Acorus, Calamus, Shi Chang Pu 石菖蒲Sweet FlagVacha (Ayurveda) Vasambu (Siddha) Shi Chang Pu 石菖蒲 (TCM) Shu dag ཤུ་དག (A. calamus, Tibetan) Waj, Waj e Turki (Unani) |

|
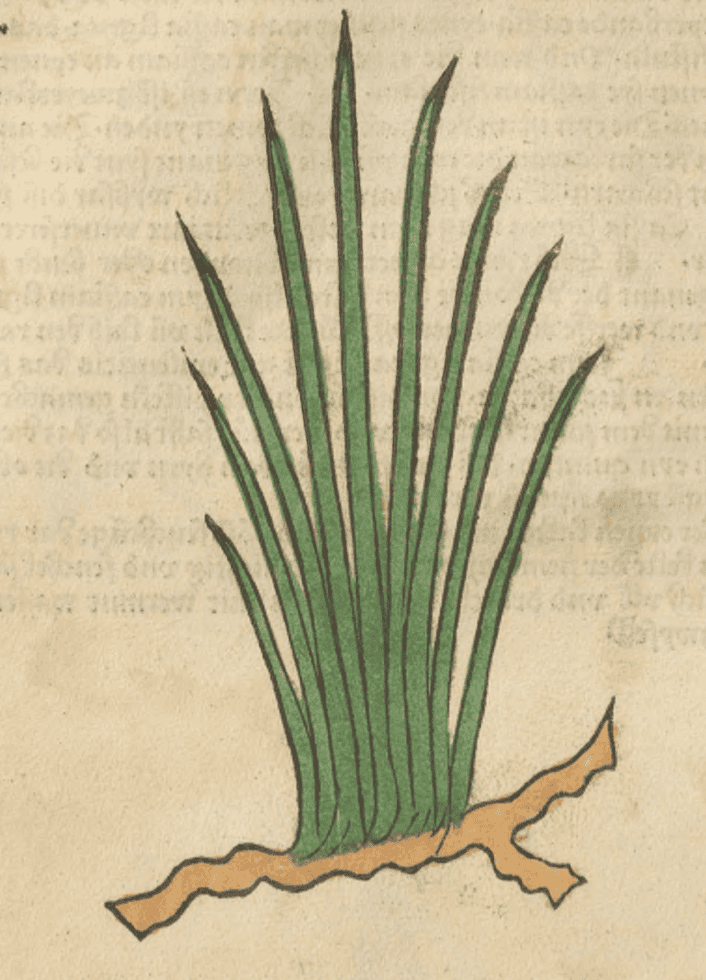 Gart der Gesundheit, Cuba, 1485
Gart der Gesundheit, Cuba, 1485 |
 Ortus Sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501
Ortus Sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501 |

|

|
|
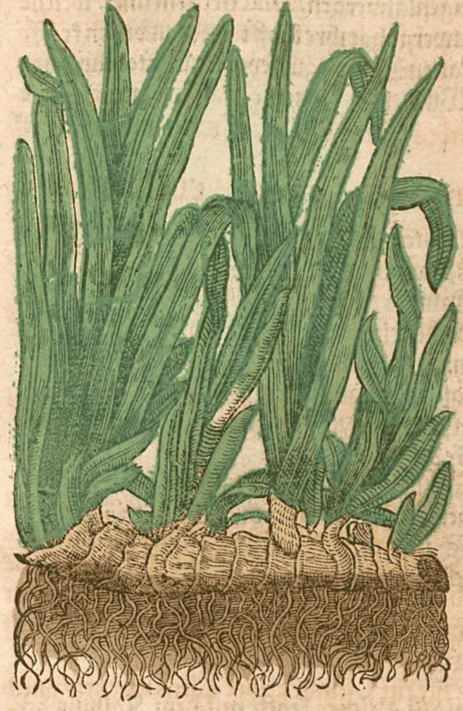
Calamus (Acorum verum, Acorus of Dioscorides) Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578 |
Pseudoacorus New Kreuterbuch, Matthiolus, 1563 |
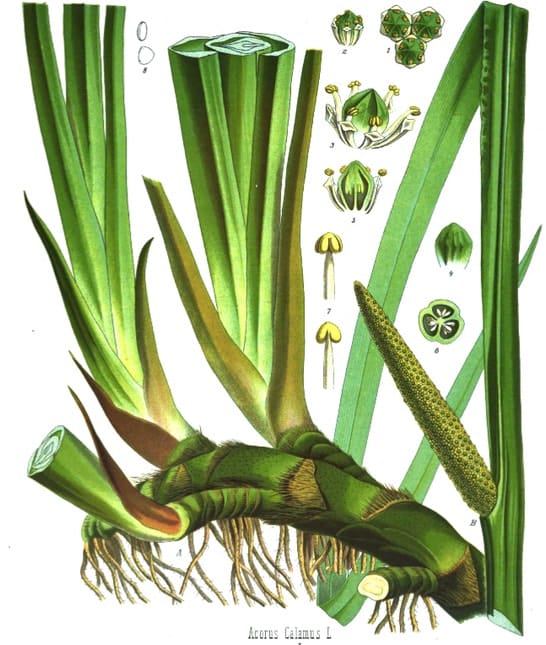 Acorus calamus
Acorus calamusKohler’s Medizinal Pflanzen, 1887
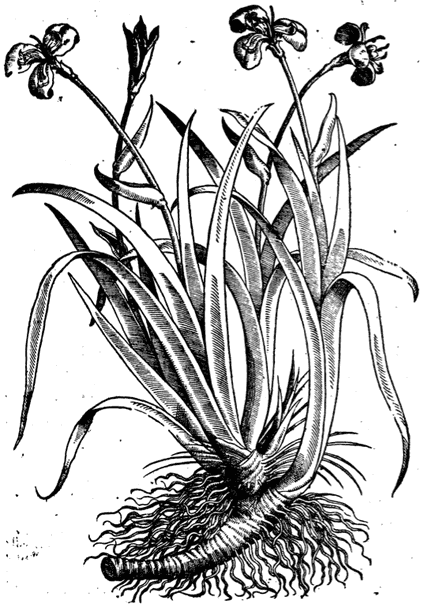
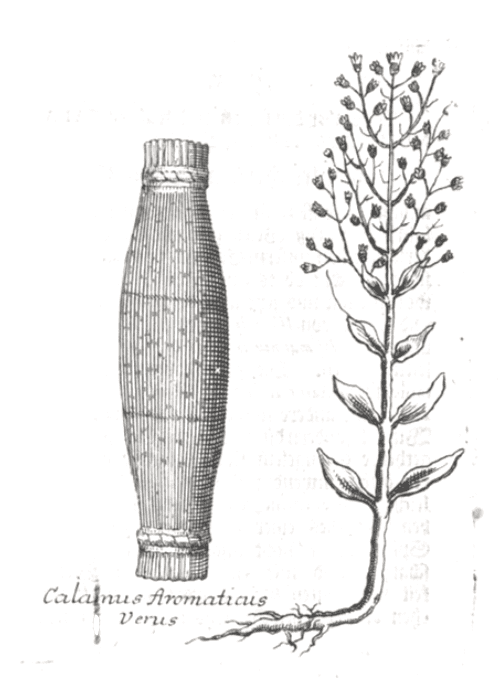 The ‘True’ (original) Acorus of the ancients
The ‘True’ (original) Acorus of the ancientsMuseum Museorum, Valentini, 1704
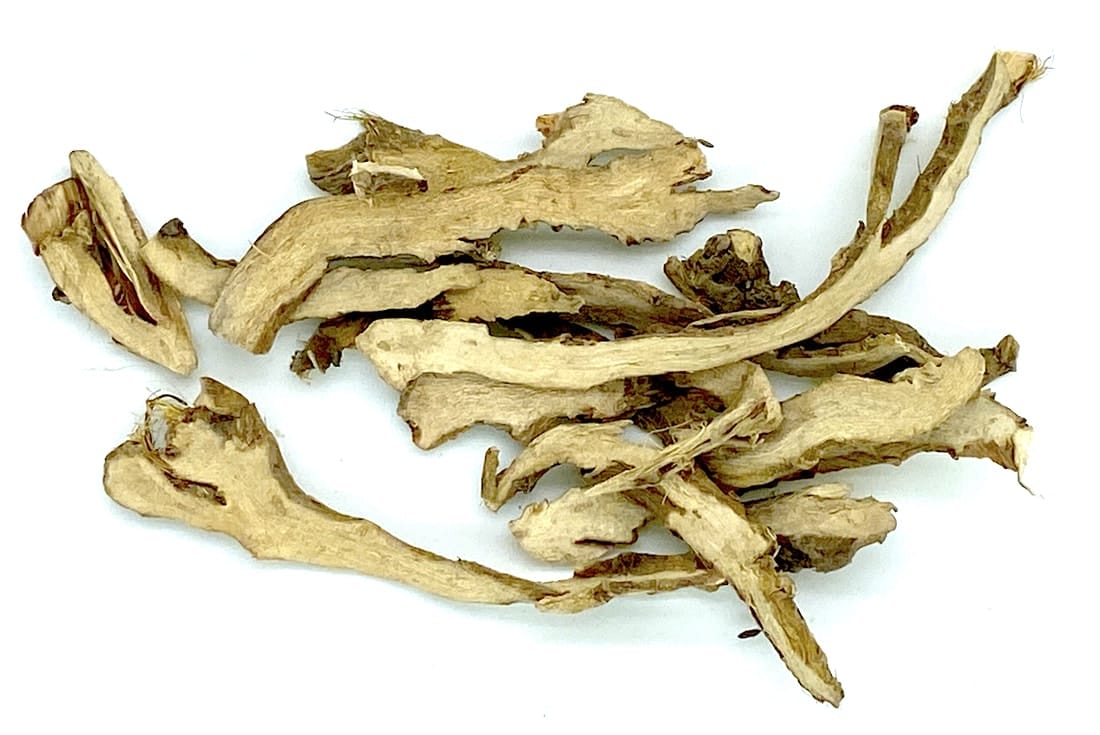
 Calamus root
Calamus root(bottom left shows underside of the root, bottom right shows upperside)
(A Manual of materia medica and pharmacology, Culbreth, 1906)
 Calamus (A. calamus) used in Tibetan Medicine. (Adam, 2016)
Calamus (A. calamus) used in Tibetan Medicine. (Adam, 2016) |
 Calamus used in TCM
Calamus used in TCM(Adam, 2022) |
Botanical name:
Acorus calamus (syn A. vulgaris, A. aromaticus, A. odoratus; Calamus aromaticus)
TCM recognises 3 main varieties of Acorus:
- Acorus tatarinowii (Shi Chang Pu)
- Acorus calamus (Shui Chang Pu); Shu dag nag po ཤུ་དག་ནག་པོ (Tibetan)
- Acorus gramineus (Jin Xian Pu); Shu dag dkar po ཤུ་དག་དཀར་པོ (Tibetan)
Due to the potential risk of toxicity of ß-asarone, the American Acorus calamus. var. americanus has been recommended.
Note that in ancient formulas of the West, ‘Acorus’ is Iris pseudoacorus, although Calamus may generally be used in its place. Many authors and herbals covered them under the same heading and treated them as one.
