Codonopsis, Dang Shen, 党参
Dang Shen (TCM) Codonopsis tangshen
Codonopsis tangshenCurtis’s Botanical Magazine, 1906
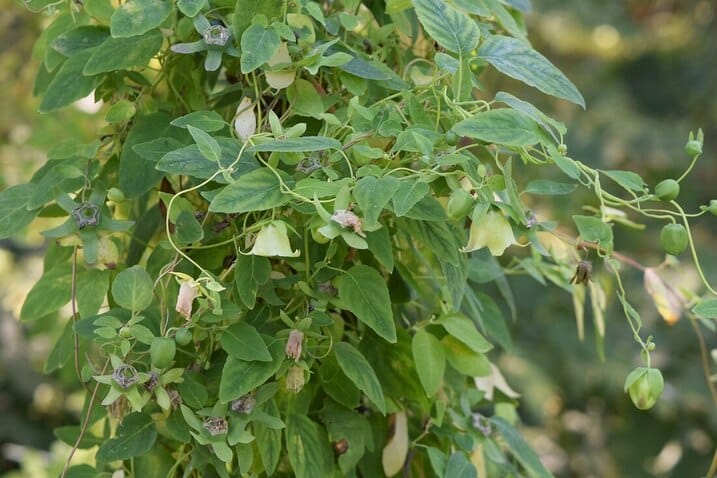 Codonopsis pilosa
Codonopsis pilosa(Photo by Kenraiz) (Wikimedia)
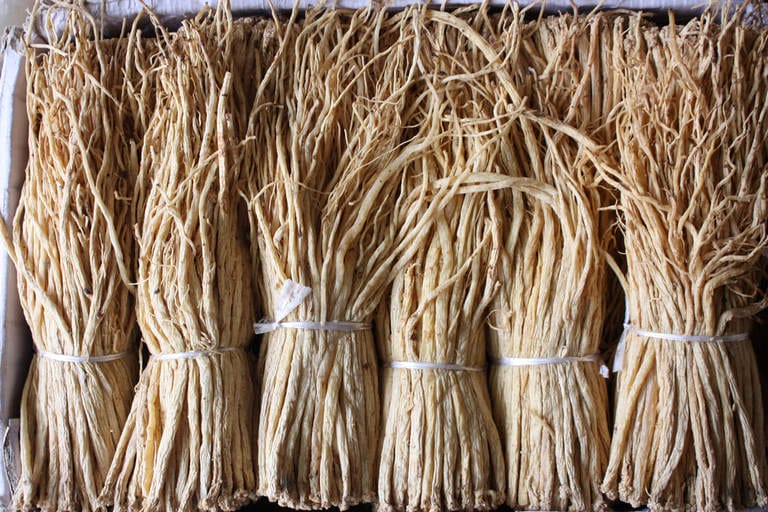 Bunches of Codonopsis Dang Shen at the Chengdu Medicine Market (Adam, 2009)
Bunches of Codonopsis Dang Shen at the Chengdu Medicine Market (Adam, 2009)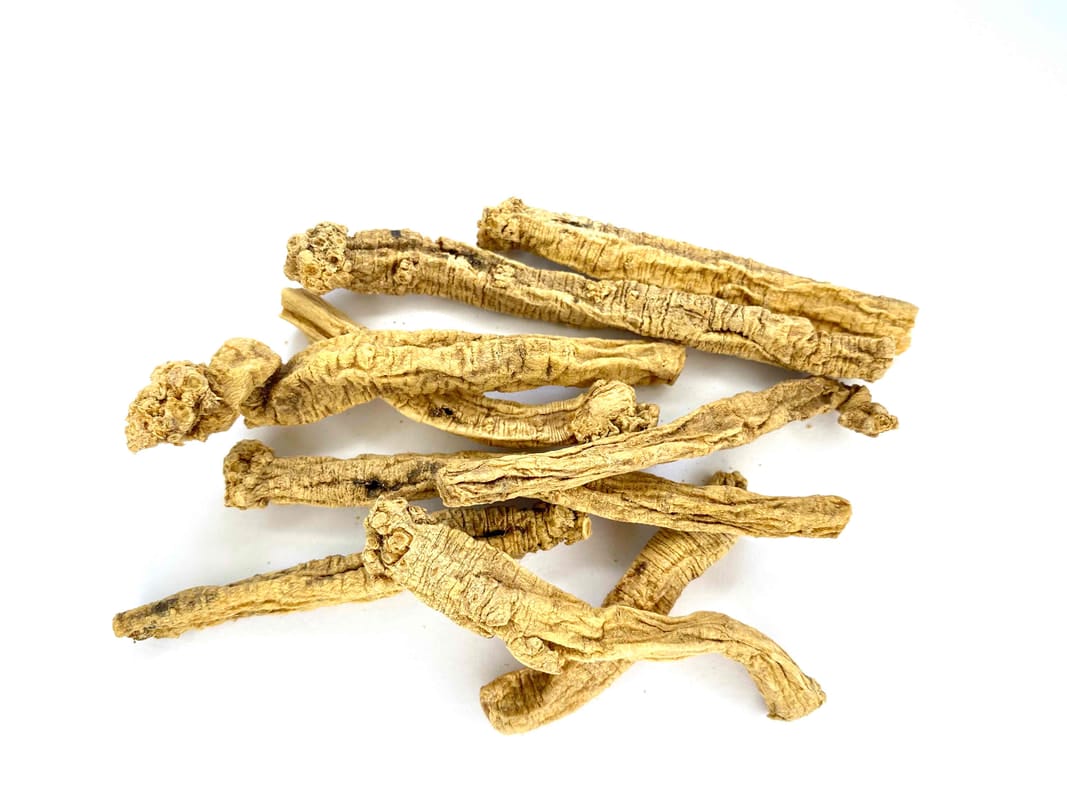 Codonopsis Dang Shen pieces as typically available in the West (Adam, 2023)
Codonopsis Dang Shen pieces as typically available in the West (Adam, 2023) Members CLICK HERE for the PRO VERSION
Members CLICK HERE for the PRO VERSIONBotanical name:
Codonopsis pilosula, C. tangshen; many local species are used including C. tibulosa, C. clematidea, C. nervosa
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral, Sweet.
Classifications:
N. Qi Tonic
Uses:
1. Tonifies the Spleen and Stomach, Increases Qi:
-poor appetite, fatigue, weakness, loose stool
-chronic digestive disorders with Qi deficiency
-Prolapses of the Stomach, Uterus or Bowels
2. Tonifies Lung Qi:
-chronic Cough, shortness of Breath, copious sputum from Spleen deficiency
-useful in chronic Lung disease, COPD etc
Comment:
