Cremastra seu Pleione, Shan Ci Gu 山慈菇
Shan Ci Gu (TCM)
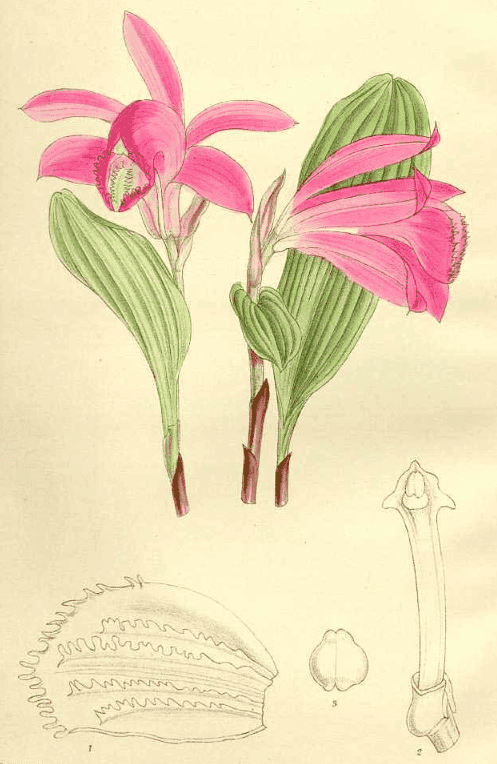 Pleione bulbocodioides
Pleione bulbocodioidesCurtis’s Botanical Magazine, vol. 140 (1914)
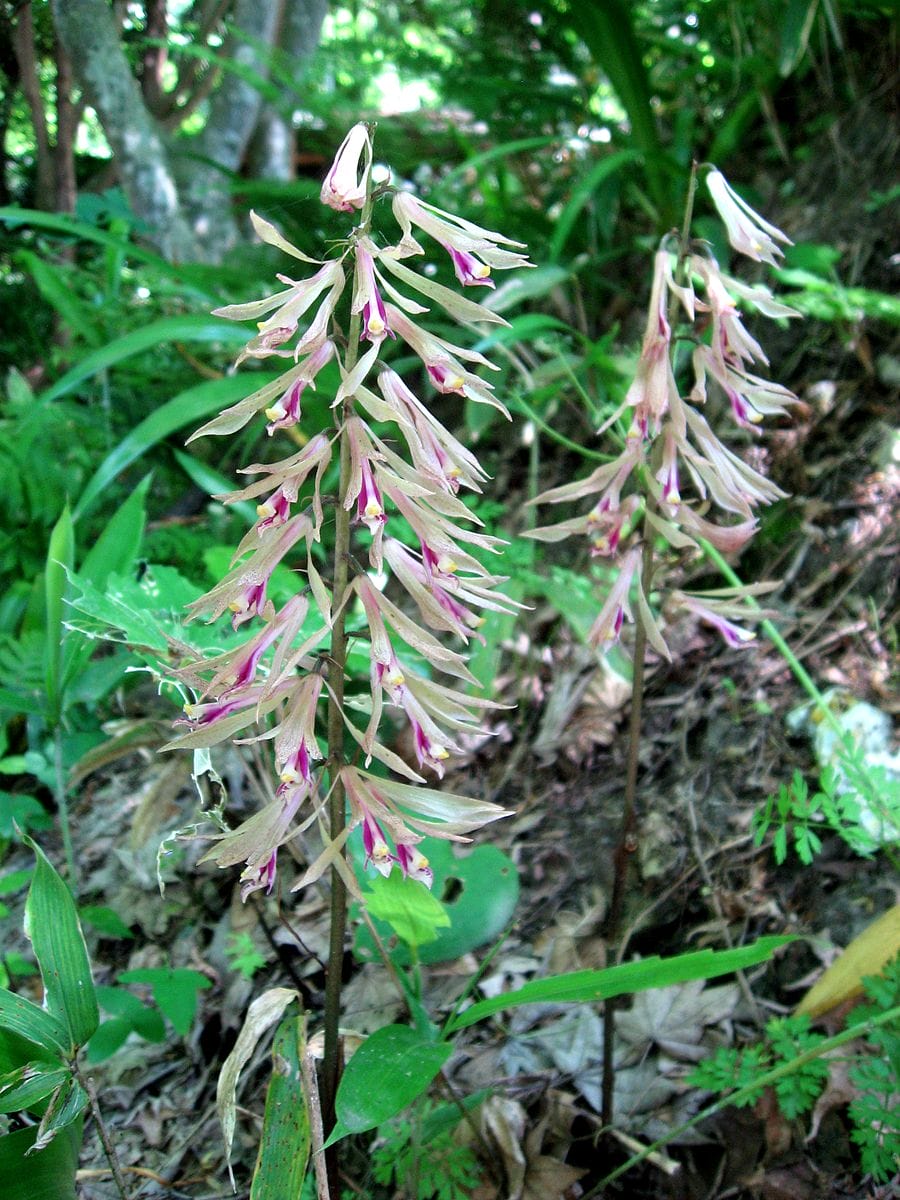 Cremastra appendiculata
Cremastra appendiculata(Photo by Qwert1234) (Wikimedia)
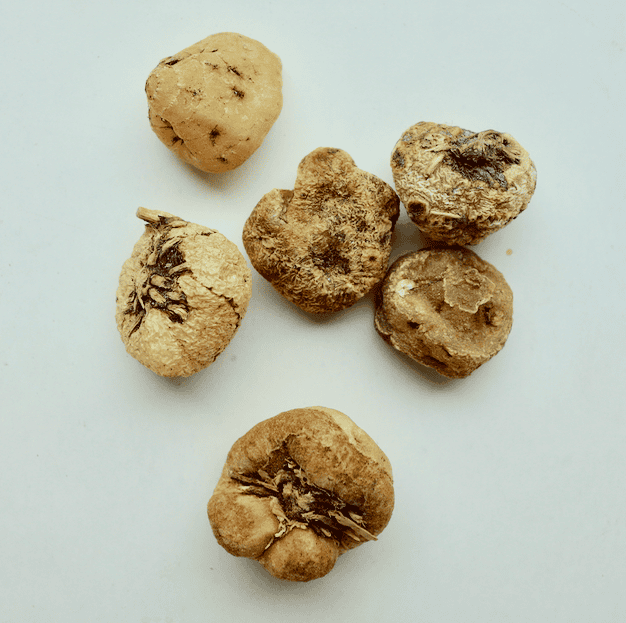 Shan Ci Gu from the Chengdu Medicine Market (Adam, 2017)
Shan Ci Gu from the Chengdu Medicine Market (Adam, 2017)Botanical name:
Two different plants supply this medicine:
- Cremastra appendiculata
- Pleione bulbocodioides, P. yunnanensis
Parts used:
Bulb
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Sweet, slightly Pungent. Slightly toxic
Classification:
B. Clears Heat and Toxin
Uses:
1. Clears Phlegm, Heat and Toxin, Resolves Swellings:
-toxic Sores, Lesions, Boils, Carbuncles, Abscesses
-Scrofula, Lymphatic Swellings, Phlegm nodules
-Toxic Bites of Snakes, poisonous Insects and Dogs
2. Resolves Toxicity, Clears Masses:
-hardness of the Liver and other abdominal organs
-masses and tumors of the abdomen
-it has recently become a favored herb in the treatment of various Cancers
Dose:
Decoction: 3–9 grams
Powder: 500mg–3 grams
Used internally and topically to toxic sores and swellings
Main Combinations:
1. Abscesses, Boils, Carbuncles:
i. Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Gall (Wu Bei Zi) and Musk
2. Scrofula:
i. from Phlegm, Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Galangal
3. Cirrhosis, Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Eupolyphaga Tu Bie Chong
4. Thyroid Tumors, Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Paris root (Chong Lu), Salvia Dan Shen, Self Heal (Xia Ku Cao)
