Indigo, Qing Dai 青黛
Pigmentum IndicumQing Dai (TCM)
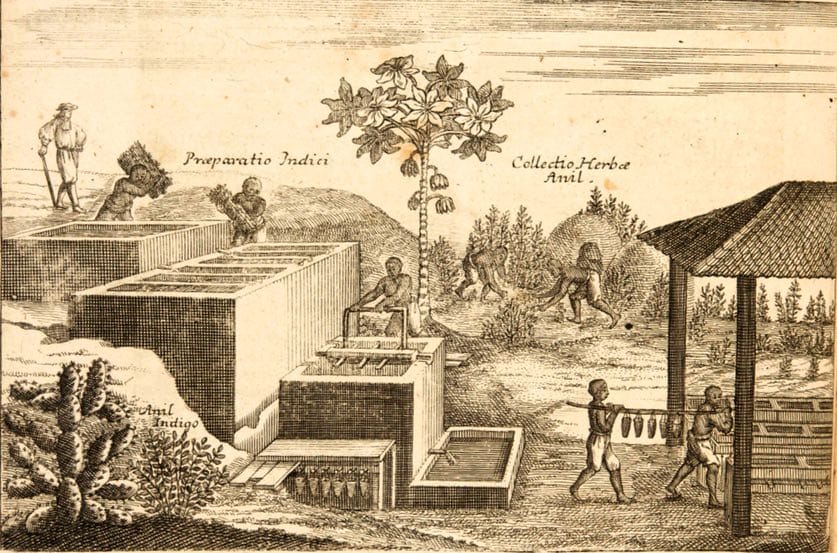 The processing of Indigo
The processing of Indigo(Museum Museorum, Valentini, 1704)
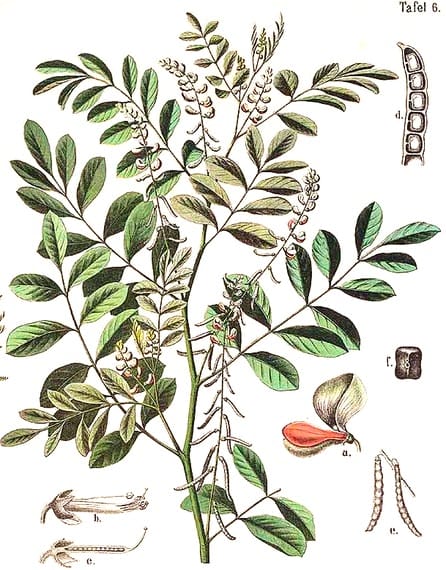 Indigofera tinctoria
Indigofera tinctoriaAusländische Culturpflanzen in bunten Wand-Tafeln, (?)
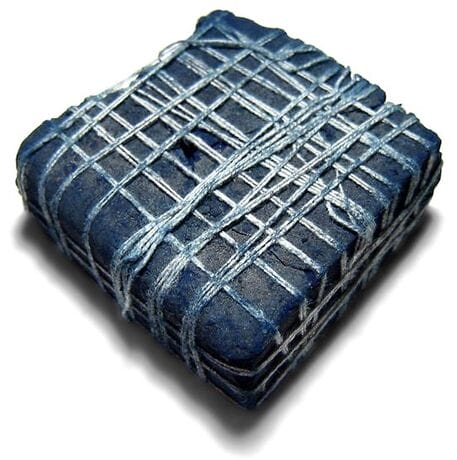 A Block of Indian Indigo
A Block of Indian Indigo(Photo by Palladian) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Several plants supply Indigo:
- Baphicacanthus cusia
- Polygonum tinctorium
- Isatis indigotica (syn Isatis tinctoria)
- Indigofera tinctoria, I. anil, I. argentea
Parts used:
Indigo extracted from any of the above plants
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Salty
Classification:
B. Clears Heat and Toxin
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Poison, Cools the Blood:
-Influenza, Epidemic diseases
-rashes and spots from hot toxin
-Bleeding from excess Heat
-swelling, pain and redness of the mouth or throat; Mumps
-traditionally used for the poison of Snakes or Rabid Dogs.
