Acanthus, Bears Breech
Acantha, Brank Ursine, Bearfoot Ortus Sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501
Ortus Sanitatis, Cube, Johann von, 1501

|

|
|
Dioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563 |
Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578 |
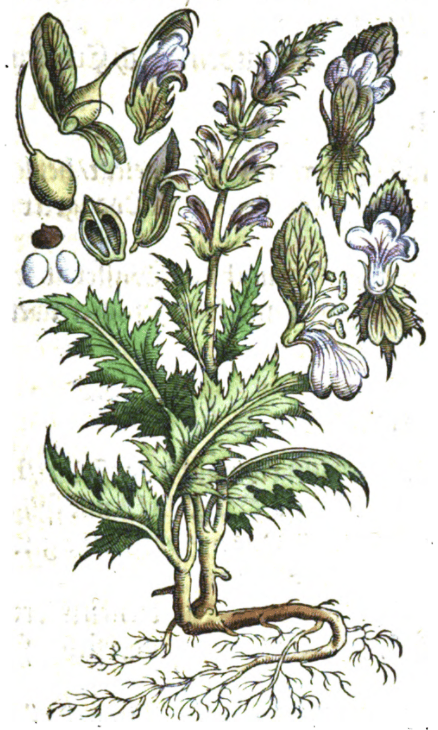 Kreutterbuch, Matthiolus, 1586
Kreutterbuch, Matthiolus, 1586Botanical name:
Acanthus mollis
Parts used:
Root and Leaves (leaf only externally)
Temperature & Taste:
Temperate
Uses:
1. Nourishes the Yin, Clears Heat:
-Consumption, Spitting of Blood
-Wasting
-a mild diuretic that can be used in Yin deficiency
-One of the 5 Emollient plants
2. Moves the Blood, Promotes Healing:
-good for internal Bruising, Strains, Wounds
-Hernias, Ruptures (Dioscorides)
3. Externally:
-bruised and applied to Dislocations, Hernias, Cramps, Numbness, aches and pain in the joints of the hands and feet, and to Gout
-externally to heal Bones, Burns: crushed roots or decoction (since Dioscorides)
-leaf is used externally for Erysipelas and Inflammations (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
-formerly usually used in Enemas and Cataplasms
-used externally as Comfrey
Dose:
1 dram of the powdered root in wine
Note:
One of the 5 Emollient plants
Substitute:
1. Mallow
2. Brank Ursine was used as Comfrey, and was used as a substitute for it. Comfrey may therefore be used in its place.
Main Combinations:
1. Edema for pituitous Humors of the Bowels, Bears Breech, Marshmallow, Pennyroyal, Oregano, Camomile, Aniseed, Cumin (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
2. Wounds and Bruising of the Bones, Bears Breech root decocted with bran and applied relieves pain (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
3. Looseness of the Joints, Bears Breech leaf and root decocted in wine with bran added and applied. (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
Cautions:
None noted.
It is cool and moist, so is not suitable for Cold and Weak digestion.
