Cupping

|
“Scarification with Cupping possesses the power of evacuating offending matter from the head; of diminishing pain of the same part; of lessening inflammation; of restoring the appetite; of strengthening a weak stomach; of removing vertigo and a tendency to faint; of drawing deep-seated offending matter towards the surface; of drying up fluxions; checking hemorrhages; promoting menstrual evacuations; arresting the tendency to putrefaction in fevers; allaying rigors; accelerating and moderating the crisis of diseases; removing a propensity to somnolence; conciliating natural repose; removing heaviness. These, and many analogous maladies, are relieved by the judicious application of the Cucurbits, dry or bloody.” (Herodotus, 413 BCE) |
|
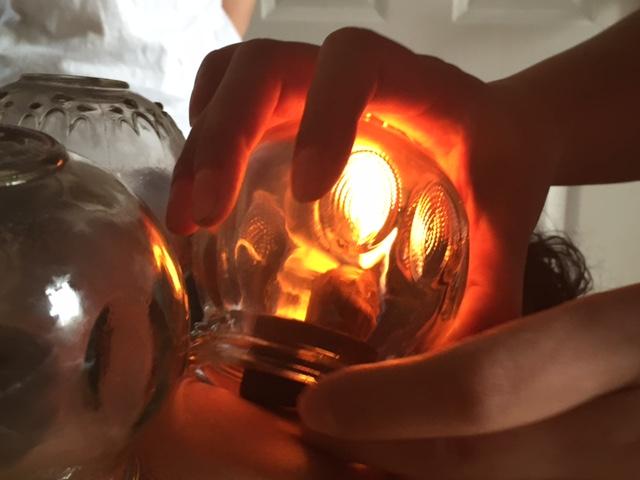
Introduction Cupping is the application of suction cups to various parts of the body. Cupping is used in all traditions of the Silk Road, again showing the sharing of theory and treatment from early times. The origins of Cupping are uncertain, but are ancient. Cupping is mentioned in the Ebers Papyrus (1550BCE) and was used by the Babylonians. Cupping was an advanced and intricate therapy by the time of Hippocrates (c 400 BCE). The earliest record of Cupping in China is reportedly from the Physician Ge Hong (281–341 CE). Traditional Cupping instruments tended to be hollowed out horns which were applied, then sucked through a small hole at the tip. This type of ancient cupping appears in both East and West. Later, Bamboo and clay pots were used. In modern times, glass and plastic cups are used. Cups with a vacuum plungers commonly being used to avoid the necessity of using Heat. |
 Bronze Cupping vessel, Egypt, circa
Bronze Cupping vessel, Egypt, circa 300BCE–300CE (Welcome collection) |

|
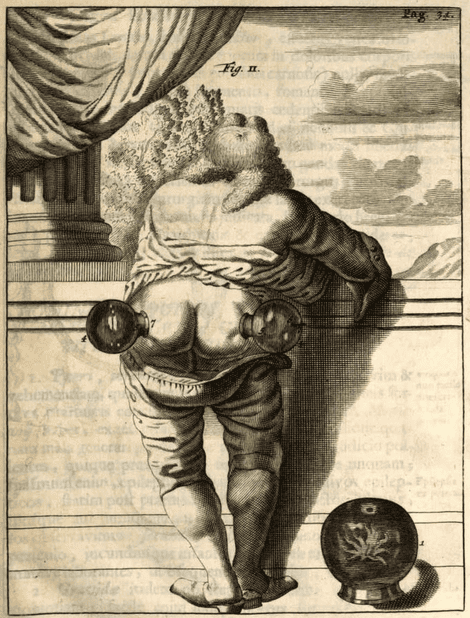
|
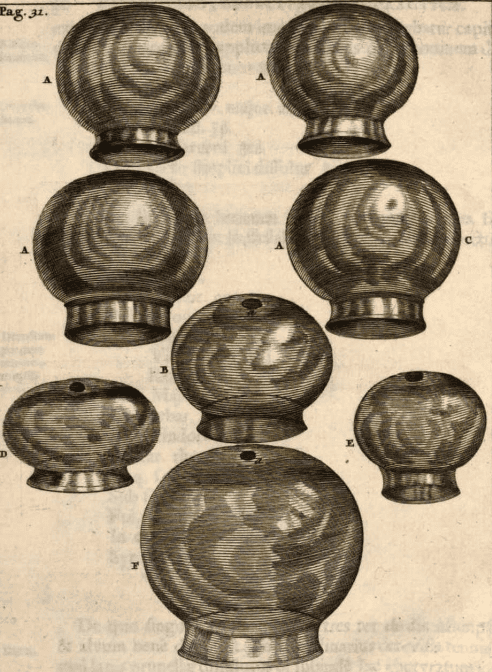
(Exercitationes practicae, Frederick Dekkers, 1696)
There are several varieties of Cupping:
1. Cupping with Vacuum (‘Suction Cupping’), traditionally through a hollow horn, today applied with suction pumps
2. Cupping with Fire (‘Fire Cupping’)
3. Cupping with Scarification (‘Wet Cupping’); applying cups after lancing, needling, or scarifying.
The First 2 can be classified as ‘Dry Cupping’, with the Third is called ‘Wet Cupping’ and is actually a form of Bloodletting. What is today usually called ‘Wet Cupping’ was traditionally known as Scarification. Sometimes scars are rubbed with plant juices to cause scarring, hence the name. When needles or very light lancing is performed, no permanent scarring occurs.