-‘epidemic disease with headache, chills and fever’. (Kai Bao Ben Cao)
-‘quickly assuages swellings and inflammations’. (Galen)
-detoxifies the toxin of various drugs (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
2. Clears Liver Heat, Settles Wind to Stop Tremors:
-red eyes, restlessness, sore throat, Fever with Convulsions
3. Clears Lung Heat:
-Cough, Bronchitis and Chest pain from Lung heat
4. Externally:
-topically for red, itchy skin conditions such as Eczema
-topically for mouth or throat sores and ulcers
-topically for red, painful swellings and sores, Carbuncles, Abscesses
Dose:
1–3 grams in pills or powders. Pills can be coated with Indigo; it can be taken in powders or pills, or dissolved into strained decoctions; it can be used topically.
Comment:
Indigo is a concentrated extract of cooling plants used to clear Heat and Poison. The purple powder was traditionally used as a dye and for early tattoo-making. It is very Cold, dry and Salty. It clears Heat from the Blood, Throat, Lungs and Liver in particular. It is also useful for strong heat causing Febrile Convulsions and can be used topically to clear Heat and Poison.
Main Combinations:
1. Heat of the Blood with red spots and rashes and fever, with Rehmannia Sheng Di Huang and Gypsum Shi Gao
2. Febrile convulsions in children, with Gastrodia Tian Ma and Bezoar
3. Heat with mouth or throat sores, red eyes, with Talcum and Licorice
4. Strong Liver Fire with restlessness and convulsions, with Genitana Long Dan Cao and Coptis Huang Lian
5. Spitting Blood, Clam shell (Ge Ke) (10 parts), Indigo (Qing Dai) (1 part). Form a powder (as in Dai Ge San from Wei Sheng Hong Bao [A Great Precious Sanitation])
6. Mouth sores or ulcers that don’t heal, topically with Borneol Camphor and Alum
7. Sore Throat, Stomatitis, Gingivitis, Indigo, Coptis Huang Lian, Phellodendron Huang Bai, Mint (Bo He), Platycodon Jie Geng, Catechu (Er Cha)
8. Ulcerative Colitis: 2 grams per day were used for 33 patients over 52 weeks. After 4 weeks and 52 weeks there was a 67% and 73% clinical remission, respectively. Rate of mucosal healing at 4 weeks and 52 weeks was 48% and 70%, respectively. Four patients (12%) had severe adverse effects, including 3 with colitis. (see here)
9. Carbuncle, Abscess, Indigo, Rhubarb, powder, mix with egg white and apply. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
10. Hot, itchy, painful Sores, beat Purslane to a paste, mix in Indigo and apply. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Major Formulas:
Ke Xue Fang
Shuang Liao Hou Feng San
Cautions:
1. Use cautiously in people with Stomach Coldness
2. Use cautiously in patients with Ulcerative Colitis as research has shown a percentage of side effects in these patients.
Main Preparations used:
-
Extra Info
- Research
GENERAL / REVIEW
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
–A Comprehensive Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacology, Clinical Applications, Adverse Events, and Quality Control of Indigo Naturalis
–Isatis tinctoria L. (Woad): A Review of Its Botany, Ethnobotanical Uses, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities, and Biotechnological Studies
ANTI-BACTERIAL
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
–An In Vitro Study of the Antimicrobial Effects of Indigo Naturalis Prepared from Strobilanthes formosanus Moore
ANTI-VIRAL
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
VIRAL-INDUCED LUNG INJURY
–Beneficial effect of Indigo Naturalis on acute lung injury induced by influenza A virus
ANTI-OXIDANT
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
–Qing–dai powder promotes recovery of colitis by inhibiting inflammatory responses of colonic macrophages in dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice
IMMUNOMODULATORY
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
DERMATITIS:
–Efficacy and safety of indigo naturalis ointment in Treating Atopic Dermatitis: A randomized clinical trial.
