Delphinium brunonianum, Bya rgod spos བྱ་རྒོད་སྤོས་Musk LarkspurBya rgod spos (Tibet) Sprika (Ayurveda) Ke Shen Mi Er Cui Que (D. cashmirianum) (TCM) |

|
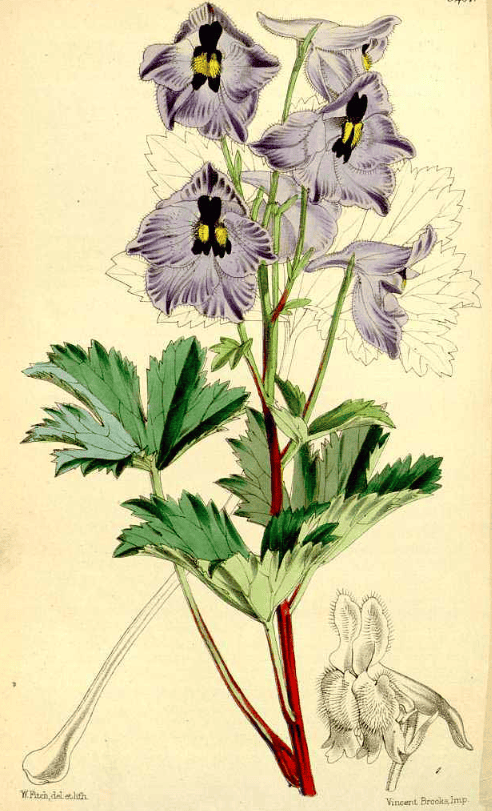 Delphinium brunonianum
Delphinium brunonianumCurtis’s Botanical Magazine (1864) |