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm and dry in the third degree. Pungent, Bitter
Classification:
2A APERIENT MEDICINES. 2B ATTENUATERS. 2C INCIDERS. 2G. CLEANSING. 2H. CARMINATIVES. 2I. ANTISPASMODICS 2S. STRENGTHENING MEDICINES
3C. ALEXIPHARMICS. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3G. EMMENAGOGUE. 3K. EXPECTORANT. 3M. ARTHRITIC 3O. EMETICS
4a. CEPHALIC. 4c. CARDIAC. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4i. UTERINE. 4k. ARTHRITIC
TCM:
J. Aromatics that Open the Orifices
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Damp-Phlegm, Benefits Brain and Nerves: (TCM, West, Tibet, Ayurveda)
-Clears Wind, Damp and Phlegm and also clears Blood stagnation or bruising from head trauma
-Special medicine to restore Memory and Brain function
-Epilepsy, Headache, Vertigo, Dizziness, Paralysis
-Dullness of the Senses, Deafness, Loss of Speech, Stuttering, Head Trauma
–odontalgia and heaviness of the tongue (Avicenna)
-Heart Wind affecting the Brain and Nerves (Tibet)
-promotes alertness and increases intelligence and memory (Ayurveda)
-‘Long term use makes one feel happy and vigorous, have a good Memory and Spirit and enjoy a Long Life. It invigorates Wisdom’. (Shen Nong Ben Cao)
-ameliorates harmful effects of narcotics, especially Cannabis (Ayurveda)
2. Moves the Blood and Qi, Clears Damp, Resolves Stagnation: (TCM, West, Tibet, Ayurveda)
-Anxiety with Palpitations; Arrhythmia; old TCM herbals listed it for ‘Insufficient Heart Qi’ (TCM, West)
-promotes Menstruation, used for stoppage or painful Menstruation
-moves the Blood; internally and externally for Bruising, Trauma, Blood stagnation
-Swellings and Tumors
-“improves the complexion” (Avicenna)
-clears Damp and Melancholy (Confected root is good for Melancholy)
