Centella, Pennywort, Ji Xue Cao 积雪草
Indian Pennywort, Gotu KolaBrahmi, Mandukaparni (Ayurveda)
Ji Xue Cao (TCM)
 Kirtikar, Basu, Indian medicinal plants, Plates, 1918
Kirtikar, Basu, Indian medicinal plants, Plates, 1918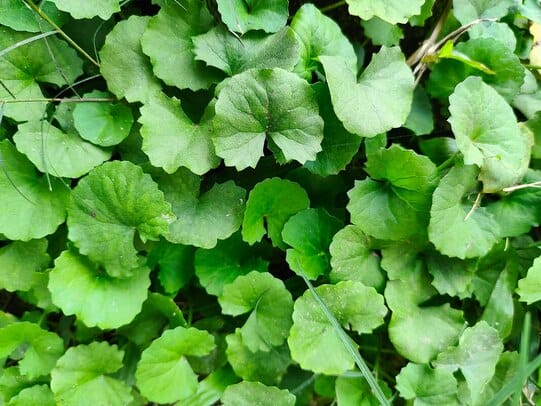 Centella asiatica
Centella asiatica(Photo by Md. Siddiq Hasan) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Centella asiatica (syn. Hydrocotyle asciatica)
The European C. vulgaris has been used similarly.
In India, Brahmi also encompasses Bacopa monieri
Parts used:
Herb
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Pungent, Sweet
Classifications:
4j. NERVINES
TCM:
B. Clears Heat & Damp N. Tonics
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Damp (Ayurveda, TCM):
-Diarrhea, Dysentery
-Jaundice (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-Strangury, Urinary Tract Infection, Cystitis, Hematuria
-adjunct for Urinary stones
2. Clears Toxin, Disperses Toxin (Ayurveda, TCM):
-Fever, High Fever, Eruptive Fevers
-Acute Sore Throat, Laryngitis, Tonsillitis
-Infectious Diseases
-resist various Toxins and Poisons.
-Toxic Swellings and Sores, Boils and Furuncles.
-special traditional remedy in India and elsewhere for Leprosy and other obstinate skin diseases including Tuberculosis of the skin.
-Food poisoning and Drug Intoxication
3. Clear Heat and Phlegm, Stops Cough:
-Cough, Wheezing, Asthma
-has been used for Tuberculosis
4. Clears Heat, Stops Bleeding:
-heat-type bleeding of the Nose, Bladder, Lungs, Stomach or Bowels
5. Clears Heat, Moves the Blood, Resolves Swellings:
-Toxic Swellings and Tumors, including Cancer.
-internally and topically for bruising following Trauma. (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
6. Nourish the Kidneys and Liver, Benefits the Brain:
-powerful tonic in Ayurveda.
-promotes Intellect and Wisdom, increase Memory, prevent Senility, and promote Longevity.
-help mental and physical development in children
-childhood Epilepsy and Stuttering in children (2 leaves every morning).
-Insanity, Mental disorders.
7. Externally:
-skin diseases including Scabies, Leprosy
-Ulcers, old and stubborn Wounds etc.
-Applied to scarring, including post-operative scarring
Dose:
Decoction: 15–30 grams dry; 30–60 grams fresh
Powder: 2–5 grams
Indian Classics preferred to give the fresh juice, usually with Milk, Ghee, Honey or Licorice.