Codonopsis is regularly used as a modern substitute for Ginseng in TCM, especially in decoction due to the expense of Ginseng. Ginseng is required in cases with severe deficiency. Generally 2–4 times the dose of Codonopisis is used to replace Ginseng.
Dose:
Decoction: 6–12 grams
Powder: 2–5 grams
Substitute:
1. Ginseng
2. Atractylodes Bai Zhu

Main Combinations:
Generally as for Ginseng
1. Spleen deficiency with Fatigue, Poor appetite, Codonopsis Dang Shen with … available in PRO version
2. Spleen deficiency with Phlegm and Damp, Codonopsis Dang Shen with … available in PRO version
3. Diarrhea from Deficiency and Damp, Codonopsis Dang Shen, … available in PRO version
4. Chronic Cough from Deficiency:
i. Codonopsis Dang Shen with … available in PRO version
ii. from Lung Qi deficiency, Codonopsis Dang Shen, … available in PRO version
5. Qi and Blood deficiency, Codonopsis Dang Shen with … available in PRO version
6. Excessive sweating from Qi or Yang deficiency, Codonopsis Dang Shen and … available in PRO version
Major Formulas
Note that most of the major formulas listed below are intended to use Ginseng. Codonopsis is regularly used in place of Ginseng unless there is severe deficiency.
Bu Zhong Yi Qi Tang
Gui Pi Tang
Li Zhong Wan
Liu Jun Zi Tang
Si Jun Zi Yang
Cautions:
Use with caution in cases with excess pathogens. Generally, pathogens need to be relieved before using tonics.
Main Preparations used:
As for Ginseng
