Careya arborea, Kumbhi
Kumbi, Wild Guava, Slow-Match TreeKumbhi, Kumbhikah (Seed) (Ayurveda)
Kumbi (Siddha)
Baokhumba, Bai Khumbi (Seed) (Unani)
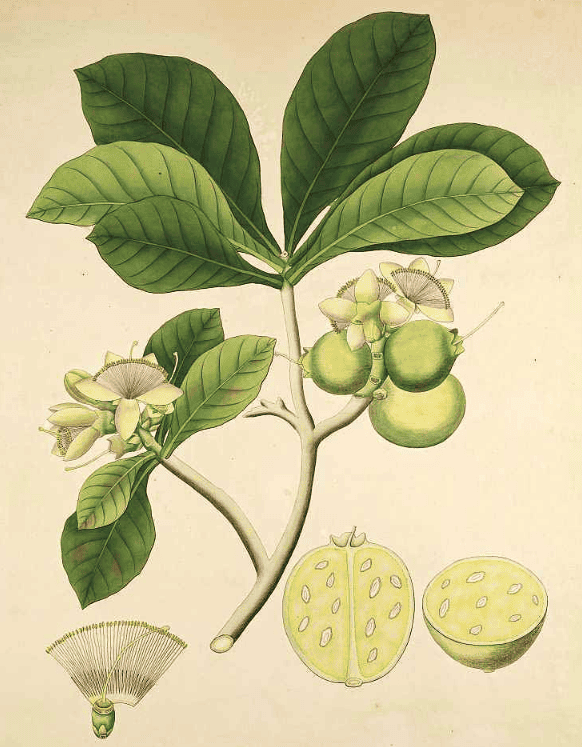 W. Roxburgh, Plants of the coast of Coromandel, vol. 3 (1819)
W. Roxburgh, Plants of the coast of Coromandel, vol. 3 (1819)Botanical name:
Careya arborea, C. herbacea
Parts used:
Stem Bark; Seed; dried Fruit
Temperature & Taste:
BARK: Warm, dry.
SEED: Warm, dry. Pungent, astringent
Uses:
STEM BARK:
1. Clears Heat, Stops Leakage:
-Diarrhea, Dysentery
2. Clears Wind-Heat, Resists Poison:
-Fever; Colds, Influenza
-Eruptive Fevers, Small Pox
-Hepatoprotective
-root is used for Snake Bite
3. Externally:
-paste of the bark can be applied to Fractures
-Leucoderma
-fresh bark is chewed for Stomatitis
-leaf poultice is applied to Ulcers
SEED:
1. Warms the Kidneys:
-chronic urinary diseases
-diabetes
2. Clears Phlegm, Stops Cough:
-Cough
3. Resists Poison:
-chronic skin diseases including Leprosy
4. Kills Worms:
Dose:
Decoction (1 in 10): 4–12 drams
Bark Powder: 500mg–1 gram
Seed Powder: 2–6 grams (API)
Corrective:
1. Myrtle (Myrtus communis) (Unani)
Substitute:
1. Leaves can be used in place of the Bark
2. Careya arborea has been used as a substitute for Myrica esculenta in some parts of India..
Main Combinations:
1. Jaundice, Careya, Mimosa, Achyranthes, Ziziphus mauritiana, taken with milk.
2. Fractures, applied Careya bark with Litsea
3. Leucoderma, bark paste is mixed with Neem oil and applied
4. Remittent Fever, leaf and flower of Careya is given with Black Pepper
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
Seed is toxic.
