Picrasma quassioides, Ku Mu 苦木Indian QuassiaKu Mu (TCM) Kashshing (Ayurveda) |

|

|
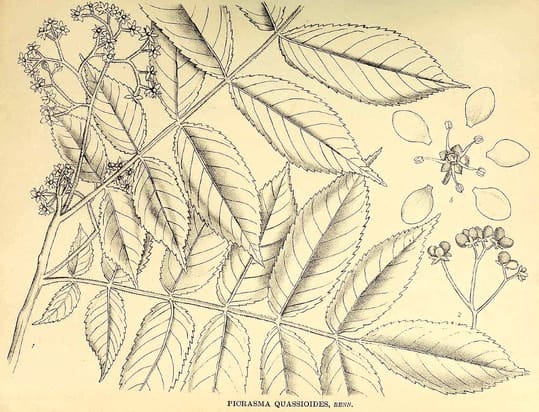 Picrasma quassioides
Picrasma quassioidesKirtikar, K.R., Basu, B.D., Indian medicinal plants, Plates, vol. 2 (1918)
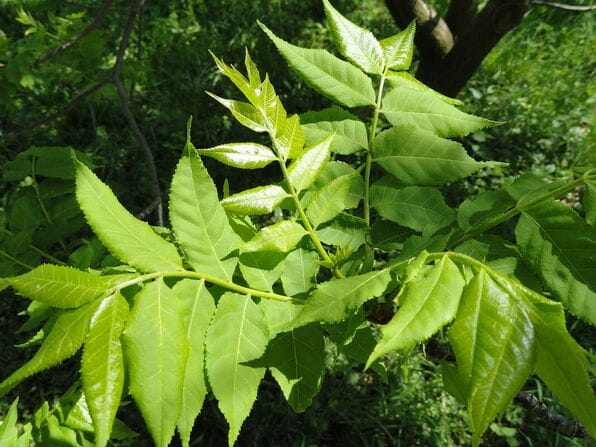 Picrasma quassioides
Picrasma quassioides(Photo by Daderot) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Picrasma quassioides
Parts used:
Branches and leaves (TCM)
Wood and Bark (Ayurveda)
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Very Bitter
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Heat, Resists Toxin:
-Common Cold or Flu from Wind-Heat (TCM)
-Fever (Ayurveda)
-acute pain and swelling of the Throat
-Snake Bite
-Boils, Eczema (TCM); Scabies (Ayurveda); Herpes simplex
2. Clears Heat, Resolves Swellings:
-Liver obstruction, swelling or hardness; Cirrhosis
-has been used for Cancer
3. Clears Damp-Heat:
-Diarrhea, Dysentery
-Gastro-duodenal Ulcers
4. Kills Worms:
-the Wood is used to kill parasites and insects (India)
-the Wood used in enemas for Worms (esp. Thread-worms)
-tincture can be used to kill head lice
5. Stimulates Digestion:
-as a strong bitter, it has been used to stimulate digestive activity, taken before meals to stimulate appetite.
Dose:
Branch in Decoction: 3–4.5 grams
Leaf in Decoction: 1–3 grams
Wood in Powder: 300–600mg
Sufficient amount may be used topically
Substitute:
1. It is a substitute for Quassia (P. amara, P. excelsa)
2. Clerodendrum serratum and Premna herbacea are used for this medicine in some parts of India
3. Samadera indica
Main Combinations:
1. Liver Heat, Fever, Picrasma with Picrorrhiza
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
1. Avoid overdose. Excess use irritates gastric mucosa and can induce vomiting. Chronic use of the related P. excelsa (Quassia) has been associated with loss of vision.
2. Avoid use during Pregnancy and breastfeeding