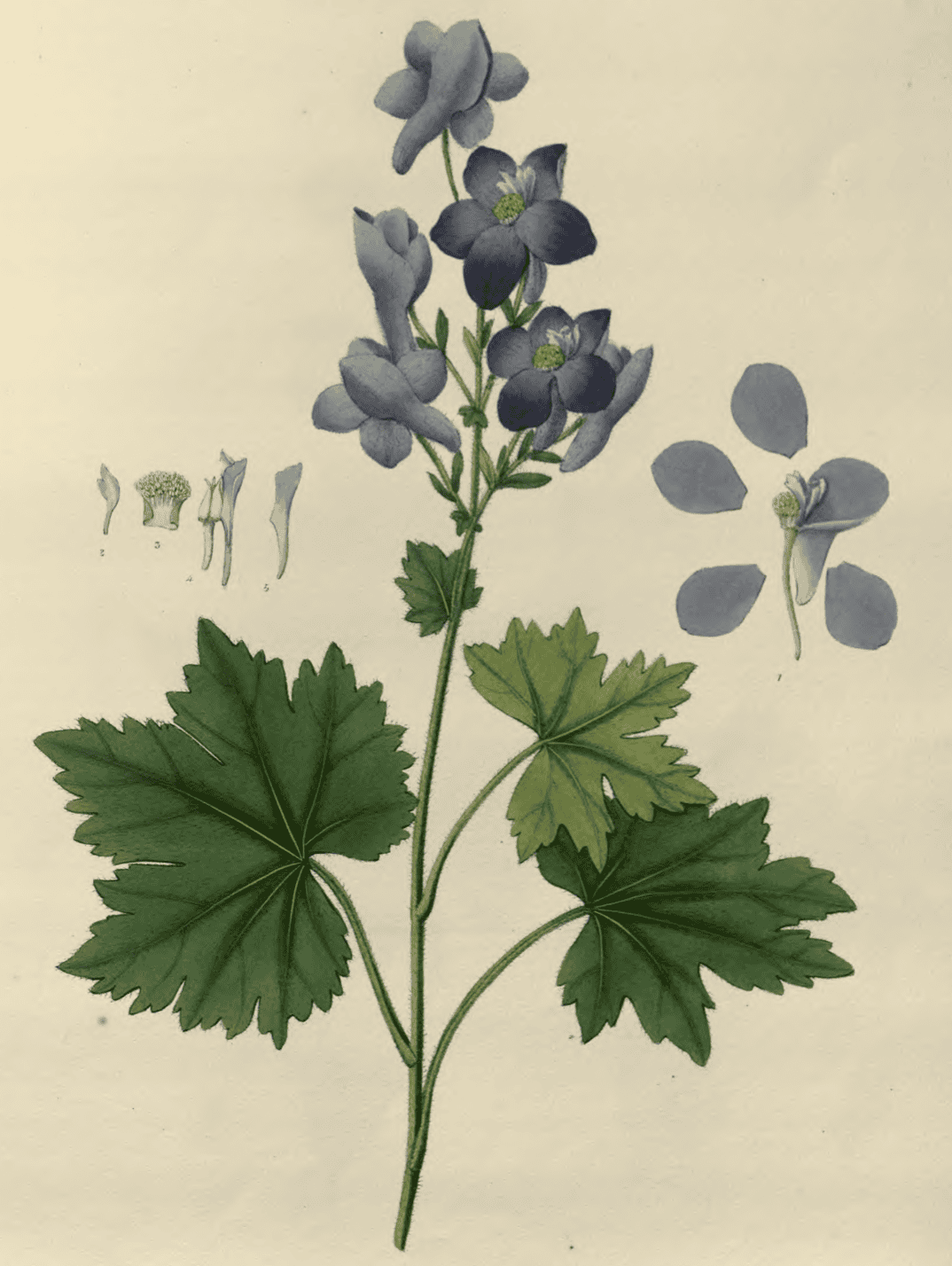 Delphinium cashmerianum
Delphinium cashmerianumIllustrations of the Botany … of the Himalayan Mountains, Royle, 1839 |
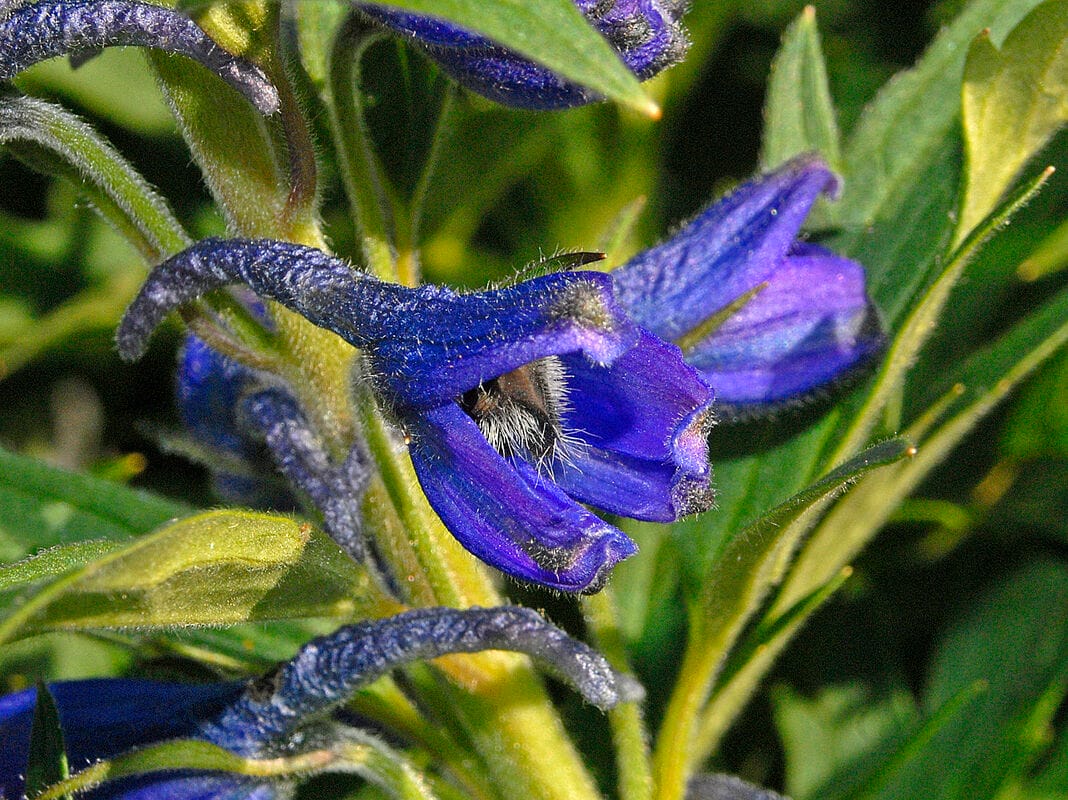 Delphinium brunonianum
Delphinium brunonianum(Photo by Hectonichus) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Delphinium spp.
