Assafoetida, Asafetida, A Wei 阿魏Asafoetida, Devil’s DungHing, Hingu (Ayurveda) Perunkayam (Siddha) A Wei 阿魏 (TCM) Hilteet (Unani) Shing kun ཤིང་ཀུན (Tibetan) |

|
 Ortus sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501
Ortus sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501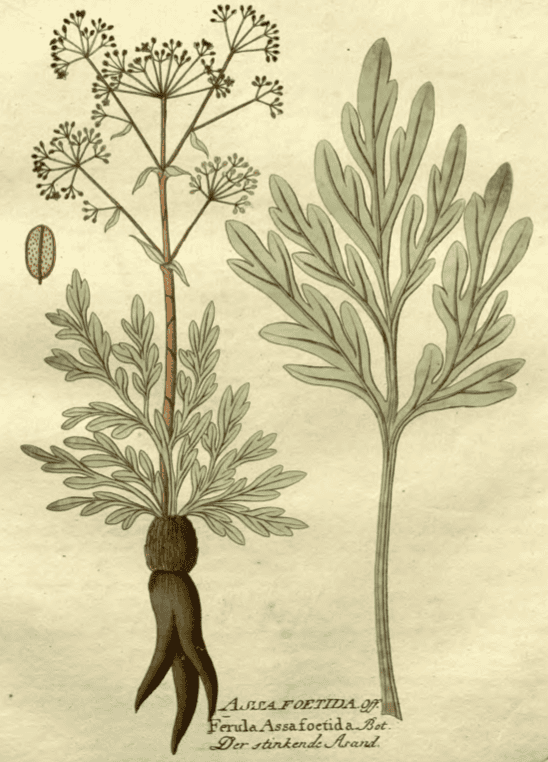 Icones Plantarum Medcio-oeconomico, Vietz, 1800
Icones Plantarum Medcio-oeconomico, Vietz, 1800 Ferula asafetida
Ferula asafetidaAtlas der officinellen pflanzen (2), Felix, 1899
 Lump of raw Asafetida gum
Lump of raw Asafetida gum(Adam, 2022)
Botanical name:
Ferula asafetida
Other related sources include F. sinkiangensis
Parts used:
Gum
‘The root has similar therapeutic functions’ (Li Shi Zhen)
Temperature & Taste:
Hot, dry. Pungent, bitter.
“Hot in the beginning of Fourth degree and Dry in the Second degree”. (Avicenna)
Classification:
2H. CARMINATIVES 2K. RESOLVENT 2Q. ANODYNE
3G. EMMENAGOGUE 3K. EXPECTORANT
4j. NERVINES
TCM:
J. Regulate Qi O. Promotes Digestion
Uses:
1. Warms the Womb, Moves Qi and Blood (West, Ayurveda):
-painful and difficult Menstruation
-chiefly for Suffocation of the Uterus: Hysteria and PMS
-Sterility, Habitual Miscarriage
-“Dissolves the coagulated blood in the abdominal cavity” (Avicenna)
2. Warms the Stomach, Benefits Digestion (West, TCM, Ayurveda, Tibetan):
-indigestion, colic, abdominal pain, poor appetite
-taken before meals to strengthen a weak stomach
-Food Stagnation
-‘dissolves indigestion due to overeating of meat’. (Zhu Zhen Heng)
3. Clears Wind, Stops Spasms (West, Tibetan Medicine):
-good for Wind diseases from Wind-Phlegm / Wind-Damp
-Spasms, Convulsions, Epilepsy, Neurasthenia, Nervous Prostration, Depression, Insanity
-“Its actions in Epilepsy resemble those of Peony”. (Avicenna)
4. Warms the Kidneys (West, TCM, Ayurveda, Tibetan):
-Impotence, Premature Ejaculation, Spermatorrhea
-Arthritis, Edema (Tibetan Medicine)
5. Clears Cold Phlegm, Stops Cough (West, Ayurveda, Tibetan):
-spasmodic Cough, Asthma, chronic Bronchitis, Whooping Cough, Peri-pneumonia
-internal Abscesses (Avicenna)
-‘useful in internal tumours’ (Avicenna)
6. Clears Wind, Resists Poison (West, TCM, Ayurveda, Tibetan):
-used since ancient times as an antidote to Evil, Infectious and Epidemic diseases
-effective to prevent and treat Influenza; also Malaria
-“applied on bite of Rabid Dog as also on Insect stings particularly that of the Scorpion and Tarantula”. (Avicenna)
-‘disperses invading pathogenic Wind’ (Li Xun)
-antidote to Aconite and Opium poisoning; also other Poisons
-‘detoxifies toxin of all kinds of mushrooms and vegetables’. (Da Ming)
7. Kills Worms:
-used for Worms
–Gu syndrome (diseases caused by Parasites) (TCM)
8. Externally:
-Vulnerary; used for Wounds, Bruises
-externally for swelling of the Spleen, ‘suffocation of the Uterus’
-fumes of Asafetida and Goat’s horn, being burnt, was inhaled for Epilepsy
-smoke inhaled for Rhinitis and Sinusitis
-a small piece wrapped in linen or gauze can be put into the ear before sleep for Tinnitus.
-“Used as a kohl (collyrium) with honey, it proves beneficial in early stages of Cataract”. (Avicenna)
