Clematis, Dbyi mong དབྱི་མོང༌Dbyi mong དབྱི་མོང༌ (Clematis spp)Dbyi mong khra po དབྱི་མོང་ཁྲ་པོ (C. montana) (Tibet) Dbyi mong nag po དབྱི་མོང་ནག་པོ (C. tibetana) (Tibet) Dbyi mong dkar po དབྱི་མོང་དཀར་པོ (C. rehderianum) (Tibet) Dby mong ser po དབྱི་མོང་སེར་པོ (C. orientalis var. intricata) (Tibet) Chuan Mu Tong (C. montana) (TCM) Gan Qing Tie Xian Lian (C. tangutica) (TCM) Xi Zang Tie Xian Lian (C. tibetana) (TCM) |

|
 C. montnana
C. montnanaRevue horticole, serié 4, vol. 80: (1908)
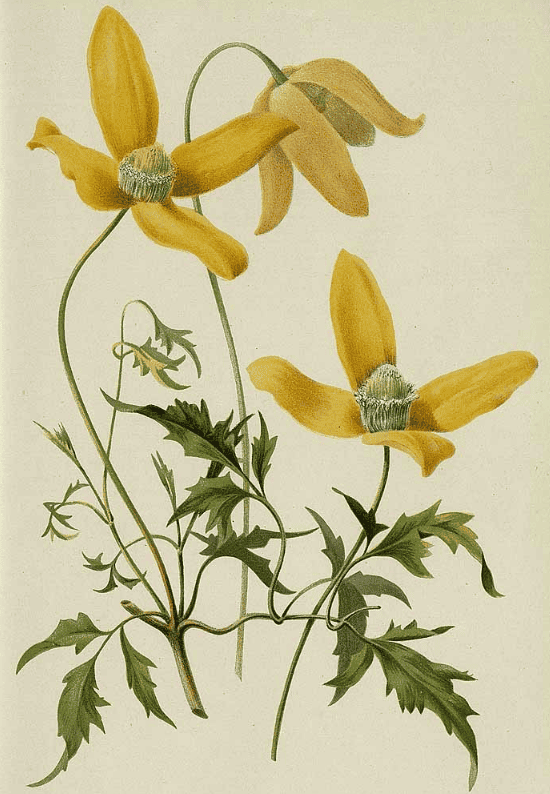 C. tangutica
C. tanguticaRevue horticole, serié 4, vol. 74: (1902)
Botanical name:
Clematis spp.
Several distinct varieties are used in Tibet:
- C. montana (also used for Chuan Mu Tong in TCM)
- C. orientalis var. tangutica
- C. tangutica
- C. tibetana (Black variety)
- Dbyi mong dkar po: C. rehderianum, C. alpina, C. aethusaefolia (White variety)
- Dbyi mong ser po: C. orientalis var. intricata (Tibet)
- Dbyi mong nag po C. tangutica
- C. armandii (used for Chuan Mu Tong in TCM)
Parts used:
Stem (Tibet, TCM)
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, slightly Sweet (Herb, Tibet)
Cold, Bitter (Stem, TCM)
Uses:
1. Warms the Spleen and Stomach: (Tibet, TCM)
-Cold abdominal pain, indigestion
-diarrhea from lack of digestive heat (Spleen Yang deficiency)
2. Warms the Spleen, Clears Damp Accumulation: (Tibet, TCM)
-Damp and Lymph diseases
-Food stagnation with abdominal fullness
-abdominal tumors from Cold and Damp
3. Resists Poison:
-Welling Abscess and Sores (TCM)
-Necrotic Sores and to draw out Pus (Tibet)
-Damp Sores
CLEMATIS CHUAN MU TONG
The stem of either C. armandii or C. montana is used in TCM as Chuan Mu Tong.
1. Clears Heat and Damp, Promotes Urine:
-Damp-Heat Edema, Strangury
-Dysuria, Dysuria with Blood, Dysuria caused by Stones
2. Moves the Blood, Opens the Channels, Eases Pain:
-Muscle and Joint pain, Arthritis
-Amenorrhea,
Dose:
Decoction: 3–6 grams
Powder: 1–3 grams
Comment:
1. As with many Tibetan herbs, the sources are complex and there are a number of variations recognised and used in different areas where Tibetan Medicine is practiced.
2. Despite the source potentially being the same (C. montana, C. armandii), the indications are different enough to separate them. Dbyi mong is viewed as Warm in Tibetan Medicine whereas Chuan Mu Tong is classed as Cold in TCM. Further, the whole above-ground plant is used in Tibetan Medicine, whereas only the stem is used in TCM. This may effect the use and effects. Note, however, that the common function between the systems is in the treatment of Damp.
Correctives:
Licorice
Substitute
Atragene sibirica (grass) is used in Buryat region
Main Combinations:
Major Formulas:
Cowrie Ash 8 (‘Gron thal brgyad pa)
Cautions:
1. Very heating (in Tibetan Medicine) so not used in Hot disorders
2. Toxic in overdose.