Functions of Dry Cupping:
1. Opens the Skin Pores to drain Wind, Cold, Heat, Damp, Blood and Humors to the Skin and out through the Pores.
2. Cupping draws stagnation from deeper in the muscles, tissues or organs to their surface to be cleansed out.
3. Cupping can draw Blood, Fluid and Humors from one place to another, for example, away from a ‘Noble’ organ.
4. Cupping reduces pain, clears Inflammation, resolves stagnation and increases circulation.
5. Cupping draws Bruising from deeper in the muscles to the surface where it is resolved by the Body.
6. Short Cupping increases Circulation, prolonged Cupping drains excess.
|
Functions of Wet Cupping: 1. Wet Cupping has the similar effect to Bloodletting. It clears Blood stagnation and Draws ‘Bad’ Blood. 2. Dry Cupping removes Blockage of Qi, Wet Cupping removes Blockage of Blood. 3. Wet Cupping more effectively clears Heat, Bile and Inflammation and is more draining. 4. Wet Cupping Draws from Deeper in the Body 5. It also stimulates Immunity and promotes formation of Red Blood cells. |

Left: Scarification, or Wet Cupping, showing the lanced areas beginning to Bleed after applying a Cup. (Calcutta Unani Medicine College, Adam, 2019) |
Recent research (Khosrow) has demonstrated that their is quite a variation in the Blood removed via wet cupping compared to regular Bloodletting (Phlebotomy). Blood samples from a number of subjects was compared before and after removal of Blood, half using Hijama (Wet cupping) and half Phlebotomy. There was a significant difference between serum values of triglyceride, cholesterol, urea, and uric acid, all levels being higher in the wet cupping group
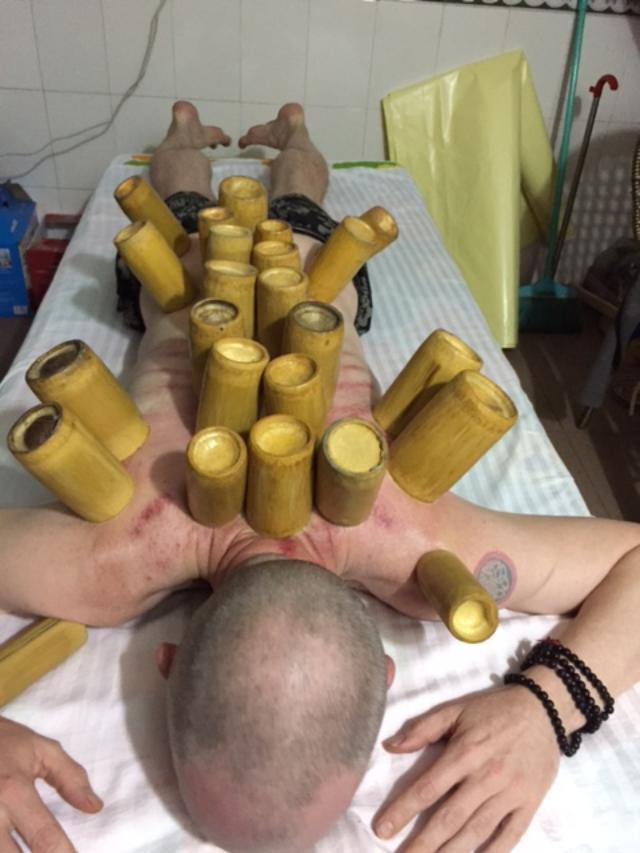
|

|
How to Cup
|
“The best way to apply Cupping glasses, is to heat them first in hot water, by putting them in the water when cold, and so letting them heat with the water, and so apply them close to the part of the body to be cupped, and as they cool, so the air in them will condense, , and to avoid Vacuum, draw the Humors through the pores of the skin“. (Culpeper) |
1. The patient should sit or lie down so that the place to be cupped is exposed.
2. Often the place to be cupped is rubbed or massaged prior to applying cups. Some systems recommend oiling the body although usually the place can be cupped directly without massage or applying oil.
