Daphne gnidiumDaphne gnidium: Thymelaea, Flax-leaved Daphne, Coccum Cnidi, Granum Cnidi |

|

|
 Daphne gnidium
Daphne gnidiumOrtus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491
 Daphne gnidium
Daphne gnidiumDioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563 |
 Daphne gnidium
Daphne gnidiumKrauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578 |
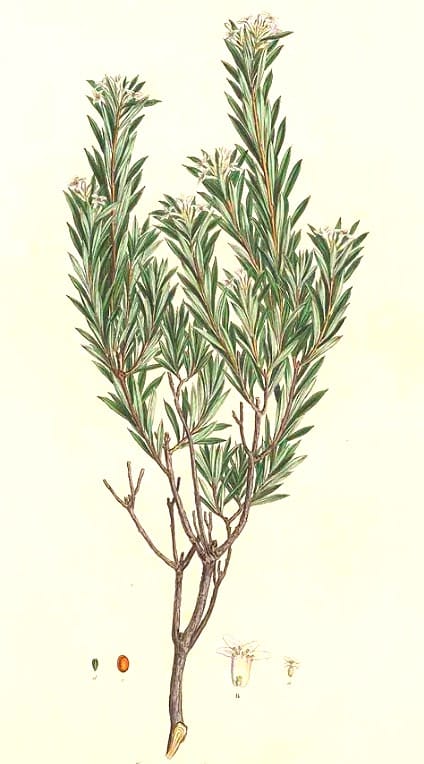 Daphne gnidium
Daphne gnidiumJ. Sibthrop, J.E. Smith, Flora Graeca, vol. 4 (1823)
Botanical name:
Daphne gnidium
Parts used:
Seed (leaf also)
The bark is used similarly to Daphne Mezereon.
Temperature & Taste:
Hot, dry. Pungent. Toxic
Uses:
1. Clears Damp, Purges Water:
-serious cases of Edema in strong individuals; Ascites:
-purges water through the bowels
2. Externally:
-Kills Lice
-used as a vesicant
-topically to Cancer, Lupus
Dose:
Boiling lessens their virulence
Of the Seed: 3 can be taken as a dose. Wirtzung (1598) said “The ancient Physicians were want to give 7 or 8 seeds of it, wrapped up in a green Fig or Date. but experience does teach us, that 3 of the seeds are sufficient enough to purge the body”.
Leaf in decoction: 300–600mg (traditionally 10–12 grains) will purge and sometimes vomit.
Comment:
1. The seed of this variety of Daphne is used, the bark of Mezereum (D. mezereum) and Laureola (D. laureola) are used; the leaves of the different species have also been used on occasion. All parts share similar effects.
Main Combinations:
Major Formulas:
Ointment of the Resin of Daphne Gnidium
Lard 10 oz.
White Wax 1 oz.
Resin of Daphne Gnidium ½ dram
Strongly rubefacient.
Cautions:
1. Highly irritant. Avoid overdose. Moderate doses may induce diarrhea and vomiting.
2. Not used in Pregnancy, the very young, old, or weak
