Sarracenia, Pitcher Plant
Indian Cup, Small-Pox Plant, Saddle plant, Side-Saddle plantHuang Ping Zi Cao (S. flava, Yellow Pitcherplant)
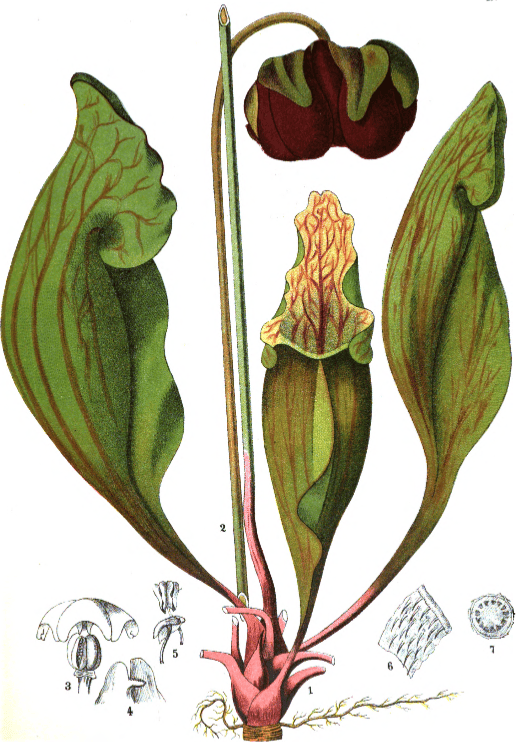 Sarracenia spp.
Sarracenia spp.Medicinal Plants, Millspaugh, 1892
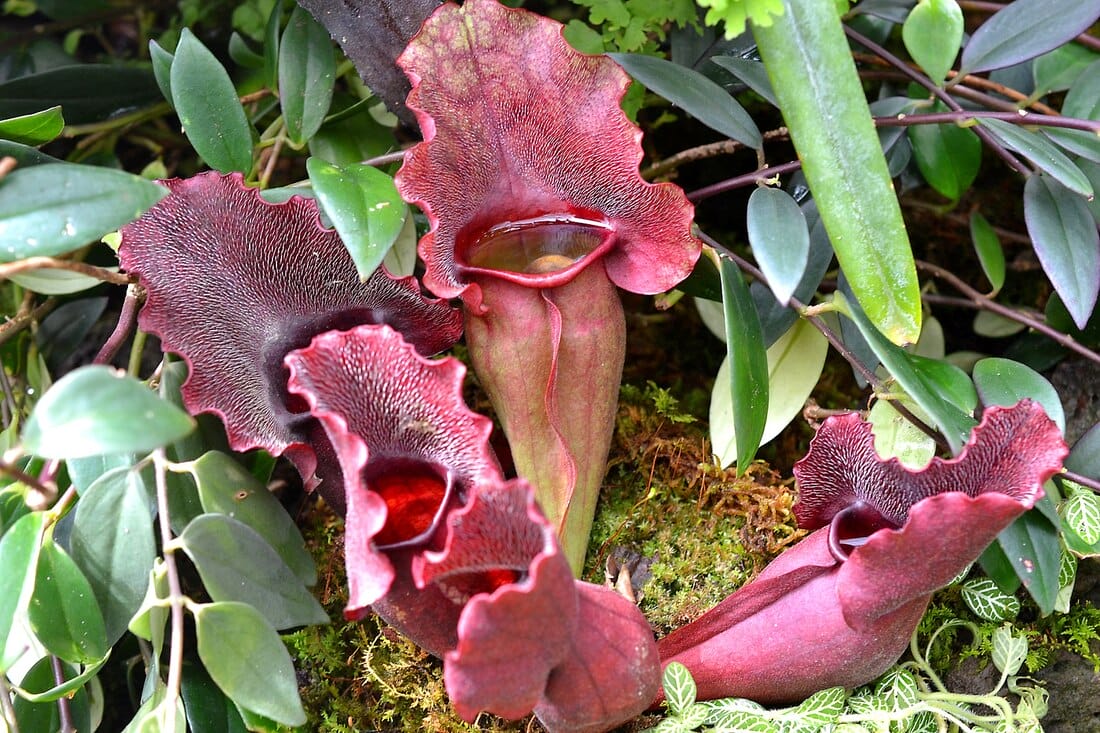 Sarracenia purpurea
Sarracenia purpurea(Photo by incidencematrix) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Sarracenia spp.
- S. purpurea (most commonly used species)
- S. flava
- S. variolatus
Parts used:
Many authorities recommended using only the fresh plant.
Whole fresh plant when budding, before the leaves have fully expanded, or the fresh root gathered after fruiting.
King said the leaf was equally effective as the root, and also recommended the powder.
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Bitter, slightly Sour
Constituents:
Piperidine Alkaloids: sarracenin (similar to veratrin), coniine, gamma-conicein
Sarracenia acid
Tannin, resin
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Heat, Resists Poison:
-Measles, Chicken Pox, Small Pox
-prophylactic in Small Pox (King’s)
2. Clears Damp-Heat, Promotes Urine:
-Heat and Damp affecting the Stomach, Liver or Intestines
-obstructed Urine
-Indigestion
3. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation:
-Chlorosis, Amenorrhea
Dose:
Powder: 1–2 grams (20–30 grains–King’s), 3–4 times daily.
Infusion: 1–3 fluid ounces, or 1 oz. to a pint, taken in teacupful doses.
Tincture of the Fresh Plant (1 in 5): 1 fluid dram
Fluid Extract: 10–20 drops
Comment:
A number of authors regarded this as specific for Small Pox, both to prevent and to cure (for example, Family Botanic Guide, Fox, 1924). However others, and specifically many European practitioners found it to be inert, and certainly ineffective against Small Pox. This was almost certainly due to the dry material being too old and therefore to have lost its strength. This led some to say only the fresh plant or root should be employed to make a Tincture or Fluid Extract. However, others (King’s) regarded the powder as effective. We may therefore assume fresh and dried products to be effective, as long as the dried product is freshly dried and prepared. In any case, the fresh plant or root appears to be more certain and effective, and therefore, should be used where possible. A number of modern sources (including PDR for Herbal Medicines) regard it as obsolete.
Main Combinations:
1. Promote Menstruation, Pitcher plant (Sarracenia), Blue Cohosh
2. Chicken Pox, Calendula with Pitcher plant (Sarracenia), Pennyroyal (1 oz. each), Senna (half oz.). Steep in 3 pints of boiling water and drink freely. (Family Botanic Guide, Fox, 1924)
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
None noted. The plant is said to contain traces of the toxic alkaloid Coniine (Hoffman).
