Cardamomum, Lesser CardamomSukshmaila (Ayurveda)Heel Khurd (Fruit, Unani) Dana Heel Khurd (Seed, Unani) Sug smel སུག་སྨེལ (Tibetan) |

|
 Ortus Sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501
Ortus Sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501 |
 Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491
Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491 |
Icones Plantarum Medcio-oeconomico, Vietz, 1800
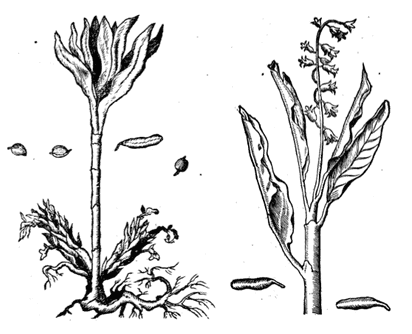
|
|
|
Indiae Utriusque re Naturali et Medica, Pisonis, 1658 |
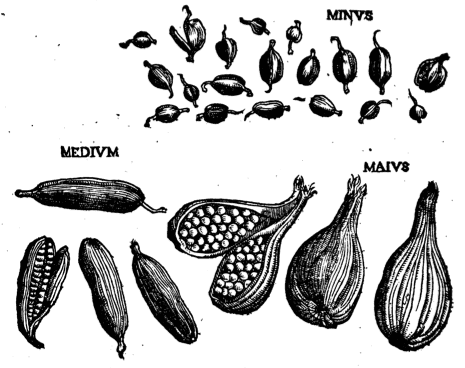
Lesser, Medium and Greater Cardamons New Kreuterbuch, Matthiolus, 1563 |
 Lesser Cardamon (Adam, 2016)
Lesser Cardamon (Adam, 2016) Members CLICK HERE for the PRO VERSION
Members CLICK HERE for the PRO VERSIONBotanical name:
Elettaria cardamomum (Lesser Cardamon)
There are a number of different Cardamons; the main types are:
- Lesser Cardamon: Elettaria cardamomum (syn. Amomum caradmomum); Ela (Ayurveda); Heel Khurd (Unani); Sug Smel (Tibetan)
- Greater Cardamon: Amomum subulatum; Sha Ren (TCM); Bahula, Bhadra (Ayurveda); Heel Kalan, Qaqule Kubar (Unani) (see Amomum)
- Grains of Paradise: Aframomum spp.; Heel Habshi (Unani)
Parts used:
Fruit
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, Sweet
Classification:
3C. ALEXIPHARMIC. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS
4a. CEPHALIC. 4c. CARDIAC. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4j. NERVINE
Uses:
1. Moves Qi, clears Damp, Warms the Stomach:
-poor appetite (Commission E), nausea, distention, indigestion, vomiting
-“It strengthens the Stomach.” (Avicenna)
2. Clears Phlegm, Stops Cough:
-Phlegm obstructing the Chest; tightness of the Chest
-Cough, Bronchitis (Ayurveda, Commission E); Asthma in Ayurveda
3. Warms the Kidneys, Promotes Urine:
-Cold Kidneys with copious pale urine, lower back pain
-Cystitis, Nephritis, Gonorrhea, scanty, difficult or suppressed Urine
-Gravel and Stones
4. Rasayana (Tonic):
-in India regarded as a strengthening tonic; it is a Brain, Heart and Liver tonic, promoting strength
-In Tibet as a special medicine to strengthen the Kidneys.
Dose:
With wine for obstructed or difficult Urine
Powder: 250mg–3 grams;
Decoction 3–6 grams (up to 12 grams)
Substitutes:
… available in PRO version
Correctives:
… available in PRO version
Comment:
The Cardamons are similar in effect and smell. However, Lesser (Green) Cardamon is more focused on the Kidneys, while the Greater Cardamon is a specific medicines for the Spleen. In various texts, the Greater and Lesser have been recommended as acceptable substitutes for one another, so their use is similar. They are also often combined in formula.