-“Corroded molars are filled with Asafetida or it is pasted with Frankincense on the teeth” (Avicenna)
-“Malignant necrotic swellings are scarified and asafetida is applied thereon with good results.” (Avicenna)
-“It is also a good remedy for the external and internal Abscesses”. (Avicenna)
Dose:
Powder: 250mg–1500mg (up to 3 grams has been given)
Tincture (1:5 in 80% alcohol): 1–2 mls.
Correctives:
1. Barberry; White Sandalwood
2. Aniseed; Tragacanth. (Unani)
Substitute:
1. Galbanum
Preparation:
The drug is obtained in hot countries by making a cut in the head of the root and collecting the resin. In cold countries, the root is beaten, the juice is extracted and dried in the sun or in an oven.
1. Stir-fried Asafetida:
In Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine it is usually stir-fried in a little ghee for internal use. This removes the nauseous taste, makes it more agreeable to the stomach, and reduces its harshness. It also facilitates powdering.
2. Vinegar-prepared Asafetida:
In the Western Tradition it was sometimes dissolved in vinegar. This guides its effects to the Liver, helps move Qi and Blood, and was used for Hysteria, Epilepsy, Apoplexy and menstrual disorders. Vinegar also corrects the unpleasant taste and smell.
Adulteration:
“All varieties of Asafetida are adultrated before drying with Sagapenum and the flour of broad bean”. (Avicenna)
Main Combinations:
1. To promote Menstruation, cleanse the Uterus, to promote Labor, and for Hysteria;
i. Asafetida with Myrrh, Asarum, Feverfew, Calamint
ii. Asafetida with Myrrh, Sagapen, Madder, Rue, Mint
iii. Asafetida with Myrrh, Rue, Pennyroyal, Madder, Mugwort
iv. Asafetida with Myrrh, Calamint, Rue, Savin
v. Asafetida with Myrrh, Saffron, Iron sulphate
vi. Asafetida, Saraca indica, Turmeric (Ayurveda)
2. Hysteria:
i. Asafetida with Valerian
ii. Asafetida (1 dram), Carrot seed (½ dram); with Honey of Roses, make 5 pills and take one each morning. (The Secrets of Alexis, 1615)
iii. Asafetida with Camomile and Rue
iv. Asafetida with Ginger and Black Pepper and form Pills (Ayurveda)
v. and to strongly promote Menstruation, combine Asafetida with Aloes and form Pills (Ayurveda)
vi. Asafetida with Myrrh, Parsley root, Peony root, Cumin, Balm, Mint, Rue
vii. Asafetida with Myrrh, Saffron, Castoreum, Camphor, Amber
viii. Asafetida, Galbanum, Myrrh, Valerian, Saffron, Castoreum (Sydenham’s Pilulae Antihysterica)
3. Infertility, Asafetida with Nutmeg, Withania
4. Asthma or Bronchitis:
i. combine Asafetida with Horehound
ii. Asafetida with Saffron
iii. spasmodic Cough, Whopping Cough, Asafetida, Adhatoda, Long Pepper
5. Wind diseases: combine Asafetida with Aloeswood, Nutmeg, Costus, Clove, Fennel (Tibetan Medicine)
6. Epilepsy, Seizures:
i. Asafetida with Oxymel (Gerard)
ii. Asafetida with Calamus, Long Pepper (Ayurveda)
7. Nervous diseases, Spasms:
i. Neurosis, Asafetida with Valerian
ii. Asafetida with Valerian and Mint
iii. Asafetida with Valerian and Amber
8. Hypochondriac Melancholy, Asafetida with Bull Bile, Rhubarb