3. Clears Damp, Moves Qi, Benefits the Stomach: (TCM, West, Tibet, Ayurveda)
-promotes appetite and digestion; Indigestion, Colic, Diarrhea
-obstructions of the Liver and Spleen
-Cold phlegm of the Lungs; Cough, Bronchitis
4. Clears Damp, Promotes Urine, Warms the Kidneys: (West, Tibet, Ayurveda, TCM)
-Edema or obstructed Urine from Cold and Damp
-lack of Bladder control
-“According to some people it is also useful in strangury” (Avicenna)
-increases Libido and Sexual Energy; Arabs regarded it as a longevity tonic (Confected Root)
-“acts as a stimulant and increases libido” (Avicenna)
-Arthralgia, Rheumatoid Arthritis (TCM, Tibetan Medicine)
5. Resists Poison: (West, Tibet, TCM)
-classically used against various Poisons
-Snake bite, Rabies
-Worms, Parasites
-Boils, Toxic Sores, Diphtheria
-acute Cough, Whooping Cough
-Infectious and Epidemic diseases; Plague; both to preserve and cure
-root steeped in vinegar and chewed preserves from Infection during Epidemics (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
-expressed juice relieves toxin of Croton and Euphorbia species (TCM)
6. Emetic
-decoction has been used as an emetic
7. Externally:
-applied as a fomentation for colic and abdominal pain
-applied to Wind-Cold_damp type nerve, muscle and joint pains
-“useful for treating corneal thickness and opacity” (Avicenna)
-externally for Sores and Scabies
–Pityriasis and Leukoderma (Avicenna)
-decocted in wine and gargled to clear Phlegm and Damp from the Head
-pain of the stomach or abdomen, powder, fry and apply the powder while hot (TCM)
Dose:
Decoction: 3–6 grams, added at the end of boiling;
Powder: 500mg–2 grams (up to 5 grams daily)
Correctives
1. Cochlospermum religiosum; Tragacanth
2. Honey
Substitutes:
1. Orris, Valerian, Pyrethrum
2. Chrysanthemum indicum and Cumin (Unani)