Main Combinations:
1. Kidney disorders, urinary obstructions, stones of the Bladder, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
2. Suppressed Urine, Lesser Cardamon … available in PRO version
3. Painful or Difficult Urination (Dysuria):
i. Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
ii. Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
4. Stones:
i. Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
ii. Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
5. To promote Conception, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
6. Female tonic, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
7. Hysteria, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
8. Loss of appetite, indigestion, Colic, Atonic Dyspepsia:
i. Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
ii, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
iii. Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
iv. Atonic Dyspepsia, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
9. Nausea, Vomiting, Less Cardamon, … available in PRO version
10. Phlegm disorders, Lesser Cardamon, … available in PRO version
11. Lung disorders from excess Phlegm, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
12. Cough, Asthma from Phlegm:
i. take Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
ii. chronic cough and Asthma, … available in PRO version
13. Bronchitis, Asthma, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
14. To warm and stimulate the Heart and Kidneys, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
15. Melancholy, Lesser Cardamon with … available in PRO version
Major Formulas
Six Excellent Medicines (Tibetan Medicine)
Tincture of Cardamon
Powder for Loss of Appetite (Nicholas)
Powder Helpful for Epilepsy (Alexander)
Powder for Melancholy (Philon)
Powder for Foul and Intolerable Appetite in Women (Nicholas)
Troches for Heart Weakness
Electuary of Aloeswood (Diaxyloaloes) (Mesue)
Triphera of the Saracens (Triphera Saracenica Magna)
Cardamon 7 (Sug smel 7) (Tibetan Medicine)
Cardamon 10 (Sug smel bcu pa) (Tibetan Medicine)
Camphor 14 (Tibetan Medicine)
Aloeswood 31 (Tibetan Medicine)
Aloeswood 35 (Tibetan Medicine)
Cautions:
Dry, so not suitable in Yin deficiency.
Main Preparations used:
Distilled Oil, Distilled Water, Confection of Cardamom
-
Extra Info
- History
- Research
|
‘The small cardamom, in Sanskrit Ela, is mentioned by Susruta. In the Nighantas it bears various synonyms, such as Truti, Kapota-varni “grey,” Korangi, and Dravidi “coming from the Dravidian country.” The large or Nepal cardamom (Amomum subulatum) is called Sthulaila “large Ela,” and is described separately. Both kinds arc considered to be digestive, pungent, light and hot, and are recommended in phlegmatic affections, such as cough, asthma, piles, and diseases of the bladder and kidneys. These two cardamoms are described by Ibn Sina under the name of kakulah; he also describes separately under the name of hilbawa another kind of cardamom as more easily digested than the kakulah. This latter cardamom is the true Cardamomum majus or Nutmeg cardamom of Africa to which Pereira has given the name of Amomum korarima. We think that there can be no doubt that the Greeks were acquainted with the cardamoms of India which they appear to have first obtained from the Persians through Syria and Armenia. Dioscorides says:— “Choose that which is tough, well filled, closed; if not in this state, it is too old |
and has lost its aroma. The taste is pungent and somewhat bitter.” With respect to the name Katiddus, the Greeks appear to have applied it to this spice in much the same way as the Persians applied the name kakalah, which originally meant the fruit of some other plant which was used for flavouring bread. In the Burhan it is stated that the name kakulah is also given by some to a fruit like Sapandan (a kind of cress), which is the same as Ilachi. Besides the two Indian cardamoms, there is a large kind of cardamom which comes from Ceylon, now found in commerce. Dr. Trimen, in his Systematic Catalogue of the Flowering Plants and Ferns of Ceylon, speaks of the plant which produces it as Elettaria cardamomum, Maton, var. major— the Ensal of the Singhalese. As a masticatory and for flavouring food, the Malabar or small cardamom is preferred by the natives, but the other kinds, which are cheaper and of less delicate flavour, are largely used by the sweetmeat makers.’ (Pharmacographia Indica, Dymock, 1893) |