5. Fixed masses in the Breast, Creamastra Shan Ci Gu, Vaccaria Wang Bu Liu Xing, Lonicera Jin Yin Hua, Borneo Camphor (Bing Pian)
6. Cancer:
i. Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Black Nightshade (Long Kui)
ii. Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Scutellaria barbata Ban Zhi Lian, Hedyotis Bai Hua She She Cao
iii. Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Wasp Nest (Feng Fang) and Scorpion (Quan Xie)
7. Toxic Sores, Creamastra Shan Ci Gu with Realgar (Xiong Huang)
Cautions:
1. Take care with correct identification as it is sometimes substituted with toxic species. Adulterants include Tulipa edulis and Iphigenia indica which both contain the toxic colchicine. They are toxic in overdose with lethal doses having been reported with doses of approximately 30 grams. (Bensky)
2. Use cautiously in weak patients.
Toxicity:
1. Contains traces of colchicine.
2. Overdose appears at doses of 15–45 grams and symptoms usually appear 2–4 hours follwing intake. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, general pain a lethargy. Serious cases lead to spasms, convulsions and respiratory depression.
Antidotes:
1. 5–10 Egg Whites or Milk can be given immediately.
2. Nausea and vomiting can be relieved by giving Ginger juice (10mls) and Vinegar (250mls).
3. Severe diarrhea can be treated with a decoction of fresh Ginger, Saposhnikovia Fang Feng, Cinnamon (Rou Gui), with a little salt, sugar and vinegar added. (Chen & Chen)
CITES listing:
All 3 primary species are listed on CITES as potentially endangered with repeated harvesting.
