Camptotheca, Xi Shu 喜树Happy TreeXi Shu (TCM) |

|
 Camptotheca acuminata
Camptotheca acuminataManual of Vascular Plants of the Lower Yangtze Valley China (Wikimedia)
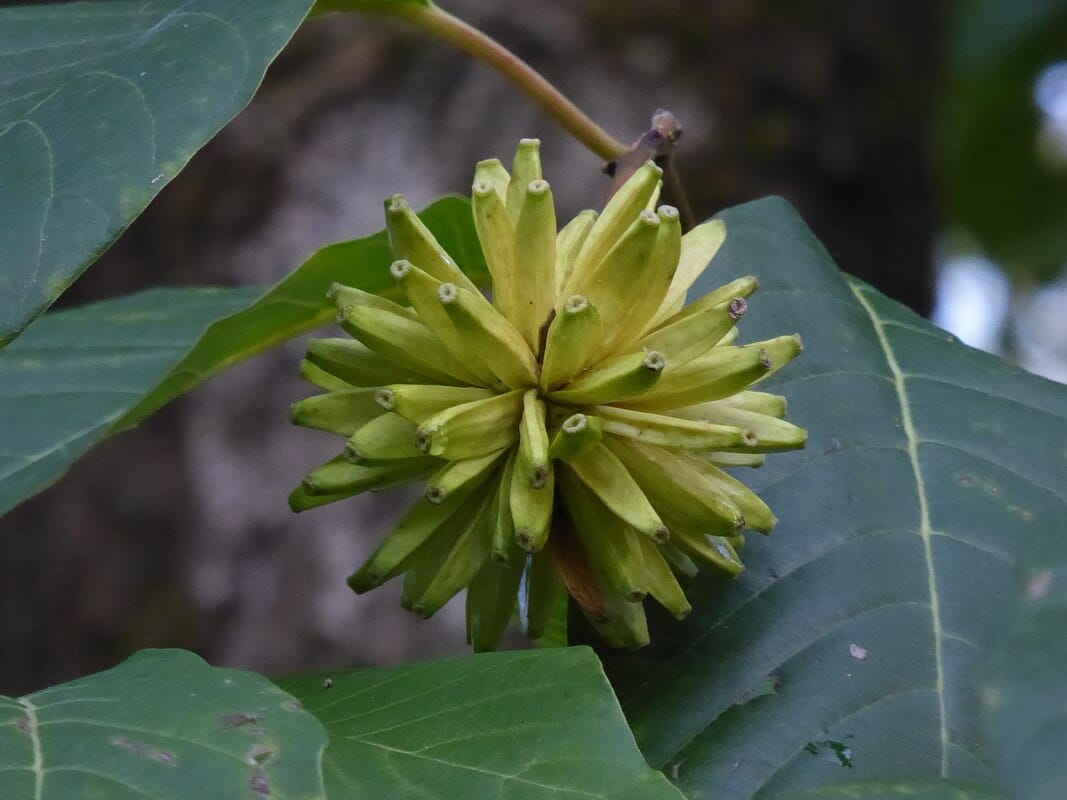 Camptotheca mature fruit
Camptotheca mature fruit(Photo by Syrio) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Camptotheca acuminata
Parts used:
Fruit; Root bark
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Bitter, Pungent, Toxic
Classification:
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Toxin:
-Herpes, Psoriasis (topical)
-Toxic Sores
–Hepatosplenomegaly caused by schistosomiasis
2. Moves the Blood, Clears Stasis, Resolves Masses:
–various Cancers including Esophageal, Lung, Breast, Ovarian, Stomach, Liver, Colorectal, Head and Neck, Bone etc.
–choriocarcinoma, lymphosarcoma
-acute and chronic Leukemia
3. Externally:
-topically for Psoriasis, Herpes, Toxic Skin Sores
Dose:
1. The Fruit is generally regarded as stronger in effect, but is more toxic than the root-bark.
2. Begin with lower doses increasing as needed
3. It should not be cooked in iron vessels
Fruit in Decoction: 3–9 grams
Root-bark in Decoction 10–15 grams
Main Combinations:
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
1. Avoid overdose.
2. Do not cook in Iron pots.
3. Use cautiously in Immunosuppressed. Immunosuppression caused by camptothecin was temporary; immunity recovered after 9 days of drug withdrawal
Toxicity:
Isolated camptothecin has been used in Cancer therapy, but was discontinued due to severe toxicity, particularly hemorrhagic cystitis. However, less toxic analogues have seen a resurgence of interest. As with other toxic medicines used in Cancer therapy, there can still be use for the whole plant rather than its isolated compound.