3. Cumin with one-third part Rhubarb (as a carminative,and for Spleen and Liver) (Avicenna)
Preparation:
1. Confected Calamus:
In the west it was confected where it is regarded as a Brain and Kidney tonic, strengthening the Mind and Kidneys, and being aphrodisiac.
2. Stir-fried Calamus:
The dried root can be lightly stir-fried. This reduces its pungent, dispersing nature while keeping its warming, drying nature. It is better for treating children. (TCM)
3. Carbonised Calamus:
The root is stir-fried until scorched and blackened. This is better for Diarrhea and is used in Siddha medicine.
Main Combinations:
Calamus, Galangal
Calamus, Peony
Calamus, Rue
Mind, Brain, Nerves
1. Amnesia, to increase Memory:
i. Calamus (1 part), Lucerne seed (2 parts); powder, mix with Ghee and Honey
ii. Calamus with Frankincense, Cyperus rotundus, Black Pepper (Unani and Western)
iii. Calamus with Ginseng, Poria Fu Ling and Polygala Yuan Zhi. (TCM; proven effect)
2. Strengthen the Brain, Mental Fatigue, Stress, following Brain Injury, and during periods of Intense Study, combine Calamus with Gotu Kola (Ayurveda)
3. To enhance mental clarity, and for speech impediments, Calamus with Centella, Convolvulus Shankhapushpi (Ayurveda)
4. Wind-Heat diseases of the Head such as Epilepsy and Seizures, Calamus with Tabasheer
5. Epilepsy, Hysteria, Headache, Vertigo:
i. Calamus with Peony, Mistletoe and Sandalwood
ii. Calamus, Curcuma Yu Jin, Alum Ming Fan, Cinnabar (Zhu Sha) (TCM)
iii. Calamus, Peony, Mistletoe, Aloeswood, Juniper berry, Cinnamon, Clove, Rosemary, Sage, Calendula, Lavender
6. Tremors, Cal;amus with Stoechas, Oregano, Mild, Calamint, Ground Pine, Germander, Sage, Cowslip (as in Experienced Syrup for Tremors)
7. Mental disorders, Schizophrenia:
i. Calamus, Rauwolfia serpentina. These two medicines are often combined for various mental disorders in Ayurveda.