9. Jaundice: “Its ingestion with dry fFg proves to be useful in Jaundice”. (Avicenna)
10. Abdominal Obstruction, Asafetida, Aloes, Gum Ammoniac, Dandelion extract, Rhubarb
11. To promote Digestion and increase digestive Heat, Asafetida with Ginger, Cardamon, Fennel (Ayurveda)
12. All Wind diseases of the digestive system: combine Asafetida with Ginger, Pepper, Long Pepper, Cumin seed, Ajowan seed, Nigella seed, Rock Salt (Ayurveda, Hingashtak)
13. Severe Abdominal pain, Asafetida with Long Pepper, Ginger, Calamus, Sonchal Salt, Indian Sorrel
14. Heart disorders from Wind, Heart pain, Asafetida, Arjuna, Chebulic Myrobalan (Ayurveda)
15. Diarrhea associated with weakness of the Stomach, combine Asafetida with Raisin (Gerard)
16. Dysentery, Asafetida, Coptis Huang Lian, Costus Mu Xiang
17. Chronic Malaria, Asafetida with Cinnabar (equal parts), mixed with rice gruel and made into pills. Take before meals with decoction of Ginseng. (Li Shi Zhen)
18. Abscesses, Carbuncles etc., combine Asafetida with Rue and Saltpeter (Gerard)
19. In enemas, Asafetida with Camomile
Major Formulas
Powder for Severe Sore Throat
Troches for the Womb
Troches of Gums
Asafetida Powder (Hingvastaka Churna) (Ayurveda)
Asafetida 8 (Shing kun brgyad pa)
Asafetida 25 (Shin kun nyer lnga) (Tibetan)Aloeswood 9 (A gar dgu pa) (Tibetan)
Boladi Vati (Ayurveda)Caraway 8 (Go snyod brgyad pa) (Tibetan)
Increase Awareness Pills (Tibetan)
Mental Happiness (Sems kyi bde skyid) (Tibetan)
Nutmeg 14 (Dza ti bcu bzhi) (Tibetan)
1. Pills of Asafetida:
i. Asafetida, Galbanum, Myrrh (8 parts each), Amber oil (1 part) (Edinborough)
ii. Asafetida, Valerian extract (equal parts). Dose: 10–20 grains
iii. Asafetida (2 drams), Camphor, Musk (1 dram each), Ambergris (½ dram). Make 100 pills. Used for Angina pectoris. Dose: 2 pills. (Nouveau Formulaire Medicale et Pharmaceutique, 1820)
iv. Asafetida, Amber (2 drams), Mastic (1 ½ drams), Myrrh (1 dram), Tincture of Castor (sufficient). Dose: 12 grains thrice daily. Emmenagogue. (Nouveau Formulaire Medicale et Pharmaceutique, 1820)
2. Antispasmodic Bolus:
i. Asafetida, Castoreum (1 scruple each), Extract of Valerian (1 dram). Make 4 boluses. Nervous headache, tic douloureux, gastrodynia, epilepsy etc. (Ricettario clinico, 1825)
ii. Asafetida, Castoreum, Valerian, Amber (each ½ ounce), Camphor (1 scruple), Syrup of Amber (sufficient to make boluses). Used for Hysteria, Neuroses, Neuralgia and Nervous Vertigo. (Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1824)
3. Hysteric Pills (Pilulae Antihysterica):
i. Asafetida, Galbanum, Valerian extract (4 grams each), Castoreum, Saffron (1 gram each), Opium (500mg); make 100 pills. (Selle)
ii. Asafetida (5 grams), Galbanum, Myrrh (2.5 grams each), Castoreum (1250 mg), Valerian tincture (q.s). to make 100 pills sprinkled with saffron powder. (Sydenham)
iii. (Hysteric and Antispasmodic Pills) Asafetida (10 grams), Iron powder (2.5 grams), Castoreum (1250mg), Quassia extract (q.s.) make 150 pills. (Heim)
4. Nervine Boluses:
i. Asafetida (1 scruple), Extract of Valerian (2 scruples), Honey and Licorice powder (sufficient). Make 8 boluses; Dose: 2 every 2 hours.