PSORIASIS
–A traditional Chinese remedy points to a natural skin habitat: indirubin (indigo naturalis) for psoriasis and the Malassezia metabolome.
–An alkaloid-rich phytopharmaceutical prepared from Qing Dai against IL-17A-induced psoriasis.
–Anti-psoriatic effects of indigo naturalis on the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes with indirubin as the active component.
–Clinical assessment of patients with recalcitrant psoriasis in a randomized, observer-blind, vehicle-controlled trial using indigo naturalis.
–Comparison of indirubin concentrations in indigo naturalis ointment for psoriasis treatment: a randomized, double-blind, dosage-controlled trial.
–Indirubin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice by inhibiting inflammatory responses mediated by IL-17A-producing γδ T cells.
–Clinical efficacy and IL-17 targeting mechanism of Indigo naturalis as a topical agent in moderate psoriasis
–A Comprehensive Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacology, Clinical Applications, Adverse Events, and Quality Control of Indigo Naturalis
–Topical Botanical Agents for the Treatment of Psoriasis: A Systematic Review.
–Plant extracts for the topical management of psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
ANTI-TUMOR / ANTI-CANCER
–From natural dye to herbal medicine: a systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis
–Enhancing effects of indirubin on the arsenic disulfide-induced apoptosis of human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells.
–Antitumor activity of novel indirubin derivatives in rat tumor model.
–Review Molecular mechanisms of indirubin and its derivatives: novel anticancer molecules with their origin in traditional Chinese phytomedicine.
–Indirubin enhances tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis through modulation of nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway
–A Comprehensive Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacology, Clinical Applications, Adverse Events, and Quality Control of Indigo Naturalis
LEUKEMIA
–Antileukemic effects of indigo naturalis constituents by “target constituent knock-out” coupled with semipreparative liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
–Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia.
–Multicenter randomized trial of arsenic trioxide and Realgar-Indigo naturalis formula in pediatric patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia: Interim results of the SCCLG-APL clinical study.
ANTI-ANGIOGENIC
–Indigo naturalis and its component tryptanthrin exert anti-angiogenic effect by arresting cell cycle and inhibiting Akt and FAK signaling in human vascular endothelial cells.
–A Comprehensive Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacology, Clinical Applications, Adverse Events, and Quality Control of Indigo Naturalis
COLITIS
–Comparison of the anti-colitis activities of Qing Dai/Indigo Naturalis constituents in mice.
–Qing–dai powder promotes recovery of colitis by inhibiting inflammatory responses of colonic macrophages in dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice
–Indigo Naturalis Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating the Intestinal Microbiota Community.
ULCERATIVE COLITIS / INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE:
–Indirubin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through the inhibition of inflammation and the induction of Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells
–Short-term and long-term outcomes of indigo naturalis treatment for inflammatory bowel disease.
–Indigo naturalis is effective even in treatment-refractory patients with ulcerative colitis: a post hoc analysis from the INDIGO study.
–Efficacy of Indigo Naturalis Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Series.
–Efficacy of Indigo Naturalis in a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of Patients With Ulcerative Colitis.
–Treatment with indigo naturalis for inflammatory bowel disease and other immune diseases.
–Mechanisms of indigo naturalis on treating ulcerative colitis explored by GEO gene chips combined with network pharmacology and molecular docking.
–One-year clinical efficacy and safety of indigo naturalis for active ulcerative colitis: a real-world prospective study.
–The combination of indirubin and isatin attenuates dextran sodium sulfate induced ulcerative colitis in mice.
–Efficacy and safety of short-term therapy with indigo naturalis for ulcerative colitis: An investigator-initiated multicenter double-blind clinical trial
–Efficacy of Indigo Naturalis Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Series
–Indigo naturalis (Qing dai) for inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
WOUND HEALING:
–Indigo enhances wound healing activity of Caco-2 cells via activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