Correctives:
Coriander seed
Substitute:
Bacopa monieri is a synonymous herb in Ayurveda
Main Combinations:
1. Fever, Centella with Basil and fresh Ginger (Ayurveda)
2. Benefit the Brain in old age, improve Memory:
i. Centella with Calamus
ii. Ginkgo leaf, Centella, Sesame seed, Frankincense
iii. Ginkgo leaf, Centella, Withania, Calamus
iv. Centella, Bacopa, Withania, Chebula, Indian Spikenard
3. Calm the Mind and Nerves in anxiety, nervousness:
i. Centella with Convolvulus Shakhapushpi
ii. Centella with Lotus seed, Convolvulus Shakhapushpi
iii. Centella with Ammi, Hydrocotyle asiatica, Withania (Ayurveda)
iv. Centella with Indian Spikenard, Saffron
v. Centella with Rauwolfia, Indian Spikenard, Licorice
vi. Centella with Sandalwood, Convolvulus Shakhapushpi
vii. Centella, Chrysanthemum indicum (Ye Ju Hua), Bacopa, Convolvulus Shanhapushpi
4. Nervous disorders:
i. Centella with Tribulus seed, Indian Spikenard
ii. Centella with Indian Spikenard, Bacopa, Convolvulus Shankhapushpi, Valerian, Nutmeg (usually in Ghee form)
iii. Nervous debility, Centella with Celery seed, Indian Spikenard, Valerian (wallichi) (Ayurveda)
5. Spasms:
i. Centella with Mucuna
6. Epilepsy:
i. Centella with Valerian, Peony
ii. Centella with Calamus, Costus, Asparagus racemosa
7. Mental disorders, Insanity:
i. Centella with Costus
ii. Centella with Datura
iii. Centella with Fumitory, Dodder
iv. Mental disorders from Wind-Heat, Centella with Eclipta (Han Lian Cao), Indian Spikenard, Convolvulus Shankhapushpi
iv. Centella, Bacopa, Withania, Convolvulus Shanhapushpi
8. Skin Inflammation and Blood diseases:
i. Centella with Licorice and Milk (Chakradatta)
ii. Centella with Neem, Swertia
iii. Centella with Fumitory
iv. Centella with Andrographis, Neem, Turmeric
v. Centella with Neem, Madder, Tinospora, Psoralea
9. Arthritic diseases, Joint inflammation:
i. Centella with Bdellium, Turmeric, Tinospora
10. Cough, Consumption, Centella with Licorice and Honey
11. Diarrhea and Dysentery in children, Centella with Cumin (Ayurveda)
12. Strangury from Damp-Heat, Centella with China root (Tu Fu Ling)
Cautions:
Generally Safe.
Main Preparations used:
|
‘In Sanskrit works this plant is called Mandukaparni, and is described as a useful alterative and tonic in diseases of the skin, nervous system, and blood. Chakradatta directs the fresh juice to be given with milk and liquorice. The plant was known to Rheede by its Malayalim name of Codogam or Kutakan, and also to Rumphius. Ainslie informs us that an infusion of the toasted leaves in conjunction with fenugreek is given to children suffering from bowel complaints and fever in doses of half a teacupful, also that the leaves on the Coromandel Coast are applied to parts that have suffered from blows and bruises, having, it is supposed, the power of keeping off inflammation. In Java, according to Horsfield, they are considered diuretic, and on the Malabar Coast the plant is one of the remedies for leprosy. As a remedy in this disease it was first brought prominently to notice by Lupine (1853) and Boileau. Dr. A.. Hunter, who tried it in the Madras Leper Hospital (1855), came to the conclusion that it had no claim to consideration as a specific in leprosy, but he found it most useful in ameliorating |
the symptoms and improving the general health. In the Pharmacopoeia of India it has been made official, and is described as an alterative, tonic and local stimulant, more especially useful in syphilitic skin diseases, in which it may be used both as an internal and local remedy. Directions for making a powder and poultice are given. Recent reports from Europe (1885) confirm this statement, and there has been some enquiry for the drug in Bombay which has led to its cultivation on a small scale. In the neighbourhood of Bombay the plant is rare in a wild state, but may often be seen in gardens; it is a popular remedy for the slight dysenteric derangements of the bowels to which children are subject; 3 to 4 leaves are given with cummin and sugar, and the pounded leaves are applied to the navel. In the Concan one or two leaves are given every morning to cure stuttering; and the juice is applied to skin eruptions supposed to arise from heat of blood’. (Vegetable Materia Medica of Western India, Dymock, 1885) |
