Gelsemium elegans, Gou Wen 鉤吻Graceful JessamineGou Wen (TCM) |

|

|
 Gelsemium elegans
Gelsemium elegansFlora Malesiana (1962)
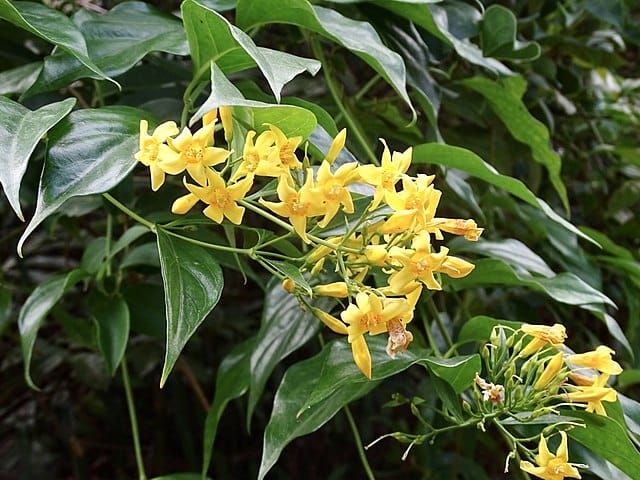 Gelsemium elegans
Gelsemium elegans(Photo by Toby Y) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Gelsemium elegans
This is one of only 3 species of Gelsemium and is native to Southeast Asia. Gelsemium sempervirens is native to the US.
Parts used:
Root, Root-bark, Whole herb. Root is strongest
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, Bitter. Toxic
Classification:
Uses:
1. Clear Wind-Damp, Eases Pain:
-Eczema, skin eruptions
-Neuralgia
-Wind-Damp joint pain, Rheumatoid pain
2. Disperses Masses, Resists Toxin:
-Scrofula
-Trauma, Bruising
-Skin Ulcers
-Tumors and Cancer
Dose:
Today it is primarily restricted to topical use.
Substitute:
Gelsemium sempervirens, native to the US may be a synonymous herb, but we have separated them due to their different uses.
Corrective:
Licorice is said to help correct its toxicity
Main Combinations:
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
1. Very toxic. Avoid overdose. ‘When people happen by mistake to eat the leaves mixed with vegetables, they die in the course of half a day.’ (Li Shi Zhen)
2. Not used during Pregnancy, while Breastfeeding, in the very young or elderly, the very weak, or those with Liver or Kidney disease.
Toxicity:
1. Very toxic in overdose. It has been responsible for a number of deaths in China. Causes Gastrointestinal, Neurological and Cardio-respiratory toxicity. The young leaf and shoot is most toxic. Toxic symptoms appear 5 minutes to 2 hours after ingestion.
2. A comprehensive toxicity evaluation in rats after long-term oral Gelsemium elegans exposure.
3. Toxicokinetics of 11 Gelsemium Alkaloids in Rats by UPLC-MS/MS.
4. Comparative toxicokinetic profiles of multiple-components of Gelsemium elegans in pigs and rats after a single oral administration.
Antidote:
Goose or Duck blood was recommended as an antidote. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Main Preparations used:
-
Extra Info
- Research
