Oxytropis, Stag sha སྟག་ཤLocoweed, CrazyweedStag sha (lit. ‘Tiger flesh’, Tibet) –Stag sha dkar po: Oxyytropis microphylla (Tibet) –Stag sha nag po: Oxytropis chiliophylla (Tibet) Duo Ye Ji Dou (TCM) |

|

|
 Oxytropis microphylla
Oxytropis microphyllaJacquemont, V., Voyage dans l’Inde pendant les années 1828 a 1832, (1844)
 Oxytropis microphylla (as Astragalus microphylla)
Oxytropis microphylla (as Astragalus microphylla)Pallas, P.S., Species Astragalorum, (1800-1803)
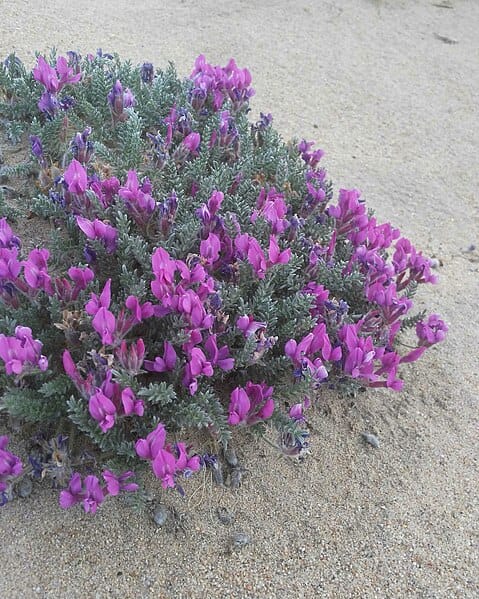 Oxytropis lanata
Oxytropis lanata(Photo by Demidenko) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Oxytropis spp.
- Stag sha dkar po: O. falcata, O. microphylla (syn. Astragalus microphylla), O. chiliophylla
- Stag sha nag po: O. reniformis, O. muricata (Mongolia)
- Sngo stag sha: O. microphylla
Other species listed for Stag sha from Buryat sources include: O. filiformis, O. glabra, O. stukovi, O. lanata, O. leptophylla, O. glandulosa
In the Buryat region, Oxytropis varlakovii is reportedly used as Stag sha nag po.
Parts used:
Whole herb with roots
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Bitter. Toxic
Uses:
1. Clears Heat, Resists Poison:
-Fever, Influenza
-Swollen Sore Throat
-Toxin, Poison; Anthrax
-Dysentery
2. Clears Heat, Resolves Swelling:
-Dermatitis, Abscesses, Leprosy
-Toxic Swellings, Tumors, Cancer
-Lymph disorders
-Inflammations associated with heat and toxicity
3. Moves the Blood, Stops Bleeding:
-various types of Bleeding
-Amenorrhea
-Trauma, Bruising
-Wounds, Fractures
4. Externally:
-powder is applied to non healing wounds
-applied to fractures
-inflammations and swellings from heat
Dose:
A method of use for Oxytropis glabra: add 1 tablespoon of the cut and dried above-ground herb to 300mls. of water and boil for 3 minutes, then let it stand for an hour, then strain. The resulting decoction can be taken in doses of 1 tablespoonful, 2–3 times daily.
Comment:
1. Oxytropis is often referred to as the “King of Herbs” in Tibetan Medicine.
2. Oxytropis is known to accumulate Selenium
Substitute:
1. Potentilla discolor and Calophaca crassicaulis have both been given as sources for Stag sha by different authors. If they are suitable substitutes and used as such has not been determined.
Main Combinations:
1. Against severe Poison, Oxytropis Stag sha with Bezoar and Rhino horn
2. Arthritic complaints, Oxytropis Stag sha with Bdellium, Frankincense and Aconite
3. Blood toxin, Oxytropis Stag sha with Cinnabar
4. Cancer, Oxytropis Stag sha with Chebula, Costus, Calamus, Aconitum ferox, Commiphora mukul, Acacia catechu, Delphinium brunonianum, and a mineral ingredient (as in Thapring of Tibetan Medicine)
Major Formulas:
Clove 35 (Li shi so lnga)
Garuda 9 (Khyung lnga ni la)
Great Yellow Compound (Sman ser chen mo)
Influenza Pills (Lo gyon ril bu)
Joyful 16 Pill (Dg’a ba bchu drug)
Notopterygium 29 Pills (Spru nag nyer dgu)
Principal 8 Turquoise Mane (Gtso brgyad gyu ral)
Przewalskia 11 (Thang phrom bcu gchig)
Red Pony (Rta zi dmar po)
Rhubarb 8 Ointment (Zab lag brgyad pa) (Tibetan)
Safflower Garuda (Gur khyung phyag rdor)
Tabasheer 7 (Cu gang bde byed)
Cautions:
1. Toxic in overdose.
2. Not used during Pregnancy, in children or those with Heart or Liver disease.
Toxicity:
Accumulates in the Brain, Kidneys and Liver
Overdose causes Arrhythmia, which resolves when discontinued.
–Subacute toxicity and chemical analysis of Tibetan medicine Oxytropis falcata
Main Preparations used:
Research:
1. GENERAL /REVIEW:–Phytochemical and Biological Studies of Plants from the Genus Oxytropis
–Chemical and Biological Characteristics of Oxytropis pseudoglandulosa Plant of Mongolian Origin
–Flavonoids in the poisonous plant Oxytropis falcata.
–[Chemical constituents of Oxytropis chiliophylla].
–[Studies on chemical constituents of herbs of Oxytropis microphylla].
2. ANTI-BACTERIAL:
–Screening for fractions of Oxytropis falcata Bunge with antibacterial activity
3. ANTI-INFLAMMATORY:
–The studies of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities and pharmacokinetics of Oxytropis falcate Bunge extraction after transdermal administration in rats
4. ANTI-OXIDANT:
–Antioxidant activities of extracts and flavonoid compounds from Oxytropis falcate Bunge.
5. ANALGESIC
–The studies of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities and pharmacokinetics of Oxytropis falcate Bunge extraction after transdermal administration in rats
6. ANTI-TUMOR / ANTI-CANCER:
–Antitumor effects of two extracts from Oxytropis falcata on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
–[Study on apoptosis of SMMC-7721 hepatocarcinoma cells induced by Oxytropis falcata and its preliminary mechanism].
–[Influences of Oxytropis falcata on proliferation of SMMC-7721 hepatocarcinoma cells and expression of MMP-2].
–Oridonin nanosuspension enhances anti-tumor efficacy in SMMC-7721 cells and H22 tumor bearing mice.
–[Influences of Oxytropis falcata on proliferation of SMMC-7721 hepatocarcinoma cells and expression of MMP-2].
7. MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA:
–Mechanism of Action of Flavonoids of Oxytropis falcata on the Alleviation of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.
8. PULMONARY FIBROSIS
–Protective mechanism of flavonoids of Oxytropis falcata bunge against IPF
–Total flavonoids of Oxytropis falcata Bunge have a positive effect on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
9. INCREASES ADRENOCORTICOL HORMONES
–Enhances secretion of Adrenocortical hormones.
10. IMPROVES INSULIN RESISTANCE:
–Total Flavonoids Extracted from Oxytropis falcata Bunge Improve Insulin Resistance through Regulation on the IKKβ/NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway.
11. UV PROTECTIVE:
–[Study on the ultraviolet protective effects of the cream of the total flavonoids from Oxytropis falcata].
12. BURNS:
–Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Oxytropis falcata Gel on Deep Second-Degree Burn in Rats.