3. Cups are applied to the area to be cupped. Cups are either heated with fire or by putting in hot water, or else vacuum cups are applied and air is sucked out.
4. Large areas like back, thighs or buttocks are cupped with larger cups, small and curvaceous areas like face, neck, shoulder tips are cupped with smaller cups.
5. Cups should not be overly painful and care is needed to protect delicate skin, especially of face, groin etc.
6. Cups are usually left on for 7–15 minutes. In some cases they are left longer. In some cases, the cups may be moved while they are on, such as dragging the cup up and down the spinalis muscles either side of the spine.
7. Cups are removed be pressing the side of the cup to release the vacuum. Modern vacuum cups have a nipple on top which can be used to release the vacuum.
8. Areas that have been cupped are wiped to remove moisture and sweat and can be gently massaged to sealed the skin and help resolve the swelling.
Wet Cupping is applied the same way except that needles or lances are used to prick or scratch points before applying cups. After 10–15 minutes, the cups are removed and the Blood will be found to be clotted. It is carefully collected and the site wiped. The practitioners should wear rubber gloves for Wet Cupping and all precautions to avoid blood contamination of the practitioner and other patients must be taken. The site must be covered to avoid infection after Wet Cupping.
Research
1. Wet cupping lowers Heavy metals in the Blood. (See research here)
2. Wet cupping removes oxidants and lowers oxidative stress. (See research here)
3. Wet cupping is effective to reduce Hypertension. (See research here)
4. Wet Cupping is effective for chronic lower back pain (See research here)
The Signs of Cupping
1. Strong red bruising indicates excess heat (inflammation) and Blood congestion.
2. Dark purplish bruising indicates stagnation, coldness or chronic Blood stagnation.
3. Lots of moisture in the Cups indicates Damp or excess fluid.
4. Black bruising indicates serious and chronic stagnation.
5. If the area feels Cold after cupping, it indicates internal cold has been drawn to the skin.
6. If the area feels Hot, heat is being drawn out.
7. If the area feels Itchy, Wind is being released.
8. Bruises resolving quickly indicate good circulation and removal of Stagnation.
9. Bruises lasting for more than 5 days indicate chronic stagnation and indicate further cupping.
Signs of Wet Cupping also involves checking the Blood.