5. Emmenagogue Pills:
i. Galbanum, Asafetida, Myrrh (½ dram each), Castoreum, Camphor, Ammonium subcarbonate (1 ½ drams), Oil of Cajeput (6 drops), Balsam of Peru (sufficient). Dose: 12–14 grains
Cautions:
1. Best not used during pregnancy (despite having been used for Threatened Miscarriage)
2. Not used in Heat conditions.
Toxicity:
1. Evaluation of Toxicity Effects of Asafetida on Biochemical, Hematological, and Histological Parameters in Male Wistar Rats
2. Acute and subchronic toxicity assessment model of Ferula assa-foetida gum in rodents
3. . Sub-acute and acute toxicity of Ferula asafoetida and Silybum marianum formulation and effect of the formulation on delaying gastric emptying
4. Severe Methemoglobinemia Secondary to Ferula asafoetida Ingestion in an Infant: A Case Report
Main Preparations used:
Pills of Asafetida (either alone, made up with Distilled Vinegar, or Compound)
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicin
|
‘Whether the substance which the ancients called Laser was the same as the modern Aasafoetida, is a question that has been often discussed during the last three hundred years, and it is one upon which we shall attempt to offer no further evidence. Suffice it to say that Laser is mentioned along with products of India and Persia, among the articles on which duty was levied at the Roman custom house of Alexandria in the 2nd century. “Hingu,” doubtless meaning Asafoetida, occurs in many Sanskrit works, especially in epic poetry, but also in Susruta. Asafoetida was certainly known to the Arabian and Persian geographers and travellers of the middle ages. One of these, Ali Istakhri, a native of Istakir, the ancient Persepolis, who lived in the 10th century, states that it produced abundantly in the desert between Sistan and Makran, and is much used by the people as a condi-ment. The region in question comprises a portion of Beluchistan. The geographer Edrisi, who wrote about the middle |
of the 12th century, asserts that asafoetida, called in Arabic Hiltit, is collected largely in a district of Afghanistan near Kaleh Bust, at the junction of the Helmand with the Arghundab, a locality still producing the drug. Other Arabian writers as quoted by Ibn Baytar, describe asafoetida in terms which show it to have been well known and much valued. Matthaeus Platearius, who flourished in the second half of the 12th century, mentions asafoetida in his work on simple medicines, known as Circa installs, which was held in great esteem during the middle ages. It is also named a little later by Otho of Cremona, who remarks that the more foetid the drug, the better its quality. Like other productions of the East, asafoetida found its way in European commerce during the middle ages through the trading cities of Italy. It is worthy of remark that it is much less frequently mentioned by the older writers than galbanum, sagapenum and opopanax. In the 13th century, the “Physicians of Myddfai,” in Wales, considered asafoetida as one of the substances which every physician “ought to know and use.” (Pharmacographia, Fluckiger & Hanbury, 1879) |
