Nelumbo Rhizoma, Lotus Rhizome, Ou Jie 藕节
Ou Jie (TCM)Tamarai Kizanku (Siddha)
 Descourtilz, M.E., Flore médicale des Antilles, vol. 8 (1829)
Descourtilz, M.E., Flore médicale des Antilles, vol. 8 (1829)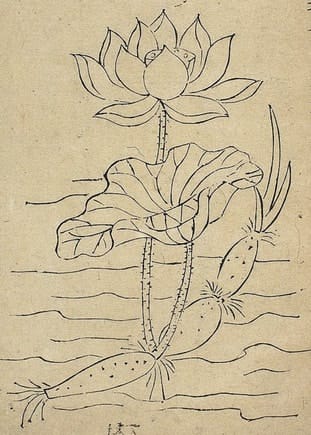 Jiu Huang Ben Cao (The Famine Relief Herbal) (1593)
Jiu Huang Ben Cao (The Famine Relief Herbal) (1593)Botanical name:
Nelumbo nucifera
Parts used:
Rhizome node
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral, dry. Sweet
Classification:
L. Stop Bleeding:
Uses:
1. Clears Heat, Stops Bleeding:
-Vomiting or Coughing of Blood from Heat of the Lungs or Stomach
-“detoxifies alcoholism” (Chen Cang Qi)
-the fresh root quenches Thirst
-it was also said to detoxify Aconite poison. (Zu Zhi Cai)
2. Calms the Mind, Settles Wind:
-has a settling effect on the Mind and Nerves and a cooling effect on Bile (Ayurveda)
-Nervousness, Anxiety, Stress, overactive mind
-“Long-term use makes one happy” (Ming Yi Bie Lu)
-“Pacifies Anger” (Chen Cang Qi)
3. Astringes the Kidneys:
-benefits Essence
-strengthening in chronic diarrhea, leukorrhea, spermatorrhea
-regarded as beneficial for the Base Chakra in Ayurveda
Dose:
1. Fresh root is best to clears Heat and Quench Thirst
2. The Steamed root or the root taken with Honey Tonifies the 5 Organs
Decoction: 9–15 grams (30–60 grams fresh)
Eaten as a food.
Substitute:
“It has slightly different functions than lotus seed.” (Li Shi Zhen)
Substitutes:
Lotus and Water Lily are very similar in use. In general the corresponding part of each plant can be used as a substitute.
Main Combinations:
1. Bleeding:
i. Vomiting Blood, Lotus Rhizome with Madder (Qian Cao Gen)
ii. Coughing Blood, Lotus Rhizome with Rehmannia Sheng Di Huang, Fritillaria Chuan Bei Mu
iii. Lotus Rhizome, Emblic Myrobalan, Madder, Safflower (Ayurveda)
2. To calm the Mind and Nerves, Lotus Rhizome with Centella, Convolvulus Shakhapushpi
Cautions:
None noted