1. Bright Blood with a saffron tint indicates excess Bile (Heat).
2. Pale and Waterish Blood indicates fluid swelling in the area.
3. Dark Blood indicates Stagnation, old Blood stasis, Coldness or Black Bile Humor.
4. Frothy Blood can indicate Wind.
5. If the Blood is dark to begin with but becomes brighter and fresher, it indicates sufficient Bleeding.
Notes & Cautions
1. Caution cupping the very young or elderly. Don’t cup too strong or for too long.
2. Avoid cold, wind (drafts) and getting wet (showering) in the hours after cupping as the skin is open.
3. Don’t Cup again until previous Cupping bruising have healed.
4. Ensure Cups are cleansed properly between patients as even in Dry Cupping spots and pimples can rupture leaving traces of Blood on the Cup.
5. According to some sources, Cancer is a contraindication. However, if the patient is strong it may be used.
6. Organ failure, Hemophilia, severe diseases are general contraindications too.
7. Avoid sun exposure over bruising from cups as these can pigment if they get sunburn.
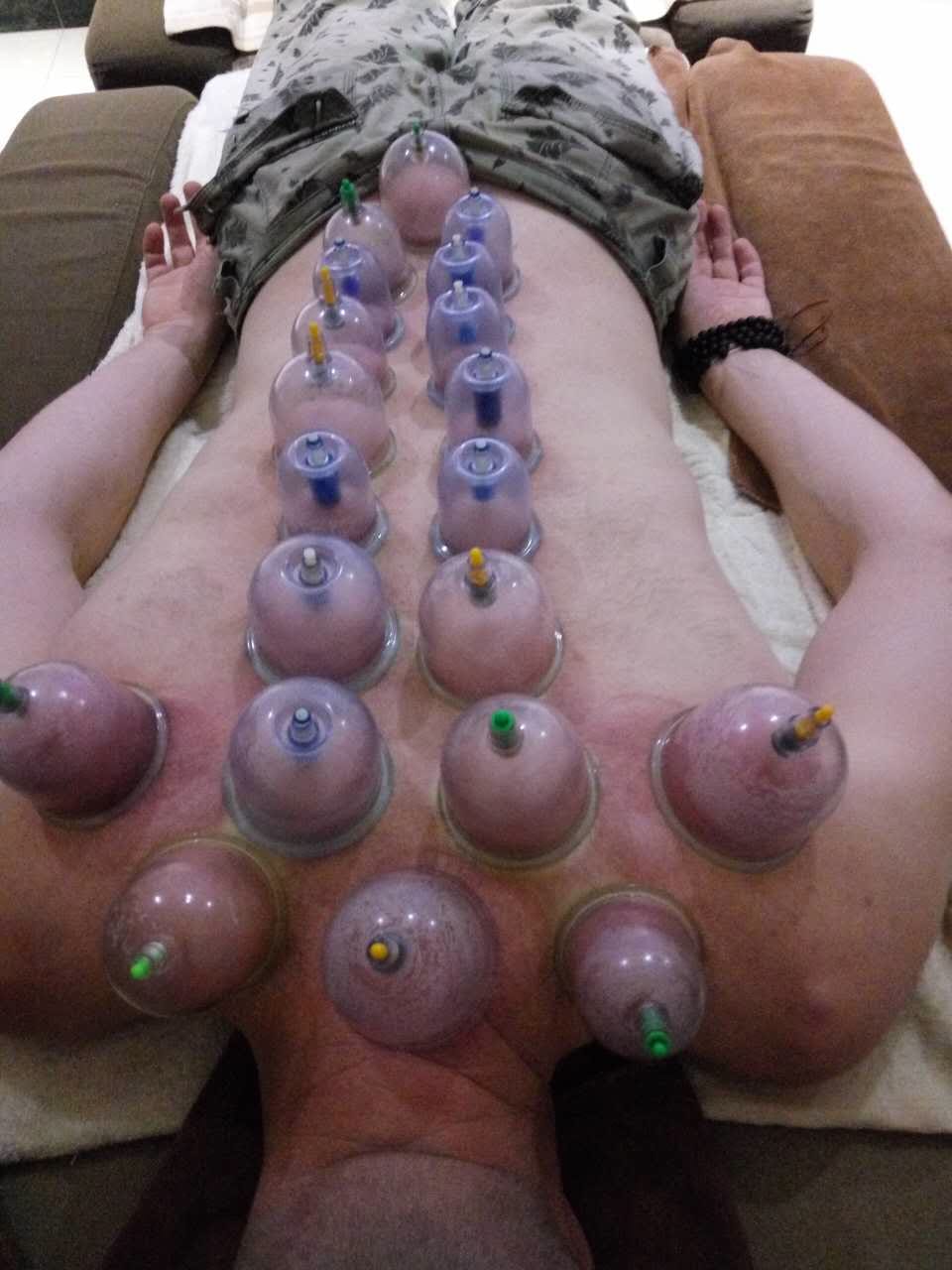
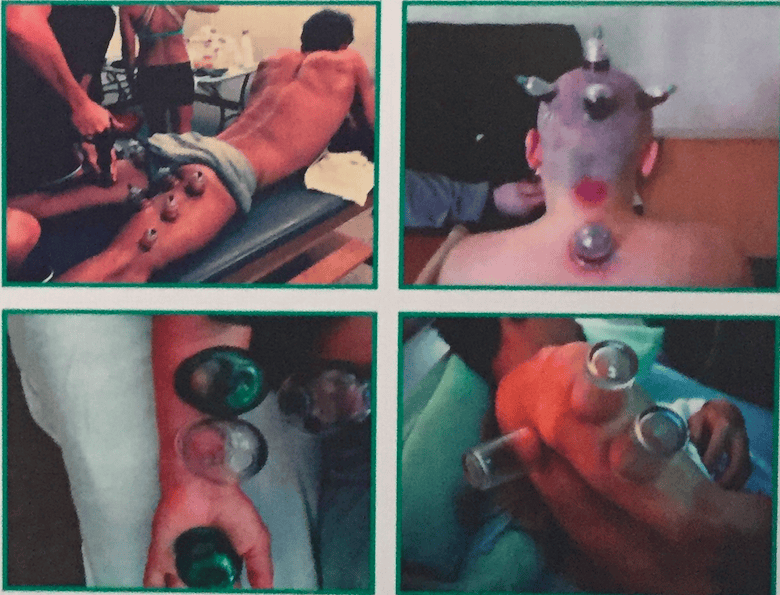 Various types of Cupping for various ailments.