ii. combine equal parts of Calamus, Costus, Gotu Kola, Licorice, Rauwolfia serpentina, Withania, Nutmeg; take 1 gram three times daily (Simple Ayurvedic Remedies, Dr. Puri, India, 2002)
Stomach, Intestines
8. Stomach weakness, Colic, Bloating, Gastritis:
i. Cold-type Colic and Griping, Calamus decocted in Wine. (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
ii. Calamus with Peppermint
iii. Calamus with Swertia (or Gentian)
iv. Calamus with Balm and Fennel seed
v. Calamus with Cardamon, Fennel, Ginger (Ayurveda)
vi. Calamus, Galangal, Zedoary, Orris (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
vii. Calamus with Aniseed, Fennel seed, Caraway, Coriander seed, Licorice, Cinnamon, Ginger, Nutmeg (as in Species Incisa)
9. Aromatic Bitters, Calamus with Orange peel, Gentian, Rhubarb, Cinnamon, Clove
10. Stomach and Kidney weakness, Calamus with Wormwood
11. Gastritis with irritation, Colic:
i. Calamus with Marshmallow and Licorice
ii. Calamus, Balm, Fennel seed, Peppermint
iii. Calamus, Wormwood, Yarrow, Calendula, Licorice
12. Epigastric pain and distention, nausea, poor appetite:
i. from Damp-Cold-Phlegm and Qi stagnation, Calamus with Orange peel / Tangerine peel (Chen Pi).
ii. from Cold and Qi stagnation, Calamus with Evodia Wu Zhu Yu (TCM)
13. Cold diseases of the Stomach, Liver, Spleen, Chronic Disease, Edema, Calamus with Saffron, Myrrh, Cumin, Aniseed, Cinnamon, Spikenard, Mint (as in Diamorusia of Mesue)
14. Spleen disease, Calamus powdered, steeped in vinegar, then decocted to half and Honey or Sugar added is effective for the Spleen. (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
Urinary:
15. Obstructed Urine, Edema:
i. Calamus with Cough grass (Dioscorides)
ii. Calamus with Celery seed (Dioscorides)
iii. Calamus with Peppermint, Juniper, Senna (Meyer)
16. Gravel, Stones:
i. Calamus, Tribulus, Shilajit (Ayurveda)
ii. Calamus with Radish seed, Parsley seed, Bitter Almonds, Cyperus rotundus, Gentian, Myrrh (as in Pills to Crumble Kidney Stones)
17. Warm and strengthen the Kidneys, Brain and Nerves; for Epilepsy, Poor Memory and to increase Libido, with Sea Holly root, Pine nuts, Long Pepper and Clove (as in Diacorum)
Other:
18. Cold-phlegm of the Lungs:
i. Calamus with Adhatoda, Licorice (Ayurveda)
ii. Calamus with Almond, Licorice, Ginger
19. Whooping Cough, Calamus powder, 2 pinches three times daily in egg white (Siddha Medicine)
20. Scrofula, Calamus with Butchers Broom, Polypody, Orris, Marshmallow, Peony root, Figwort, Squill (as in Potion for Scrofula)
21. Chronic Internal Bleeding, Calamus with Horsetail, Gentian, Houseleek (Hüttner)
22. Heart Qi Stagnation:
i. Calamus, Aloeswood
ii. Calamus, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Costus, Polygala Yuan Zhi, Zizyphus Suan Zao Ren, Curcuma Yu Jin, Aloeswood (Chen Xiang) (The Formulas of Dr. John H.F. Shen)
23. Chest oppression and Angina Pectoris from Qi and Blood stagnation:
