Notoginseng, San Qi 三七Pseudoginseng rootSan Qi, Tian Qi (TCM) |

|
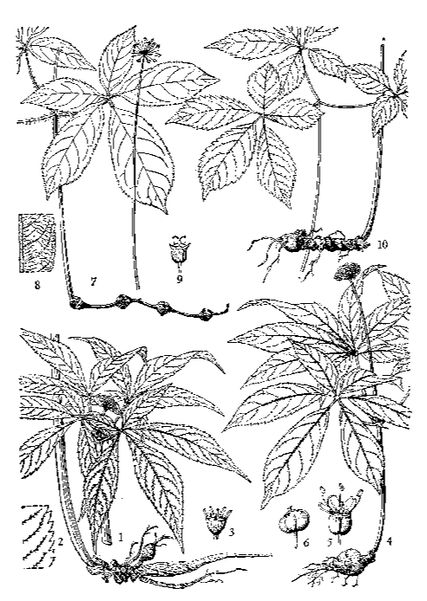 The structure of Panax notoginseng, Chinese Flora, 1959
The structure of Panax notoginseng, Chinese Flora, 1959 San Qi (Adam, Chengdu Medicine Market, 2018)
San Qi (Adam, Chengdu Medicine Market, 2018)Botanical name:
Panax notoginseng (syn. Panax pseudo-ginseng var. notoginseng)
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Sweet, slightly Bitter
Classifications:
K. Move the Blood L. Stop Bleeding:
Uses:
1. Stops Bleeding:
-all types of bleeding including Vomiting Blood, Blood in the Urine or Stool
-Bleeding from Trauma
-Profuse Menstruation, Uterine Bleeding
2. Moves the Blood, Clears Stasis, Reduces Swelling, Relieves Pain:
-internal blood stagnation; chest or abdominal pain
-obstructed Menstruation, Dysmenorrhea, Uterine tumors
-Postpartum Blood Stasis; “Good for a woman to take after delivery” (Li Shi Zhen)
-joint pain associated with Blood Stasis
-Trauma, Bruising, Sprains, Fractures
-also in the treatment of Sores and Abscesses
-all kinds of diseases due to Blood disorders’. (Li Shi Zhen)
-‘good for a woman to take the drug after child delivery’ (Li Shi Zhen)
3. Resists Poison, Resolves Swelling:
-Boils, Carbuncles, Swellings
-red and inflamed eyes
-venomous bites including Snake Bite (Li Shi Zhen)
Dose:
Powder: 1–1.5 grams
Decoction: 3–9 grams
Substitute:
1. Salvia Dan Shen root, when Charred, is regarded as having an effect very similar to Notoginseng San Qi. It can both move the Blood and stops Bleeding, while retaining a secondary Blood tonifying effect.
2. Similar properties to Dragons’ Blood (Li Shi Zhen)
3. Gynura japonica (syn. G. segetum) is called Ju Ye San Qi and has been used as a substitute for Notoginseng San Qi in Yunnan province.
Main Combinations:
1. For Bleeding:
i. Notoginseng San Qi with Red Earth
ii. Bleeding due to deficiency, Notoginseng San Qi with Astragalus Huang Qi and Donkey Hide Gelatin E Jiao.
iii. Bleeding from Trauma, Notoginseng San Qi with Dragon’s Blood, Frankincense, Myrrh
iv. Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Notoginseng San Qi with Catechu (TCM)
2. For Blood Stasis:
i. Notoginseng San Qi with Rhubarb (Da Huang)
ii. Notoginseng San Qi with Dang Gui, Peach kernel (Tao Ren), Safflower (Hong Hua)
iii. Pain and Blood stasis following Trauma, Notoginseng San Qi with Frankincense, Myrrh, Musk and Borneo Camphor.
3. Muscle and Ligament pain following Trauma:
i. Notoginseng San Qi with Cyperus rotundus (Xiang Fu) and Licorice
ii. Notoginseng San Qi with Turmeric, Frankincense
4. Coronary Heart Disease:
i. Notoginseng San Qi, Salvia Dan Shen
ii. Notoginseng San Qi with Hawthorn berry, Arjuna
iii. Notoginseng San Qi with Dalbergia Jiang Xiang, Salvia Dan Shen, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Safflower (Hong Hua) (as in Xinning Pian). This is also used for Angina Pectoria.
5. Angina Pectoris:
i. Notoginseng San Qi with Valerian
ii. Notoginseng San Qi with Saffron
iii. Notoginseng San Qi, Salvia Dan Shen, Borneo Camphor
iv. Notoginseng San Qi, Frankincense, Safflower, Borneo Camphor
v. chest pain, tightness from Qi and Blood stagnation with an intermittent pulse, Notoginseng San Qi, Amber, Red Ginseng, Salvia Dan Shen, Styrax Su He Xiang, Borneo Camphor (Bing Pian) (as in Ling Bao Hu Xin Dan of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
6. Thrombosis, Notoginseng San Qi with Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Astragalus Huang Qi, Pueraria lobata, Paeonia Bai Sho, Salvia Dan Shen
7. Osteoarthritis:
i. Notoginseng San Qi and Rehmannia Shu Di Huang
ii. Notoginseng San Qi and Achyranthes Niu Xi, Eucommia Du Zhong, Mistletoe (Sang Ji Sheng)
8. Poor Memory in the aged, Notoginseng San Qi, Ginseng, Schisandra Wu Wei Zi.
9. Cerebral Ischemia:
i. Notoginseng San Qi with Saffron (or Safflower extract)
ii. Notoginseng San Qi, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Astragalus Huang Qi
10. Breast Lumps, Nodes, Hyperplasia: Notoginseng San Qi, Spatholobus Ji Xue Teng with Dandelion (Pu Gong Ying), Laminaria Kun Bu, Paeonia Chi Shao Yao, Costus (Mu Xiang), Scrophularia Xuan Shen, Paeonia Mu Dan Pi, Self Heal (Xia Ku Cao), Safflower (Hong Hua) (as in Ru Pi Xiao Pian of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
11. Cancer, Notoginseng San Qi, Ginseng, Cordyceps, Frankincense. This is a modern Korean formula widely used in Cancer treatment.
12. Dysmenorrhea with Qi and Blood deficiency, Notoginseng San Qi, Corydalis Yan Hu Suo with Dang Gui, Paeonia Bai Shao, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Atractylodes Bai Zhu, Cyperus rotundus (Xiang Fu), Saffron (or Safflower Hong Hua) (as in Ding Kun Dan)
13. Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy, Notoginseng San Qi, Astragalus Huang Qi, Dang Gui (proven effectiveness)
14. Ulcerated Sores, apply powder of Notoginseng San Qi, Frankincense and Myrrh
15. To beautify the Skin, Notoginseng San Qi with Angelica Bai Zhi, Dang Gui, Pearl as a cream
Major Formulas:
Ding Kun Dan
Ling Bao Hu Xin Dan
Ru Pi Xiao Pian
Xinning Pian
Zhen Xiang Jiao Nag (Precious Aromatic Capsules)
Zheng Gu Shui
Yunnan Baiyao
Cautions:
1. Caution during pregnancy, avoid large doses
2. Some people may have adverse effects from therapeutic doses, such as nausea, vomiting, esophagitis and bleeding. Symptoms are rarely serious, symptoms resolve when the herb is discontinued without further problem.