Various types of Cupping for various ailments.(Calcutta Unani Medicine College, Adam, 2019)
Conditions Treated with Cupping:
1. Musculo-skeletal Pain (Topically)
2. Lumbago, Sciatica (Sacrum, Lower back, over the Kidneys, sides of the Hips)
3. Neck, Shoulder pain, Frozen Shoulder (over C7, tips of the shoulders, neck, mid scapula)
4. Cough (over the Lungs on the Upper back)
5. Colic, Abdominal Pain (Navel and Abdomen)
6. Diarrhea (Navel and Sacrum)
7. To draw Blood to a Cold part. (Topically)
8. Prolapses of Uterus or Anus (Umbilicus)
Points Typically Cupped:
1. Head: Dizziness, Baldness, Madness, Headache
(But they can hurt the Understanding and Memory and should not be used in ‘Dry Brains’)
2. Forehead: Headache, Migraine, Heaviness of the Head, Lethargy, Madness, old diseases of the Face, skin diseases of the Face, diseases of the Eyes.
3. Under the Chin: diseases of the Mouth, Throat, Gums and Teeth, Tumors under the Jaw, Pimples,
4. Back of the Head for Headache, Abscesses of the Head, strains of the Buttocks
5. Tip of C7: diseases of the Head and Eyes, Heaviness of the Head, Neck stiffness
–may be cupped instead of Bleeding Cephalic or Median Veins of the arm.
