Nerium, OleanderOleander, Rose Bay, Rose LaurelKaravira, Viraka, Ashvamaraka (White-flowered variety, Ayurveda) Raktapushpa, Raktaprasava, Ravipriya (Red-flowered variety, Ayurveda) Kaner, Chandani (Unani) Sanbul Aqleeti (Arabic) Arali (Siddha) Jia Zhu Tao (TCM) |

|

|
 Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491
Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491 |
 Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578
Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578 |
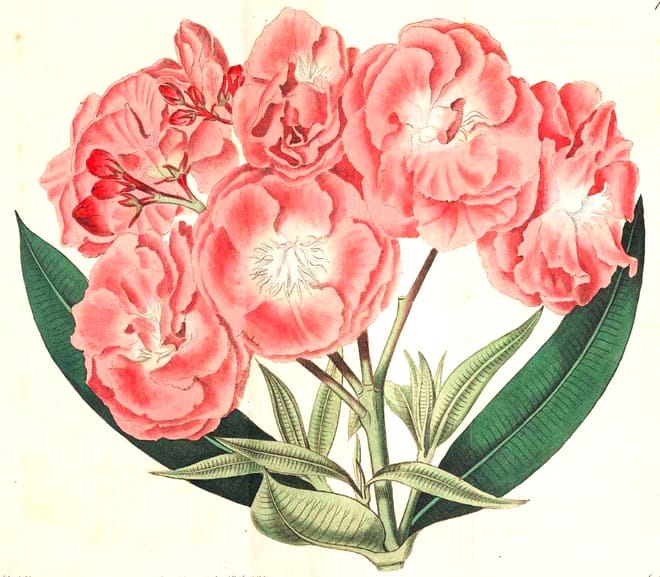 Nerium oleander
Nerium oleanderBotanical Register, vol. 1, (1815)
Botanical name:
Nerium spp.:
- N. oleander (syn. N. odorum); Red Oldeander, Rose Bay
- N. indicum; White Oleander
Parts used:
Leaf (processed); Root (or root-bark)
Temperature & Taste:
Very Warm, dry. Bitter. Toxic
“Hot in the Last phase of the Third degree and Dry in the Second degree”. (Avicenna)
Uses:
1. Strengthens and Regulates Heart: (TCM)
-functional Heart disorders; Angina, Arrhythmia, Tachycardia
-Congestive Heart Failure
-digitalis-like effect
2. Warms the Kidneys, Clears Damp, promotes Urine: (TCM)
-Edema, fluid swelling
-“Removes the Stones”. (Avicenna)
-also used as an Aphrodisiac
-leaf decoction has been used for Diabetes (Morocco)
3. Clears Phlegm, Stops Cough and Wheezing: (TCM, Ayurveda)
-Cough, Asthma (TCM)
4. Moves the Blood, Clears Stasis: (TCM)
-Amenorrhea, Dysmenorrhea
-Abortifacient (leaf, root)
-“Its leaves facilitate voluminous discharge of Menses” (Avicenna)
-Pain and bruising from Trauma
-Tumors and Cancers
5. Settles Wind, Stops Spasms: (TCM, Ayurveda)
-Vertigo, Dizziness
-Apoplexy, Epilepsy, Paralysis (leaf powder used as a snuff for Epilepsy)
-Hypertension
-Insomnia
6. Resists Poison:
-regarded as a blood purifier; Leprosy, Syphilis (Leaf)
-Malaria
-Snake and Poison insect bite
7. Externally:
-oil, paste or decoction used for skin diseases, Eczema, Psoriasis, Ringworm, Herpes, Leprosy (since Charaka)
-“Oleander is very suitable for treating Itches, Scabies and Exfoliation”. (Avicenna)
-oil of the root-bark is especially effective against Leprosy.
-powdered leaf mixed with lard is applied to Pruritus
-Corns, Warts
-Topically for Hemorrhoids
-Alopecia (Sushruta)
-Fistula in Ano
-leaf powder is applied to Wounds to promote healing
-fresh leaf paste is applied to reduce swellings
-root boiled into a paste is used for Ulcers and Sore of the Penis
-“Spraying of its decoction in houses, destroys Fleas and Termites”. (Avicenna)
Comment:
Some sources have given equivalent uses for Leaf and Root (or Root-bark).
The Root is more powerful to promote Urine and as a Heart tonic.
Leaves are more used to move the Blood, and to purify the Blood. Their use is very similar.
Dose:
1. Most used externally.
2. Leaf and Root are used in similar doses:
Powder: 30–125mg (API)
Some sources (ie. Duke) have listed doses of 1–3 grains (65–200mg)
According to Avicenna, Galen used it in doses of around 1500mg.
Externally, 1–3 grams can be decocted and applied.
Comment:
1. The Yellow-flowered variety is Thevetia peruviana
2. It is one of the Kushthaghna group of herbs in Ayurveda, used for skin diseases
Correctives:
Oil, Butter, Honey, Milk (Unani)
Substitutes:
1. Camomile, Meliot and Fenugreek are given as substitutes in Unani (for external use)
2. It actions are similar to Digitalis and Strophanthus
Main Combinations:
1. Skin diseases, Boils, Psoriasis, Lecoderma etc.:
i. Nerium bark, Cassia tora, Vernonia anthelminticaPlumbago, Ginger, Turmeric, Symplocos, Neem
ii. prepare an oil from Nerium, Aconitum ferox root, Pongamia, Barberry bark, Turmeric, Calamus, Madder, Red Sandalwood (as inVisha Taila)
2. Leprosy and other obstinate skin diseases, Nerium bark mixed with Neen oil and applied (Ayurveda)
3. Fistula-in-Ano, Nerium bark with Plumbago, Turpeth, Calamus, Gloriosa, Alstonia (equal parts), decocted in Sesame oil (as in Citrakadi Taila of Ayurveda)
4, Insect Bites: “It is a poison but sometimes it is used orally with wine and common rue in order to remove the poisonous effects of insects”. (Avicenna)
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
1. Toxic. Avoid overdose. Fatalities have been reported. Children have reportedly died after eating a handful of flowers.
2. Not used in the young, very old, very weak, or during Pregnancy or Lactation.
Drug Interactions:
1. Avoid use in those taking Cardiac Glycosides. Taking concurrently with cardiac glycosides (such as Digoxin) will potentiate toxic effects.
2. Quinidine, calcium salts, saluretics, laxatives can also potentiate effect.
Toxicity:
1. Overdoses may cause ‘arrhythmia, bradycardia, cardiodepression, confusion, cyanosis, diarrhea, headache, hyperkalemia, nausea, neurodepression, stupor, vomiting’. (Duke)
2. Toxic effects are said to resemble Nux Vomica.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity testing did not produce macroscopic or microscopic changes to any organs (Indian Herbal Remedies)
