Artemisia annua, Qing Hao 青蒿
Sweet Wormwood, Annual WormwoodQing Hao (TCM)
Nagadamani, Nagadana (Ayurveda)
mKhan nag མཁན་ནག (Tibetan)
 Dian Nan Ben Cao Tu Shuo (Illustrated Yunnan Pharmacopoeia),
Dian Nan Ben Cao Tu Shuo (Illustrated Yunnan Pharmacopoeia),Ming Dynasty (1773 edition) (Welcome, Wikimedia)
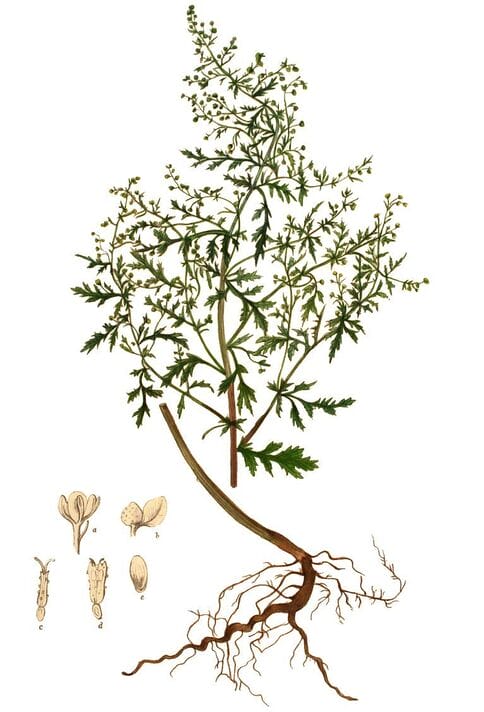 Kops, Flora Batava, 1906
Kops, Flora Batava, 1906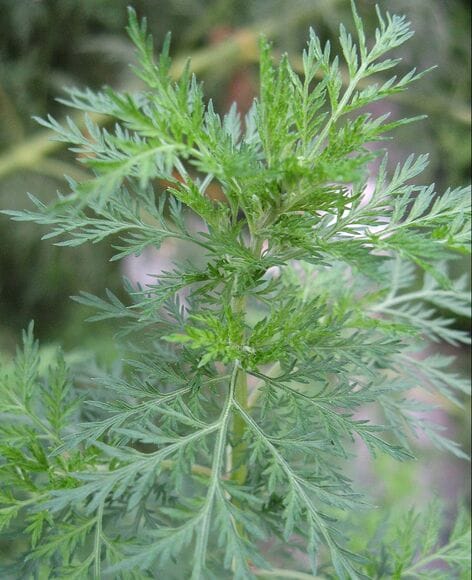 Artemisia annua
Artemisia annua(Photo by Xavierserratm) (Wikimedia)
Botanical name:
Artemisia annua
Several related species have been used including A. japonica.
Parts used:
Herb
Temperature & Taste:
Cold, dry. Bitter
Classification:
B. Clears Deficient Heat
Uses:
1. Clears Deficient Heat:
-Deficient Heat; Heat that has penetrated deeply into the body and is damaging the Blood or Yin
-Fever from deficiency, especially after Febrile disease; ‘Steaming Bone Disorder’; Tuberculosis
2. Clears Heat and Toxin from the Blood:
-boils, abscesses, itch, scabies
-Bleeding from Heat; Purpuric rashes during Fever
-red, sore and inflamed eyes
-has been used for Lupus, SLE (Duke)
-Malaria: the whole herb has been stated to be more effective than artemisinin and can be taken as an anti-malarial preventative (Duke)
3. Clears Summer-heat:
-a special herb in TCM for ‘Summer-heat’; heat disease during the hotter months with Fever, headache, dizziness
4. Kills Worms:
-Worms and Parasites
5. Externally:
-used topically for Eczema and Urticaria


Dose:
Decoction: 3–9 grams (20–40 grams for Malaria and SLE); added in the last 5 minutes (do not boil for long)
Artemisinin is given in doses of 300mg/day for SLE and Malaria
Comment:
This is a special medicine in TCM for a few reasons. 1. It clears Deficient Heat without damaging Yin, Qi or Blood. Its bitterness drains Heat, but its aromatic nature clears Heat from the deeper parts to the surface while supporting the Spleen Qi. 2. It treats ‘Summerheat’, a special type of Heat disease occurring during the Summer. 3. It is also a traditional treatment and preventative for Malarial disorders, and has been used as the source of artemisinin, a recent wonder-drug for drug-resistant strains of Malaria.
Preparation:
1. Dry-fried Qing Hao:
The cut herb is dry fried until yellowed and slightly scorched. This lessens its aromatic, dispersing nature and by some is believed to be better for Deficient Heat and Steaming Bone Disorder. It is not common today.
2. Turtle-Blood Qing Hao:
The cut herb is moistened with diluted Turtle Blood, then left to absorb. It is then dried by stir-frying in a Wok with a low heat, or in an oven. This is better to clear Heat and nourish Yin and is used for Night Sweats, Consumption and Steaming Bone disorder.
Main Combinations:
1. Deficient Heat, Artemisia Qing Hao with Lycium Di Gu Pi.
2. Chronic low-grade (Hectic) Fevers, Yin-deficient Fever, Night sweats, feeling of heat in the bones:
i. Artemisia Qing Hao with Rehmannia Sheng Di, Anemarrhena Zhi Mu.
ii. Artemisia Qing Hao with Picrorhiza Hu Huang Lian, Stellaria Yin Chai Hu, Anemarrhena Zhi Mu, Soft-Shelled Turtle shell (Bie Jia) (as in Qing Gu San from Zheng Zhi Zhun Sheng [The Level-line of Patterns and Treatment])
3. Consumption, Night Sweats, Artemisia Qing Hao with Ginseng and Ophiopogon Mai Men Dang
4. Purpuric rashes from severe heat in the Blood, or chronic low-grade Fever, Artemisia Qing Hao with Rehmannia Sheng Di Huang. In severe cases, Soft-Shelled Turtle shell (Bie Jia) is added to more strongly nourish the Yin while clearing deficient Heat.
5. Acute Summer-heat:
i. or Wind-Heat attack Artemisia Qing Hao with Forsythia Lian Qiao
ii. Artemisia Qing Hao with Agastache Huo Xiang, Eupatorium Pei Lan
iii. severe Summer-heat with thirst and dark, scanty urine, Artemisia Qing Hao with Talcum (Hua Shi), Licorice
6. Malarial Fever:
i. with Chills and Fever, Artemisia Qing Hao with Scutellaria Huang Qin and Pinella Ban Xia. (as in Hao Qin Qing Dan Tang from Tong Su Shang Han Lun [Popularized Treatise on Cold Damage])
ii. Artemisia Qing Hao with Anemarrhena Zhi Mu, unprepared Polygonum multiflorum (He Shou Wu)
7. Jaundice, Artemisia Qing Hao with Artemisia Yin Chen Hao, Rhubarb (Da Huang), Gardenia Zhi Zi.
Cautions:
1. Use cautiously in those with weak digestion and diarrhea from Cold and Weak Stomach and Spleen.
2. When larger doses have been used, some people experience nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