(But they may hurt Memory and make the Head shake)
6. Between the Scapula: diseases of the Chest and Throat, Cough, Asthma, Upper Back and Shoulder pain, Headache, Palpitations from excess,
(But they can hurt the Stomach and Heart, and cause Palpitations if the Blood is weak)
–may be cupped instead of Bleeding the Basilic Vein of the arm.
7. Under the Breast for Asthma
8. Over the Liver if dry, excess Heat, or Inflamed
9. On the Spine to clear the flow of Qi, remove Damp, benefits the Organs, and for Pain of the Back.
10. Over the Stomach for Cold and Damp, and Stomach Tumors
11. On the Umbilicus for Cold, Wind and Damp of the Abdomen, Colic, abdominal pain, Prolapses
12. Under the Umbilicus for Colic, Wind and Diseases of the Uterus and Bladder
13. Over the Kidneys for Cold Kidney and lower back pain, Cold and Damp of the Kidneys and Bladder, Abscess of the Hips, Itch and Skin diseases of the Back, Wind affecting the Uterus, diseases of the Legs in general
14. Loins: for Hemorrhoids, pain in the Back or Uterus, Scabs, Abscesses and Tumors, and to allay excess Lust.’
15. On the hands for diseases of the Head, Eyes and Ears
16. Over the Hypochondria for Bleeding of the Nose or Uterus, obstruction of Liver Qi, Liver diseases
17. Thighs: good for the whole body, cleansing the Blood and removing its excess; pain, swelling or abscess of the Buttocks, Sacrum, Testicles or Knees, Kidney and Bladder pain, Strains and Trauma of the Hips and Legs, Head diseases, watering Eyes, bad humors in the Chest or Back, chronic pain in the Uterus and to cleanse the same; it promotes Menstruation
–said to be ‘as good as any Bloodletting’ (Culpeper)
–for Abscess or Tumors of the Testicles, they were put on the inside of the Thigh
18. Below the Thighs (‘Hams’): pain, strains and Ulcers of the legs and Feet
19. Buttocks: cleanses the Blood of the whole Body, Sciatica, pain of the Sides, Back, Loins and Chest; and to draw from the Head
20. In the front of the Hips: Bladder and Uterine diseases, Abscess and Swellings of the Testicles (and Prostate)
