Tastes of Medicines
Taste is a very important aspect of the way a Herb works, and helps greatly to suggest the activity of a given Medicine. Taste has been recognised as important in all Medicine Traditions.The primary Tastes with their general effects are as follows:
- Bitter: tends to be cool, to clear Heat and Bile Humor, and stimulates appetite and digestion. Bitter herbs are some of the most potent anti-bacterial medicines and are often strong against toxin and poison. Typical examples of Cool/Cold Bitter medicines include Gentian, Rhubarb and Coptis. Some Bitter herbs which are also aromatic have been accounted warm, Wormwood being an example.
- Pungent: Pungent is sometimes called Spicy. These medicines tend to be Warm, stimulating, promote Appetite and Digestion, and clear Cold and Damp. They are often added to formulas to stimulate the activity of other medicines as the promote assimilation and circulation. Ginger and the Peppers are classical examples. Some pungent medicines work superficially and promote Sweat while others work deeper in the body and warm the Yang.
- Sweet: Sweet medicines are strengthening. They are wholesome medicines which can nourish and strengthen the Qi, Blood, Yin or Yang. They tend to contain sugars, especially polysaccharides which have proven to be effective to increase immunity, restore organ function, and help repair and strengthen body function. Licorice, Honey and Raisins are examples.
- Salty: Salty medicines are often cooling. They are often effective for resolving Phlegm and Phlegm swellings. Kelp, Salt and various other medicines derived from the Ocean are examples. Some are important to promote digestion, like Rock Salt.
- Sour: Sour medicines are usually cool. They are cutting, thinning, and open obstructions. Lemon and various unripe fruit are examples. Sour medicines are often Astringent.
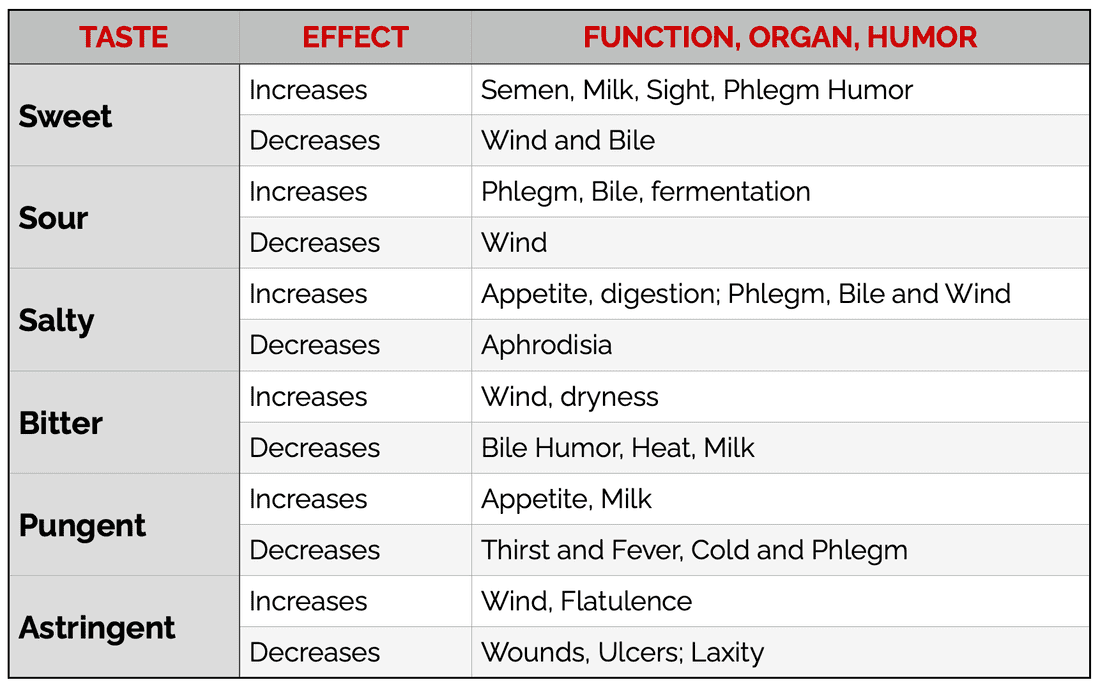
The Effects of Tastes in Ayurveda:
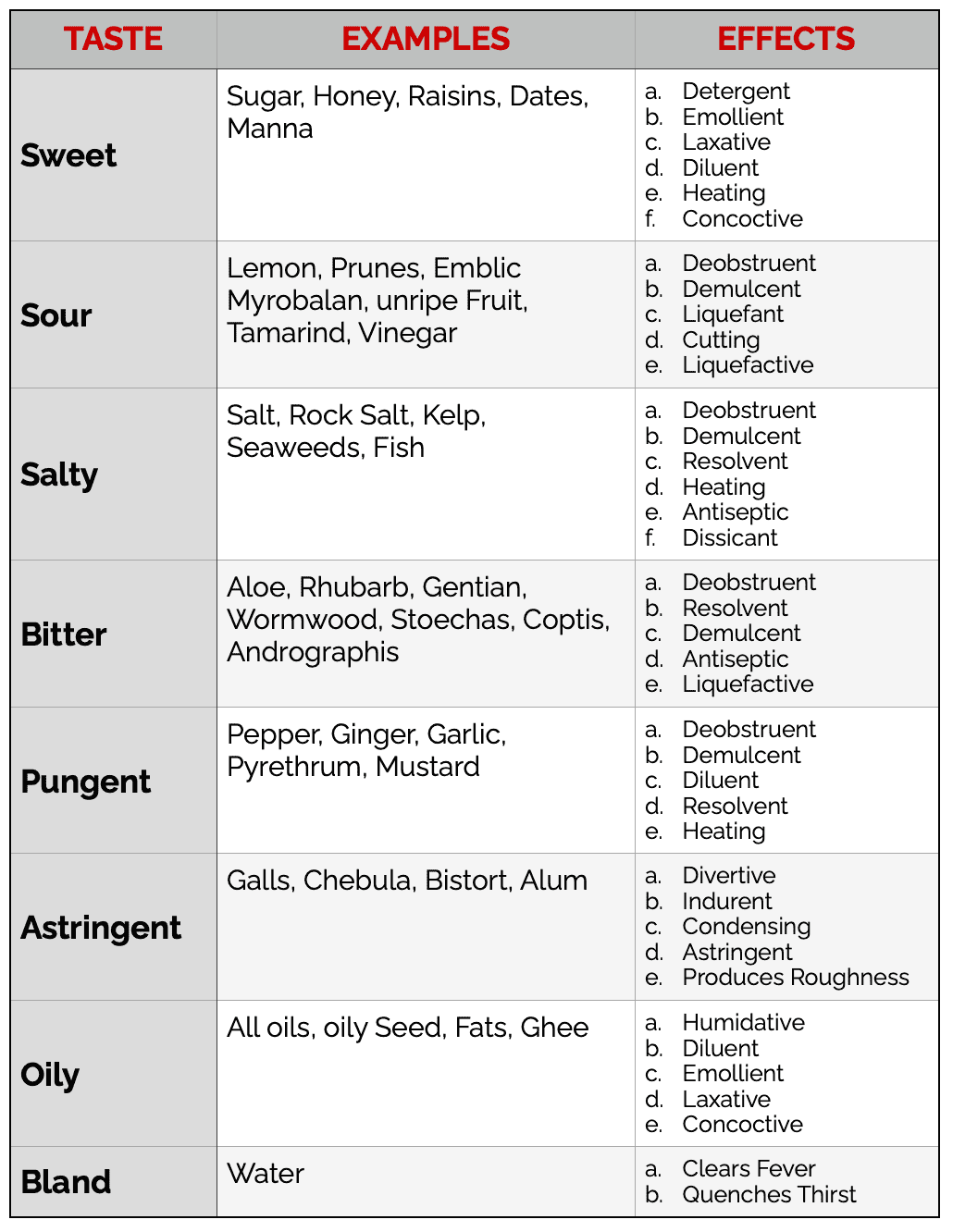
The Effect of Taste in Unani:
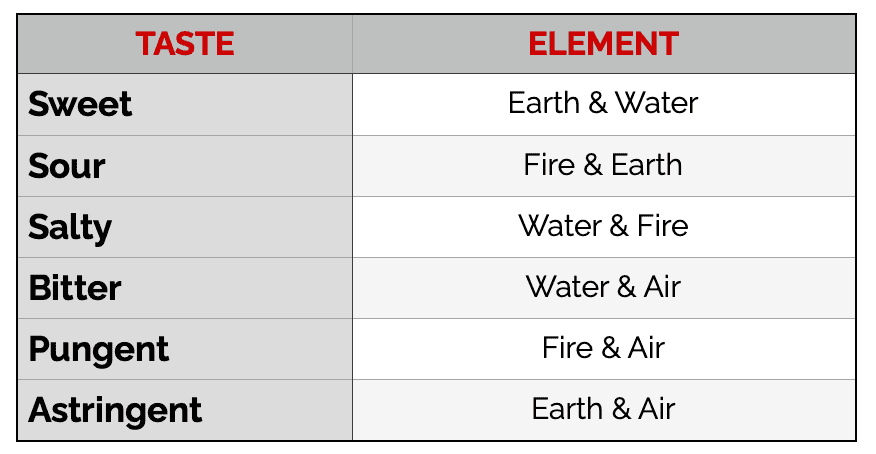
The Elements associated with the Tastes:
See also:
Temperature of Medicines
Hot or Cold? The Temperature of Medicines
Directing Medicines
Doctrine of Signatures
Humoral Medicine
Medicines used in the Various Systems