Two species supply this medicine:
- D. brunonianum (syn. D. moschatum)
- D. cashmerianum
Parts used:
Whole plant; Aerial parts
Temperature & Taste:
Cool. Bitter, Pungent. Toxic
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Heat, Resists Poison:
-frequent Colds; Cough, Pneumonia
-Fever due to Poison
-Malaria (herb decoction)
-Dysentery (Herb)
-insect Bites
-general Antidote to Poisons and Venoms
2. Clears Liver Heat:
-Skin diseases, Pruritus
-Neuralgia, Headache
-Stomachache
-Jaundice (Decoction is used in Nepal)
-Bile diseases in general
-traditionally for diseases caused by Evil Spirits (Tibet)
3. Moves the Blood, Clears Heat:
-Trauma; Wounds
-Chest tightness
4. Musk Substitute:
-an important vegetable musk substitute in Tibetan Medicine
5. Externally:
-leaf juice is applied to sores, cuts, boils, burns
-paste of flowers for Sore Throat
-paste applied to Baldness, Alopecia
SEED:
Cathartic, Anthelmintic
Dose:
Comment:
The Delphiniums are similar in appearance to the Aconites, and are often found growing in similar areas. Both contain Diterpene Alkaloids and both are toxic, although the Aconites are generally far more toxic.
Substitute:
1. Delphinium brunonianum and D. cashmirianum are used as substitutes for Valerian. Valerian, in turn, may be used as a substitute. This would suggest Indian Spikenard to also be a suitable substitute in some instances.
2. Delphinium brunonianum is also regarded as a suitable vegetable substitute for Musk
Main Combinations:
1. Cancer, Oxytropis Stag sha with Chebula, Costus, Calamus, Aconitum ferox, Commiphora mukul, Acacia catechu, Delphinium brunonianum, and a mineral ingredient (as in Thapring of Tibetan Medicine)
Major Formulas:
Delphinium brunonianum (known as Musk Larkspur) is regularly used in Tibet in place of Musk, which is regularly listed in Tibetan formulas.
Great Cold Compound Precious Black Pill
Cautions:
Toxic in overdose.
Main Preparations used:
GENERAL / REVIEW:
–An overview of the chemical constituents from the genus Delphinium reported in the last four decades.
ANTIBACTERIAL:
–In vitro and in silico evaluation of antimicrobial properties of Delphinium cashmerianum L., a medicinal herb growing in Kashmir, India
ANTIOXIDANT:
–Two Alkaloids From Delphinium brunonianum Royle, Their Anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidative Stress Activity via NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY:
–Two Alkaloids From Delphinium brunonianum Royle, Their Anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidative Stress Activity via NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway.
DIURETIC:
–Phytochemical analysis and reappraisal of diuretic activity of Delphinium brunonianum Royle and its mode of action in experimental rats.
FATTY LIVER DISEASE:
–Integrating metabolomics and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanisms of Delphinium brunonianum extract against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
–Diterpenoid Alkaloids Isolated from Delphinium brunonianum and Their Inhibitory Effects on Hepatocytes Lipid Accumulation.
DIABETES:
–Protective Effect of Butanolic Fraction of Delphinium brunonianum on Fructose-Mediated Metabolic Alterations in Rats.
–Phytochemical analysis of crude extract of Delphinium brunonianum and its effect on hypertension and metabolic perturbations in fructose fed rats.
CANCER:
–Brunonianines D-F, three new C19-diterpenoid alkaloids from the Delphinium brunonianum, with therapeutic effect on ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo.
–Brunonianines A-C, C(20)-diterpenoid alkaloids with cyano group from Delphinium brunonianum Royle.