21. Soles of the Feet: promotes Menstruation, for Sciatica, Arthritis of the legs and Feet, Headache and Migraine
–can be used instead of Bleeding the veins of the feet.
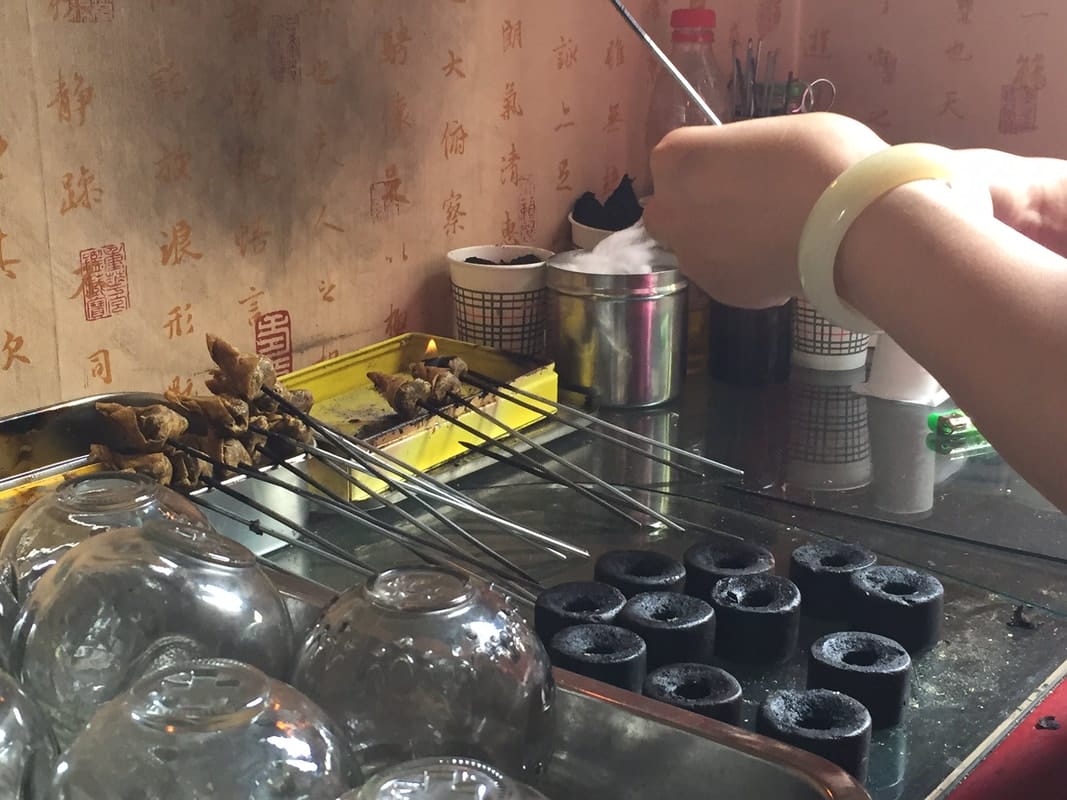

 Sample Treatments with Cupping:
Sample Treatments with Cupping:|
Abdomen, Cold & Damp: –Cup over the Stomach, Umbilicus, and either side of Umbilicus; Cup Mid and Lower back either side of Spine Apoplexy: –Neck (C7), and Shoulders (pref. with Bleeding); cup the Thighs Asthma: –Neck (C7) (pref. with Bleeding); between the Scapula Back Pain, Upper: –Cup Shoulder Tips, Mid Scapula, Between Scapula, either side of spine of Thoracic Vertebrae Back Pain, Lower: –From Kidneys to Sacrum, either side of Spine, Sacrum, Buttocks, Ankles Balding: –cup the back of the head, the Crown and Forehead (hairline) Bladder Abscess or Tumor: –Cup with Bleeding on the Buttocks Breathing difficulty –Cup the Shoulders and Mid Scapula Colic: –cup the Umbilicus Cough: –Cup between Scapula and mid-Scapula |
Diarrhea: –Cup Umbilicus; over the Spleen; over the Buttocks Ear diseases (pain, poor hearing and tinnitus): –Cup Wrist; the base of the skull below the ears –cup the wrists Eyes, Bleary, or Failing Vision: –Cup with Bleeding on Shoulder tips and C7 Eyes, ‘all eye diseases’: –Cup with Bleeding on Forehead, Crown, C7; Cup both wrists Face, Acne, Spots, poor skin: –under the Chin; back of the Head; C7 (with Bleeding) Fever: –Cup and Bleed along the whole Spine Frozen Shoulder: –Cup Shoulder tip, between shoulder and neck, mid scapula Headache: –C7, Shoulder Tips, Between the Scapula, Mid Scapula Heart Trembling (Palpitation or Arrhythmia) –cup between the Scapula (with scarifying if there is excess) Sciatica: –Cup Kidneys, Lower Back, Sacrum, Hip, along the back of the Leg, Ankles, Soles of Feet |
The following video of Hijama (Wet Cupping) was recorded at the Unani Medicine College in Kolkata (Calcutta), in March 2019. The patient is a 65 year old with osteoarthritis of the Knee.