i. Calamus, Cyperus rotundus (Xiang Fu), Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Clove (Ding Xiang) (Formulas of Dr. John H.F. Shen)
ii. Calamus, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Costus (Mu Xiang), Polygala Yuan Zhi, Curcuma Yu Jin (Formulas of Dr. John H.F. Shen)
24. Arrhythmia:
i. Calamus, Galangal, Cinnamon, Camphor
ii. Calamus, Red Coral, Frankincense, Clove
iii. Calamus, Valerian, Sandalwood, Aloeswood
25. To move the Blood and clear stagnation, Calamus with Saffron, Myrrh, Cinnamon, Seseli, Aniseed, Spikenard, Costus (as in Diamorusia)
26. Amenorrhea, Calamus, Cyperus rotundus, Asarum, Madder
27. Hysteria, Dysmenorrhea, Calamus with Cassia Wood, Agnus Castus, Rue seed, Peony, Aniseed, Cinnamon, Sugar of Rosemary (as in Tragea Hysterica)
28. Infertility, Calamus with Seseli, Peony, Cyperus, Cinnamon, Mugwort, Spikenard, Olibanum, Mastic (as in Electuary Against Sterility)
29. Quartan Fever, Calamus with Pontic Wormwood decocted in Wine (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
30. Intermittent Fever, and convalescence after Fever, Calamus with Swertia
31. Syphilis, make an ointment with Withania, Calamus and Costus in Ghee to be applied. (Ayurveda)
Major Formulas:
Aromatic Bitter Decoction
Cephalic Decoction (Charras)
Decoction for Arthritis (Mynsichts)
Syrup for the Memory
Syrup of Calamus (Wirtzung)
Syrup of Mugwort (Augustana)
Wine for Catarrh
Four Thieves Vinegar
Electuary of Calamus (Mesue)
Electuary of Saffron Greater (Diacrocon Majores) (Mesue)
Orvietan Antidote
Electuary for Gastric Pain
Electuary Against Forgetfulness
Electuary for Amnesia (Unani)
The Powder of Trithemius
Powder of Galangal Compound (Diagalanga) (Mesue)
Species Incisa (Augustine Pharmacopoeia)
Powder to Strengthen the Memory (2)
Special Powder for Memory (Wirtzung)
Powder of Nutmeg for Vertigo
Powder for Incontinence (Alexander Benedictus)
Aromatic Hysteric Powder
Troches of Coral (Diacorallium) (Nicholas)
Aromatic Pills of Aloes (Sweet Pills of Aloe, Pilulae Aloephangine) (Mesue)
Pills to Increase Memory
Calamus 4 (Tibetan)
Cantharide 37 (Tibetan)
Ding Xian Wan (TCM)
Ding Zhi Wan (TCM)
Mu Xiang Liu Qi Yin (TCM)
Sang Piao Xiao San (TCM)
Garuda 5 (Khyung Lnga) (Tibetan)
Garuda 8 (Khyung lnga mchu sder can) (Tibetan)
Greater Universal Women’s Disease Conqueror (Mo nad spyi ‘joms chen mo) (Tibetan)
Increase Awareness Pills (Tibetan)
Madder Pill (Tibetan)
Medicine for Infants (Pillaru Marundu) (Siddha)
Przewalskia 11 (Thang phrom bcu gchig)
Red Coral 25 (Rin chen byur dmar nyer lnga)
Sarasvata Churna (Ayurveda)
Settle the Lungs 8 (Glo man brgyad pa) (Tibetan)
Supreme 25 (Bla med nyer lnga)
Vajra conquering Heart Wind 17 (Tibetan)
1. Compound Tincture of Calamus:
i. Calamus
Coriander seed 2 oz. each
Alcohol 24 oz. (Pharmacopoeia Generalis, 1783)
ii. Calamus 3 oz.
Zedoary
Ginger 1 oz. each
Unripe Orange 2 oz.
Alcohol 3 pounds.
