it. The alteration Galen talks of above is a form of digestion, under the control of the Spleen.
Ayurveda says its region is the Chest, Throat, Head, Esophagus, Joints, Stomach, Chyle, Fat, Nose and Tongue with the Lungs being the Chief seat.
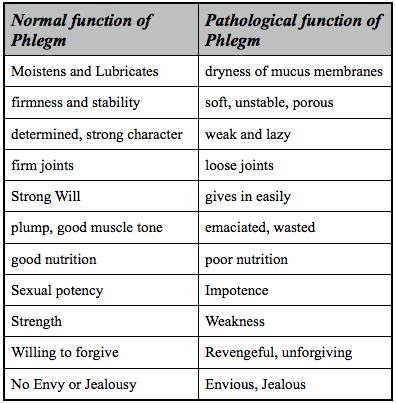
Physiological Action: preserves Body Moisture, Stabilises the Joints, gives the body firmness with proportionate Bulk and Weight; gives Courage, Strength and Endurance, and gives absence of Greed.
Pathologically: Phlegm causes Dullness; Ignorance; Heaviness, Lethargy; Joint Pain; Wheezing
Physiologically: Phlegm is related to all necessary moisture and fluid (Yin) of the body including:
a) that which helps movement (synovial fluid, Digestive Juices)
b) that which protects (secretion of mucous membranes etc)
c) such things as the Cerebrospinal Fluid, Semen, and the most watery part of the Blood (Plasma).
It is, in this respect, analogous to Yin of TCM and Radical Moisture of the Western Tradition. This is seen in the fact that Galen said the Good Phlegm is Sweet and essential for the body while the Bad kinds are Salty, Sour or Bitter etc.
Phlematic (Phlegm) Temperament
Obese or Round build, medium or large frame with more fatty than muscular tissue, soft and flabby muscles, pale complexion with thin and soft hair, pulse is slow and deep and the veins are not prominent, their movement are sluggish with a lethargic energy and they sleep more, they feel better in warm weather and with hot foods, round and full face with large, moist eyes, They have a calm disposition, sentimental, emotional, sensitive, but their mind is foggy, dull and slow with a poor memory and poor perception. They tend to have low libido but do not anger easily.
Signs of an excess of Phlegm
Cold, moist skin, excess salivation, lethargy and sleepiness, mental dullness, soft and weak pulse, pale urine with dreams of water, ice, snow, rain etc.
Typical Phlegm Diseases
Colds, Asthma, Edema, Obesity, Paralysis
Melancholy
‘Now it is agreed that all parts which are undergoing nutrition produce a certain amount of residue …
Imagine, then, some new wine which has been not long ago pressed from the Grape, and which
is fermenting and undergoing alteration through the agency of its contained heat. Imagine next two
residual substances produced during this process of alteration, the one tending to be light and air-like,
and the other to be heavy and more of the nature of Earth … Now you may correctly compare Yellow
Bile to the first of these, and Black Bile to the Latter‘ (Galen, On the Natural Faculties, 170AD)
Melancholy is also called Black Bile and Artrabilious; it is Cold and dry.
Quality. Cool, dry, astringent.
Element: Earth
Planet: Saturn
Seat: associated with the Spleen (which is also under Saturn). It is the Earthy part of the Blood, and the Spleen is of the Earth element. This also explains why TCM says the Spleen is particularly affected by an excess of Damp, for in its nature it draws the Cool and Dry portion of the Blood, and is therefore repelled by the Damp portion.
Melancholy is of two kinds:
‘Melancholy or black choler, is natural or unnatural.
Natural Melancholy, is the dregs of good blood, and is cold and dry, and hath beginning in the Liver,
and is divided into two parts; one part goes with the blood, the other part goes to the spleen.
And the property of that which goes with the blood, is to nourish the melancholy members as the bones;
and to thicken and fortify the blood.
And the property of that which goes to the spleen, is either to help to cleanse the whole body of superfluities;
or else nourish the spleen. And also to close and comfort the mouth of the stomach or ventricle, and to stir it
up by his acrimony unto hunger and desire of meat.
As the red choler does waken nature to use her expulsive quality to cast out the excrement downward: so the
black choler does waken nature in her desiring quality, to receive nourishment upward.
Unnatural Melancholy, is caused of adustion of choleric mixture, and is hotter and lighter than the other, having
in it a violent and killing nature‘. (Wirtzung)
Physiologically, Melancholy has the following effects:
That which enters the Blood:
1. Nourishes Cold and Dry parts of the Body (Bones, Retentive Faculty etc)
2. Gives stamina, strength, density, thickness and consistency to the Blood
3. helps promote staid, sober and rational mind by anchoring fantasy and imagination
That which travels to the Spleen:
1. Helps clean exhausted and worthless matter from the blood and body
2. Nourishes the Spleen with its dryness
3. Tones the Stomach, helps retention
4. its bitterness helps develop Appetite
Melancholic (Black Bile) Temperament
Lean, thin build, prominent features, small eyes with sunken cheeks, with coarse, dry, cool and rough skin, dark complexion with body hair than is thin, dark and slow to grow. Digestion is weak or sensitive, appetite is irregular, often has broken sleep or insomnia. They tend to overthink, be analytical, detail orientated with good memory retention.
Signs of an excess of Melancholy
Dry, dark skin, anxiety, depression, burning stomach pain, false appetite, thick and turbid urine. Dreams are dark, fearful, solitary
Typical Melancholy Diseases
Leprosy, Fibroid Tumors, Cancer, Spleomegaly, Constipation, Anorexia, Arthritis, Neuromuscular diseases, Anxiety, Depression, Psychiatric diseases.