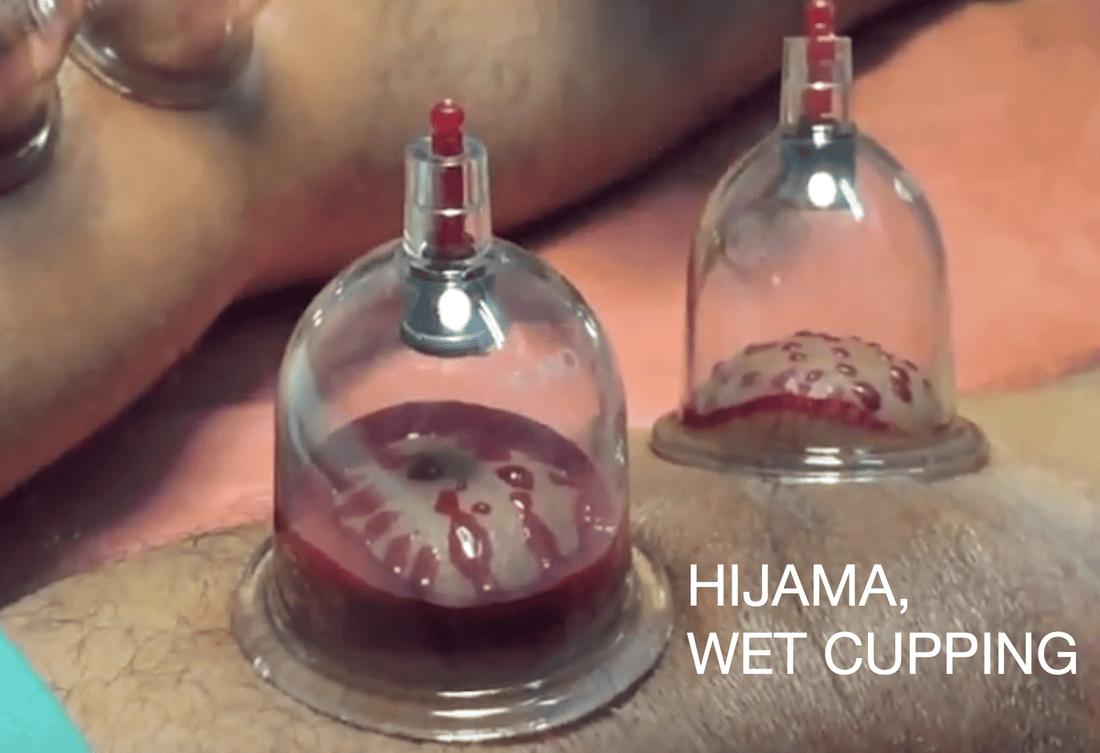 *YouTube classified this Video as only suitable for adults due to Blood.
*YouTube classified this Video as only suitable for adults due to Blood.Sources, References & Further Reading
1. Two Treatises, the first of Bloodletting … the second of Cupping and Scarifying.., Culpeper, Ruland and Cole, 1663
2. Cupping: time to re-evaluate its position, Prof. Bhikha and Dr. Saville, Tibb Institute, Feb, 2015
3. Utility of Cupping Therapy Hijamat in Unani Medicine, Ahktar & Siddiqui, Indian J. Trad. Know., Oct, 2008
4. Photos and personal communication at the Unani Medicine College, Kolkata, (Adam, March 2019)
5. Khosrow et al, Comparison Biochemistries of Obtained Blood Products between The Hijama and Phlebotomy Techniques of Traditional Islamic Remedy; Healthy Young Adults at Fasting State, Journal of Hospital and Medical Management, Aug. 2016
6. Cupping Therapy, Furhad & Bokhari, Update: February 11, 2019.
7. The Effects of Wet Cupping Therapy on the Blood Levels of Some Heavy Metals: A Pilot Study.
8. Evaluation of Bloodletting Cupping Therapy in the Management of Hypertension.
9. Study of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice (KAP study) on Hijamah (Wet Cupping) Therapy
10. Therapeutic potentials of hijama-bila-shart (dry cupping therapy): A review
You may also like:
Bloodletting
Leeching
Fire Therapy