Digest, press and filter. (Pharmacopoeia regni Poloniae, 1817)
iii. Calamus
Ginger
Coriander
Black Pepper 1 oz. each,
Alcohol (2 ½ pounds) (Niemann)
2. Stomach Tincture:
i. Calamus
Lesser Galangal
Gentian
Zedoary 1 ½ oz. each
Rhubarb 6 drams
Cochineal 2 drams
Lesser Cardamon 3 drams
Orange peel 1 oz.
Blessed Thistle 1 ½ oz.
Alcohol 5 pounds
Dose: 60–80 drops (Pharmacopoeia Hannoverana, 1819)
Cautions:
1. Avoid in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
2. Very warm and dry, therefore not suitable for Yin deficiency.
3. Avoid long term use of full doses.
4. Not used in those with Liver disease.
Toxicity:
Due to the potential Liver toxicity of ß-asarone, it should not be used long-term, or in those with Liver disease. Use for a maximum of one month, then have a break in treatment. Calamus usually forms a small part of an overall formula in which case its continued use is safe. The American Acorus calamus var. americanus does not contain ß-asarone so has been recommended.
–α-Asarone, β-asarone, and γ-asarone: Current status of toxicological evaluation.
Main Preparations used:
Distilled Water, Candied and Confected root, Distilled Oil, Extract
1. Conserve of Calamus:
i. Calamus root, soften by boiling; let it drain and pour upon it hot sugar syrup.
Used for various diseases of the Head and nerves; it sharpens the wit, eases the Headache, and is good for all old sickness, especially Rheums which fall from the head to the breast. Also ‘Commended’ for Vertigo (Wirtzung); as well as Nightmares
2. Confected Calamus root:
i. Dry Calamus root (2 parts); peel and cut it, macerate it in a sufficient quantity of hot water until it becomes soft; then pound it in a marble mortar: put it, in the same water, upon the fire, strain through a sieve, add White Sugar (3 parts) to the pulp, and evaporate to the right consistency. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
3. Distilled Water of Calamus:
i. Calamus root (1 part), Salted Water (6 parts). Macerate for several days, then distill. (Pharmacopoeia Sardoa, 1773)
ii. Calamus (1 part), Water (12 parts), macerate 24 hours, distill over 9 parts.
|
‘Sweet Flag root has been from the earliest times a favourite medicine of the natives of India, in which country it is sold in every bazaar. Ainslie asserts that it is reckoned so valuable in the bowel complaints of children that there is a penalty incurred by any druggist who will not open his door in the middle of the night to sell it, if demanded! The descriptions of Acoron, a plant of Colchis, Galatia, Pontus, and Crete, given by Dioscorides and Pliny, certainly refer to this drug. We think that the [?] of Dioscorides, which he states to grow in India, is the same, though Royle regards it as an Andropogon. The [?] of Theophrastus and the Calamus of the English Bible are considered by some authors to refer to the Sweet Flag. Celsus in the first century mentioned Calamus Alexandrinus, the drug being probably then brought from India by way of the Red Sea. We know by the |
testimony of Amatus Lusitanus that in the 16th century it used to be so imported into Venice. Rheede, moreover, described and figured Acorus Calamus as an Indian plant under the name Vacha, which it still bears on the Malabar Coast. But in the pharmaceutical tariff of the German town of Halberstadt of the year 1697, “Calamus aromaticus verus, Indianischer Calmus,” and “Calamus aromaticus nostras,” common Calmus, are quoted at exactly the same price, and Murray states expressly that in his time (1790) Asiatic calamus was still met with in the pharmacies of Continental Europe, but that it had mostly been replaced by the home-grown drug. At the present time the Calamus aromaticus of commerce is European; in all essential characters it agrees with that of India, a package of which is now and then offered in the London drug sales.’ (Pharmacographia, Fluckiger & Hanbury, 1879) |
Daoists texts on Calamus (from A Soup for the Qan, Hu Sihui et al. 2010)
Food for Beneficient Immortals:
‘Seek for sweetflag with nine joints. Dry in a cellar. After one hundred days grind into a powder. Take three times a day. If taken for a long time, it will make sensitive and bright the ear and the eye. It will increase the years and enhance longevity.’
The Baopuzi says:
Han Ju took sweetflag for 13 years. He sprouted hair on his body. He could read ten thousand words in a day. He was not cold [when] naked in winter. You should obtain sweetflag growing on rocks, with nine knots per cun. Sweetflag with purple flowers is still better.
